Description
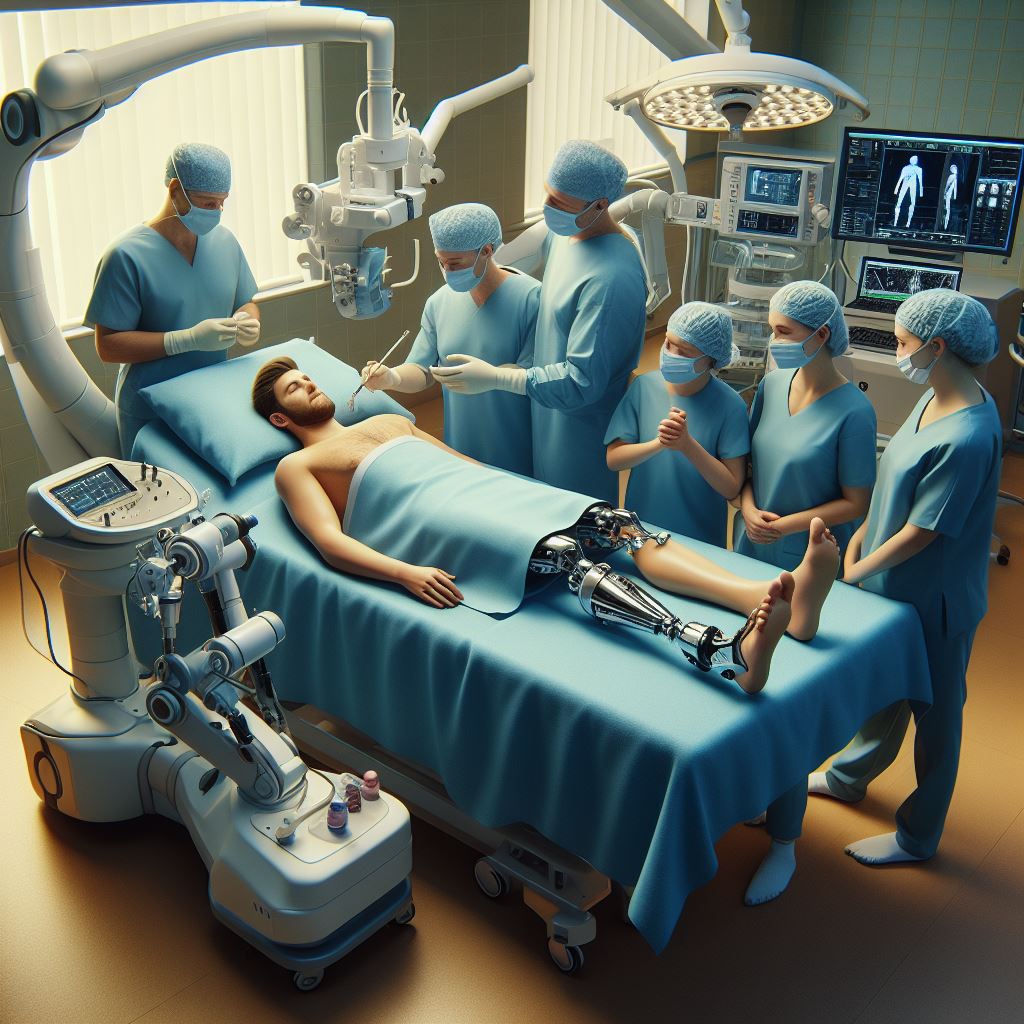
Orthopedic amputation is a surgical procedure performed to remove a limb or part of a limb due to injury, disease, or a medical condition that threatens the patient’s health or quality of life. This procedure is typically done by orthopedic surgeons and may involve amputating the foot, leg, arm, or hand.
Familiarity with Treatment:
Orthopedic amputation is a well-known procedure that has been performed for centuries to save lives and improve the quality of life for patients with severe limb issues. With advancements in surgical techniques, anesthesia, and prosthetic technology, the outcomes of orthopedic amputations have significantly improved.
Procedure:
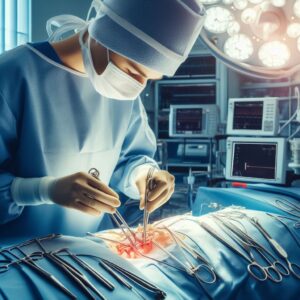
During an orthopedic amputation, the surgeon removes the damaged or diseased limb or part of the limb. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia, and the surgeon carefully cuts through skin, muscle, blood vessels, and bone to remove the limb in a controlled manner. The surgeon then closes the wound to promote healing.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Orthopedic amputation is suitable for individuals with conditions such as severe trauma, infection, peripheral arterial disease, cancer, or congenital limb deformities that cannot be treated through other means. The decision to proceed with an amputation is carefully evaluated by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
Orthopedic amputation may not be suitable for individuals who have the potential for successful alternative treatments, those with poor overall health, or those who are not willing to undergo the physical and emotional challenges of living with an amputation.
Advantages:
The primary advantage of orthopedic amputation is that it can save a patient’s life, prevent the spread of infection, relieve pain, and improve overall quality of life. An amputation can also allow for better mobility with the use of prosthetic limbs and rehabilitation.
Complications:
Complications of orthopedic amputation may include infection, wound healing issues, phantom limb pain, blood clots, muscle atrophy, and emotional adjustments to limb loss. Proper postoperative care and rehabilitation can help reduce the risk of complications.
Preoperative Care:
Preoperative care for orthopedic amputation may involve medical tests, counseling, pain management, and preoperative optimization of health conditions. Patients will also receive education about the procedure, postoperative expectations, and rehabilitation options.
Postoperative Care:
Postoperative care for orthopedic amputation includes wound care, pain management, physical therapy, and prosthetic fitting. Patients will undergo rehabilitation to learn how to use a prosthetic limb, regain strength and mobility, and adjust to life after amputation. Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring healing and addressing any issues that arise.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.