Please note all prices are just for operational fees and without used supplies & devices .
Average non-surgical (medical) treatment fees for International Patients department.
| No. | Service | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | General Wards (per night) | 300$ |
| 2 | Intensive Care Unit (per night) | 500$ |
| 3 | Chemothrapy per night | 100$ |
From: 1,400.00$
Embark on a transformative journey with our exceptional range of medical treatments. As a leading medical tour operator, we offer a comprehensive selection of world-class treatments and procedures to address your unique healthcare needs. From advanced surgeries to cutting-edge therapies, our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing top-notch care and ensuring your comfort and satisfaction. Discover a new level of healthcare excellence with our tailored treatment options. Book now to start your journey towards a healthier and happier you.
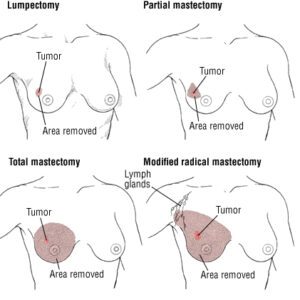
Breast reconstruction using implants, also known as implant-based reconstruction, is a surgical procedure that involves the use of silicone or saline implants to recreate breast tissue. Here is a general overview of the procedure based on the information from the search results:
Consultation and Planning: The process begins with a consultation with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast reconstruction. During this consultation, your surgeon will evaluate your individual case, discuss your goals and expectations, and explain the available options for implant-based reconstruction.
Timing of Reconstruction: Implant-based reconstruction can be performed either immediately after a mastectomy (immediate reconstruction) or at a later time (delayed reconstruction). The timing depends on various factors, including your overall health, cancer treatment plan, and personal preferences.
Placement of Tissue Expander: In immediate reconstruction, a tissue expander may be placed at the time of the mastectomy. The tissue expander is a temporary device that helps stretch the skin and create a pocket for the implant. It is gradually filled with saline solution over several weeks or months to expand the breast area.
Exchange Surgery: Once the desired size is achieved, a second surgery, known as the exchange surgery, is performed. During this procedure, the tissue expander is removed, and a permanent breast implant is placed in the pocket created by the expander. The implant can be positioned either under the chest muscle (submuscular) or on top of the muscle (subglandular), depending on various factors such as tissue quality and patient preference.
Nipple and Areola Reconstruction: Nipple and areola reconstruction can be performed as a separate procedure after the breast mound has been reconstructed using implants. This may involve tattooing techniques to recreate the pigmented area around the nipple.
Recovery and Follow-up: After the surgery, you will be given specific instructions for postoperative care, including wound care, pain management, and activity restrictions. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will be scheduled to monitor your healing progress and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Implant-based breast reconstruction is suitable for certain individuals who meet specific criteria. Here is a summary of the suitability mentioned in the search results:
Sufficient Skin Coverage: Implant-based reconstruction is suitable for patients who have an appropriate amount of skin remaining after mastectomy or those who have undergone skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy. This ensures that there is enough skin to cover and support the breast implant 1.
Non-Redundant Soft Tissue Coverage: Ideal candidates for implant-based reconstruction are patients with non-redundant soft tissue coverage. This means that they have enough healthy tissue to support the implant and achieve a satisfactory aesthetic outcome 1.
Desire for Moderate Sized Non-Ptotic Breast: Patients who desire a moderate-sized breast with minimal sagging (ptosis) may be suitable for implant-based reconstruction 1.
Good General Health: Candidates for implant-based reconstruction should generally be in good health. This ensures that they can tolerate the surgical procedure and have a lower risk of complications.
No Previous Radiation Therapy: Patients who have not undergone previous radiation therapy may be better suited for implant-based reconstruction.
Young Age and Small Breasts: Some women who are young and have small breasts may be candidates for direct-to-implant reconstruction, where the implant is placed at the same time as the mastectomy without the use of a tissue expander 2.
Based on the information from the search results, here are some factors that may make implant-based breast reconstruction unsuitable for certain individuals:
Insufficient Skin: If a patient does not have enough skin remaining after mastectomy or has undergone extensive skin resection, there may not be enough tissue to adequately cover and support the breast implant.
Radiation Therapy: Previous radiation therapy to the chest area can affect the success and outcomes of implant-based reconstruction. Radiation can compromise the quality of the skin and underlying tissues, increasing the risk of complications such as poor wound healing, implant malposition, and capsular contracture.
Unsuitable Soft Tissue Coverage: Patients who do not have sufficient non-redundant soft tissue coverage may not be suitable for implant-based reconstruction. Adequate soft tissue coverage is necessary to achieve a satisfactory aesthetic outcome and minimize the risk of complications.
Desire for Large or Ptotic Breasts: Implant-based reconstruction may not be suitable for patients who desire larger breast sizes or have significant breast sagging (ptosis). Other reconstructive techniques, such as autologous tissue reconstruction using flaps, may be more appropriate in these cases.
Health Conditions: Certain health conditions or medical factors may make implant-based reconstruction less suitable. These can include compromised general health, active smoking, and pre-existing scars on the breast, which can adversely affect skin perfusion and healing.
Implant-based breast reconstruction offers several advantages, as mentioned in the search results:
Shorter Hospital Stay and Recovery Time: Implant reconstruction generally requires a shorter hospital stay and recovery time compared to other reconstruction options. This is because the surgery is less extensive, allowing for a quicker recovery process 1.
Choice of Size and Shape: With implant reconstruction, you have the opportunity to discuss and choose the desired size, shape, and volume of the breast implants. Implants come in various sizes and shapes, allowing for customization to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome 2.
No Need for Microsurgery: Unlike some other reconstruction techniques, implant reconstruction does not require microsurgery. This makes it a shorter and less complex procedure, reducing the surgical time and potential complications associated with microsurgical techniques 2.
Potential for Direct-to-Implant Reconstruction: In some cases, direct-to-implant reconstruction may be possible, where the implant is placed at the same time as the mastectomy without the need for a tissue expander. This can be advantageous for certain patients, particularly those who are young, have small breasts, and have no health problems 3.
Availability of Different Implant Types: There are different types of implants available, including saline and silicone implants, with various shapes and sizes. This allows for flexibility in choosing the most suitable implant type for your individual needs 3.
Implant-based breast reconstruction, like any surgical procedure, carries the risk of complications. Here are some potential complications associated with implant reconstruction, as mentioned in the search results:
Capsular Contracture: Capsular contracture occurs when scar tissue forms around the breast implant, causing the breast to feel firm, change shape, or become uncomfortable or painful. It is more common after radiation therapy and may require additional surgery to remove or replace the implant 1.
Infection: Infection is a potential complication after implant reconstruction. Although antibiotics are typically given at the time of surgery to reduce the risk of infection, it can still occur and may require treatment with antibiotics or, in severe cases, removal of the implant 1.
Implant Rupture: While rare, breast implant rupture can occur. This may result from trauma, aging of the implant, or other factors. If a rupture occurs, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove or replace the implant 2.
Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): BIA-ALCL is a rare type of lymphoma that has been associated with breast implants. It is important to note that BIA-ALCL is extremely rare, and the risk is considered low. If you experience persistent swelling or changes in the breast, it is important to consult with your surgeon.
Other Potential Complications: Other potential complications of implant-based reconstruction can include breast skin necrosis, implant displacement, reddening of the skin, rash, seroma, bleeding, hematoma, and implant-related complications such as implant failure or explantation 3 4.
Based on the information from the search results, here are some aspects of preoperative care for implant-based breast reconstruction:
Preoperative Testing: Before the surgery, various preoperative tests may be conducted to assess your overall health and ensure that you are a suitable candidate for the procedure. These tests may include blood work, imaging studies, and consultations with other healthcare providers if necessary.
Clearance and Documentation: It is important to have all necessary clearances and paperwork completed before the surgery. This may involve obtaining clearance from your primary care doctor or other specialists if you have any underlying medical conditions.
Preoperative Instructions: Your surgeon will provide you with specific preoperative instructions to follow. These instructions may include guidelines on fasting before surgery, discontinuing certain medications or supplements that can increase the risk of bleeding, and avoiding smoking or nicotine products, as they can impair wound healing and increase the risk of complications.
Skin Preparation: Preoperative skin preparation may be recommended to reduce the risk of infection. This can involve using an antiseptic solution, such as Hibiclens, to cleanse the skin before surgery. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by your surgeon regarding the use of any specific skin preparation products.
Marking and Consultation: Before entering the operating room, your surgeon and anesthesiologist will visit you in the preoperative waiting room. Your surgeon will mark your chest with markings on your body to facilitate the surgery. This is also an opportunity to ask any last-minute questions or address any concerns you may have.
Postoperative care following implant-based breast reconstruction is crucial for optimal healing and recovery. Here are some aspects of postoperative care mentioned in the search results:
Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Your surgeon will provide specific instructions on how to care for your incisions, including keeping the area clean and dry, changing dressings as instructed, and avoiding activities that may strain the incisions.
Pain Management: Pain and discomfort are common after surgery. Your surgeon will prescribe pain medications to help manage postoperative pain. It’s important to take the medications as directed and report any severe or persistent pain to your healthcare team.
Activity Restrictions: Following implant reconstruction, you will likely have activity restrictions to allow for proper healing. Your surgeon will provide guidelines on when you can resume normal activities, including exercise, lifting heavy objects, and driving. It’s important to follow these instructions to avoid complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Monitoring for Complications: It’s important to monitor for any signs of complications, such as infection, implant-related issues, or changes in breast appearance. Contact your surgeon if you experience persistent pain, redness, swelling, drainage, or any other concerning symptoms.
Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon are essential for monitoring your progress and addressing any concerns. These appointments allow your surgeon to assess the healing process, monitor the implants, and make any necessary adjustments or interventions.
Emotional Support: Breast reconstruction can have emotional implications, and it’s important to seek emotional support if needed. Your healthcare team may provide resources or referrals to support groups or counseling services to help you navigate the emotional aspects of the reconstruction process.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Breast reconstruction using implants, also known as implant-based reconstruction, is a surgical procedure that involves the use of silicone or saline implants to recreate breast tissue. Here is a general overview of the procedure based on the information from the search results:
Consultation and Planning: The process begins with a consultation with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast reconstruction. During this consultation, your surgeon will evaluate your individual case, discuss your goals and expectations, and explain the available options for implant-based reconstruction.
Timing of Reconstruction: Implant-based reconstruction can be performed either immediately after a mastectomy (immediate reconstruction) or at a later time (delayed reconstruction). The timing depends on various factors, including your overall health, cancer treatment plan, and personal preferences.
Placement of Tissue Expander: In immediate reconstruction, a tissue expander may be placed at the time of the mastectomy. The tissue expander is a temporary device that helps stretch the skin and create a pocket for the implant. It is gradually filled with saline solution over several weeks or months to expand the breast area.
Exchange Surgery: Once the desired size is achieved, a second surgery, known as the exchange surgery, is performed. During this procedure, the tissue expander is removed, and a permanent breast implant is placed in the pocket created by the expander. The implant can be positioned either under the chest muscle (submuscular) or on top of the muscle (subglandular), depending on various factors such as tissue quality and patient preference.
Nipple and Areola Reconstruction: Nipple and areola reconstruction can be performed as a separate procedure after the breast mound has been reconstructed using implants. This may involve tattooing techniques to recreate the pigmented area around the nipple.
Recovery and Follow-up: After the surgery, you will be given specific instructions for postoperative care, including wound care, pain management, and activity restrictions. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will be scheduled to monitor your healing progress and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Implant-based breast reconstruction is suitable for certain individuals who meet specific criteria. Here is a summary of the suitability mentioned in the search results:
Sufficient Skin Coverage: Implant-based reconstruction is suitable for patients who have an appropriate amount of skin remaining after mastectomy or those who have undergone skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy. This ensures that there is enough skin to cover and support the breast implant 1.
Non-Redundant Soft Tissue Coverage: Ideal candidates for implant-based reconstruction are patients with non-redundant soft tissue coverage. This means that they have enough healthy tissue to support the implant and achieve a satisfactory aesthetic outcome 1.
Desire for Moderate Sized Non-Ptotic Breast: Patients who desire a moderate-sized breast with minimal sagging (ptosis) may be suitable for implant-based reconstruction 1.
Good General Health: Candidates for implant-based reconstruction should generally be in good health. This ensures that they can tolerate the surgical procedure and have a lower risk of complications.
No Previous Radiation Therapy: Patients who have not undergone previous radiation therapy may be better suited for implant-based reconstruction.
Young Age and Small Breasts: Some women who are young and have small breasts may be candidates for direct-to-implant reconstruction, where the implant is placed at the same time as the mastectomy without the use of a tissue expander 2.
Based on the information from the search results, here are some factors that may make implant-based breast reconstruction unsuitable for certain individuals:
Insufficient Skin: If a patient does not have enough skin remaining after mastectomy or has undergone extensive skin resection, there may not be enough tissue to adequately cover and support the breast implant.
Radiation Therapy: Previous radiation therapy to the chest area can affect the success and outcomes of implant-based reconstruction. Radiation can compromise the quality of the skin and underlying tissues, increasing the risk of complications such as poor wound healing, implant malposition, and capsular contracture.
Unsuitable Soft Tissue Coverage: Patients who do not have sufficient non-redundant soft tissue coverage may not be suitable for implant-based reconstruction. Adequate soft tissue coverage is necessary to achieve a satisfactory aesthetic outcome and minimize the risk of complications.
Desire for Large or Ptotic Breasts: Implant-based reconstruction may not be suitable for patients who desire larger breast sizes or have significant breast sagging (ptosis). Other reconstructive techniques, such as autologous tissue reconstruction using flaps, may be more appropriate in these cases.
Health Conditions: Certain health conditions or medical factors may make implant-based reconstruction less suitable. These can include compromised general health, active smoking, and pre-existing scars on the breast, which can adversely affect skin perfusion and healing.
Implant-based breast reconstruction offers several advantages, as mentioned in the search results:
Shorter Hospital Stay and Recovery Time: Implant reconstruction generally requires a shorter hospital stay and recovery time compared to other reconstruction options. This is because the surgery is less extensive, allowing for a quicker recovery process 1.
Choice of Size and Shape: With implant reconstruction, you have the opportunity to discuss and choose the desired size, shape, and volume of the breast implants. Implants come in various sizes and shapes, allowing for customization to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome 2.
No Need for Microsurgery: Unlike some other reconstruction techniques, implant reconstruction does not require microsurgery. This makes it a shorter and less complex procedure, reducing the surgical time and potential complications associated with microsurgical techniques 2.
Potential for Direct-to-Implant Reconstruction: In some cases, direct-to-implant reconstruction may be possible, where the implant is placed at the same time as the mastectomy without the need for a tissue expander. This can be advantageous for certain patients, particularly those who are young, have small breasts, and have no health problems 3.
Availability of Different Implant Types: There are different types of implants available, including saline and silicone implants, with various shapes and sizes. This allows for flexibility in choosing the most suitable implant type for your individual needs 3.
Implant-based breast reconstruction, like any surgical procedure, carries the risk of complications. Here are some potential complications associated with implant reconstruction, as mentioned in the search results:
Capsular Contracture: Capsular contracture occurs when scar tissue forms around the breast implant, causing the breast to feel firm, change shape, or become uncomfortable or painful. It is more common after radiation therapy and may require additional surgery to remove or replace the implant 1.
Infection: Infection is a potential complication after implant reconstruction. Although antibiotics are typically given at the time of surgery to reduce the risk of infection, it can still occur and may require treatment with antibiotics or, in severe cases, removal of the implant 1.
Implant Rupture: While rare, breast implant rupture can occur. This may result from trauma, aging of the implant, or other factors. If a rupture occurs, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove or replace the implant 2.
Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): BIA-ALCL is a rare type of lymphoma that has been associated with breast implants. It is important to note that BIA-ALCL is extremely rare, and the risk is considered low. If you experience persistent swelling or changes in the breast, it is important to consult with your surgeon.
Other Potential Complications: Other potential complications of implant-based reconstruction can include breast skin necrosis, implant displacement, reddening of the skin, rash, seroma, bleeding, hematoma, and implant-related complications such as implant failure or explantation 3 4.
Based on the information from the search results, here are some aspects of preoperative care for implant-based breast reconstruction:
Preoperative Testing: Before the surgery, various preoperative tests may be conducted to assess your overall health and ensure that you are a suitable candidate for the procedure. These tests may include blood work, imaging studies, and consultations with other healthcare providers if necessary.
Clearance and Documentation: It is important to have all necessary clearances and paperwork completed before the surgery. This may involve obtaining clearance from your primary care doctor or other specialists if you have any underlying medical conditions.
Preoperative Instructions: Your surgeon will provide you with specific preoperative instructions to follow. These instructions may include guidelines on fasting before surgery, discontinuing certain medications or supplements that can increase the risk of bleeding, and avoiding smoking or nicotine products, as they can impair wound healing and increase the risk of complications.
Skin Preparation: Preoperative skin preparation may be recommended to reduce the risk of infection. This can involve using an antiseptic solution, such as Hibiclens, to cleanse the skin before surgery. It’s important to follow the instructions provided by your surgeon regarding the use of any specific skin preparation products.
Marking and Consultation: Before entering the operating room, your surgeon and anesthesiologist will visit you in the preoperative waiting room. Your surgeon will mark your chest with markings on your body to facilitate the surgery. This is also an opportunity to ask any last-minute questions or address any concerns you may have.
Postoperative care following implant-based breast reconstruction is crucial for optimal healing and recovery. Here are some aspects of postoperative care mentioned in the search results:
Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Your surgeon will provide specific instructions on how to care for your incisions, including keeping the area clean and dry, changing dressings as instructed, and avoiding activities that may strain the incisions.
Pain Management: Pain and discomfort are common after surgery. Your surgeon will prescribe pain medications to help manage postoperative pain. It’s important to take the medications as directed and report any severe or persistent pain to your healthcare team.
Activity Restrictions: Following implant reconstruction, you will likely have activity restrictions to allow for proper healing. Your surgeon will provide guidelines on when you can resume normal activities, including exercise, lifting heavy objects, and driving. It’s important to follow these instructions to avoid complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Monitoring for Complications: It’s important to monitor for any signs of complications, such as infection, implant-related issues, or changes in breast appearance. Contact your surgeon if you experience persistent pain, redness, swelling, drainage, or any other concerning symptoms.
Follow-up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon are essential for monitoring your progress and addressing any concerns. These appointments allow your surgeon to assess the healing process, monitor the implants, and make any necessary adjustments or interventions.
Emotional Support: Breast reconstruction can have emotional implications, and it’s important to seek emotional support if needed. Your healthcare team may provide resources or referrals to support groups or counseling services to help you navigate the emotional aspects of the reconstruction process.
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment. The preferred choice for many patients is choosing private care.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.