Description
Liver Transplant Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide to a Life-Saving Procedure
Liver transplant surgery is a complex but life-saving procedure for patients with end-stage liver disease or certain types of liver cancer. This surgical intervention replaces a diseased liver with a healthy one from a deceased or living donor. Understanding the intricacies of this procedure, including the evaluation process, surgical techniques, recovery, and long-term care, is crucial for patients and their families considering this option.
Why is a Liver Transplant Necessary?
Liver transplants are performed when the liver can no longer function adequately to sustain life. Common conditions that may necessitate a liver transplant include:
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver due to chronic conditions like hepatitis B or C, alcohol abuse, or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Acute Liver Failure: Sudden loss of liver function, often caused by drug overdoses, viral infections, or autoimmune diseases.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): A type of liver cancer that meets specific criteria for transplantation.
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): Chronic diseases affecting the bile ducts.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: A condition where the body’s immune system attacks the liver.
- Metabolic Diseases: Genetic disorders that affect liver function.
- Biliary Atresia (in children): A blockage of the bile ducts.
The Liver Transplant Evaluation Process:
The evaluation process is rigorous and involves a multidisciplinary team of specialists, including hepatologists, surgeons, transplant coordinators, social workers, and psychologists. The evaluation aims to determine if a patient is a suitable candidate for a liver transplant. It typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a comprehensive physical examination.
- Blood Tests: To assess liver function, kidney function, blood clotting, and other important parameters.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to evaluate the liver and surrounding organs.
- Endoscopy: To examine the esophagus and stomach for varices (enlarged veins).
- Psychosocial Evaluation: To assess the patient’s emotional and social support system.
- Donor Evaluation (for living donor transplants): Comprehensive testing to ensure the donor is healthy and a suitable match.
Types of Liver Transplant Surgery:
- Deceased Donor Liver Transplant: A healthy liver is retrieved from a deceased individual who has donated their organs.
- Living Donor Liver Transplant: A portion of a healthy liver is removed from a living donor and transplanted into the recipient. The liver has the remarkable ability to regenerate, allowing both the donor and recipient to recover normal liver function.
- Split Liver Transplant: A deceased donor liver is split into two parts and transplanted into two recipients, usually an adult and a child.
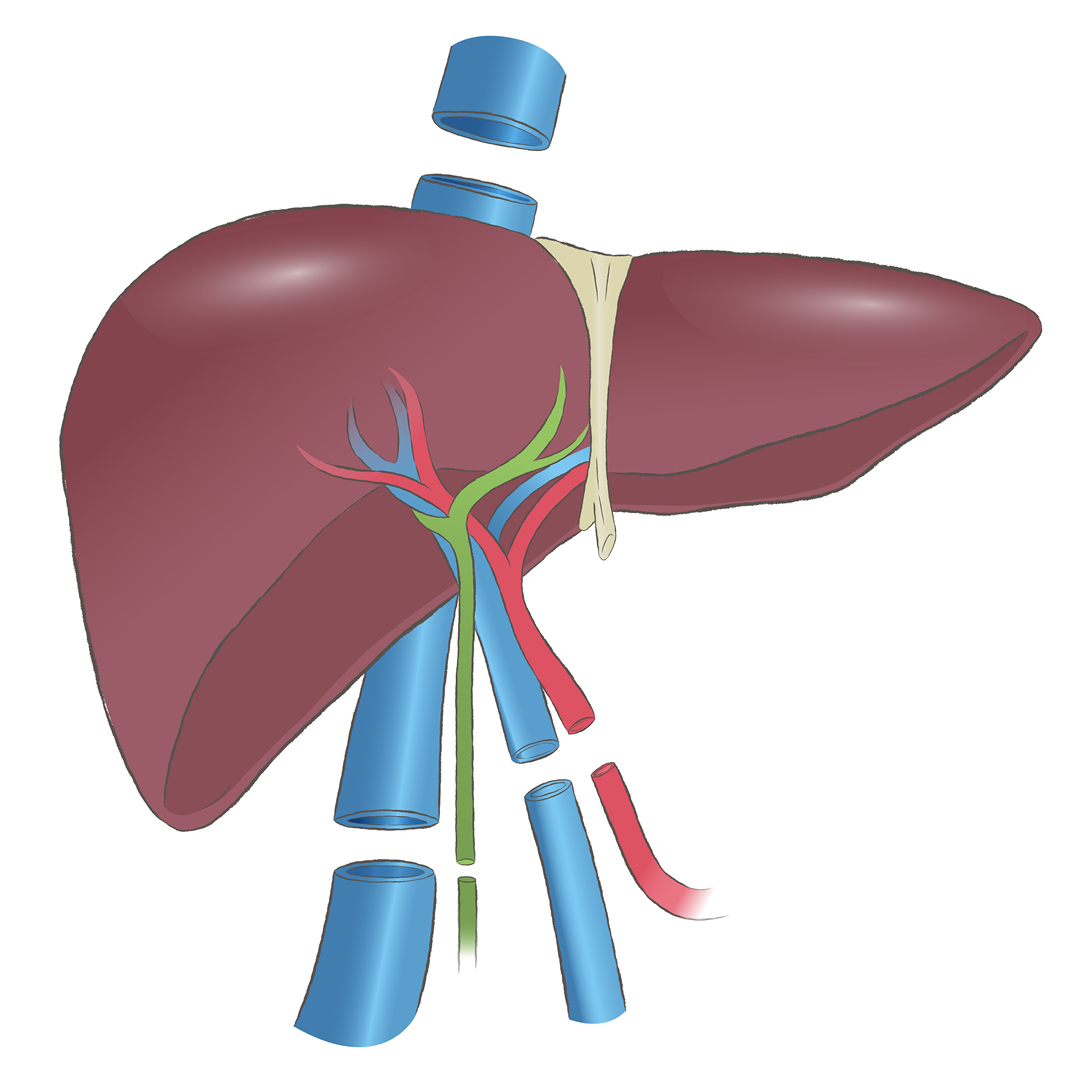
The Liver Transplant Procedure:
The liver transplant procedure is a major surgery that typically takes several hours. The diseased liver is removed, and the new liver is placed in the same location. Blood vessels and bile ducts are connected to the new liver.
Post-Transplant Care and Recovery:
After surgery, patients are closely monitored in the intensive care unit (ICU) and then transferred to a transplant unit. Post-transplant care includes:
- Immunosuppressant Medications: To prevent the body from rejecting the new liver.
- Regular Blood Tests: To monitor liver function and medication levels.
- Physical Therapy: To regain strength and mobility.
- Dietary Counseling: To ensure adequate nutrition.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular appointments with the transplant team to monitor liver health and manage medications.
Potential Risks and Complications:
Liver transplant surgery carries potential risks and complications, including:
- Rejection: The body’s immune system attacks the new liver.
- Infection: Due to immunosuppressant medications.
- Bleeding: During or after surgery.
- Bile Duct Complications: Leakage or blockage of the bile ducts.
- Blood Clotting: In the blood vessels supplying the liver.
- Primary Nonfunction: The new liver fails to function immediately after surgery.
- Side Effects of Medications: Such as kidney problems or high blood pressure.
Long-Term Outlook:
The long-term outlook for liver transplant recipients is generally good. With proper post-transplant care and adherence to medication regimens, many patients can live long and healthy lives. Regular follow-up appointments and a healthy lifestyle are essential for maintaining liver health.
Finding a Liver Transplant Center:
Choosing a reputable liver transplant center with experienced surgeons and a multidisciplinary team is crucial. Consider factors such as:
- Transplant Volume: Centers with higher transplant volumes often have better outcomes.
- Surgeon Experience: Look for surgeons with extensive experience in liver transplantation.
- Survival Rates: Compare survival rates among different transplant centers.
- Multidisciplinary Team: Ensure the center has a comprehensive team of specialists.
- Post-Transplant Support: Inquire about post-transplant support services.
Medical Tourism Considerations:
If considering a liver transplant abroad, research the transplant center’s credentials, experience, and success rates. Ensure the center adheres to international standards of care and has experience treating international patients. Consider factors such as travel logistics, language barriers, and post-operative care.
Liver transplant surgery is a complex and challenging procedure, but it offers hope for patients with end-stage liver disease. With careful evaluation, experienced surgeons, and comprehensive post-transplant care, liver transplant recipients can enjoy a significantly improved quality of life.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.