Description
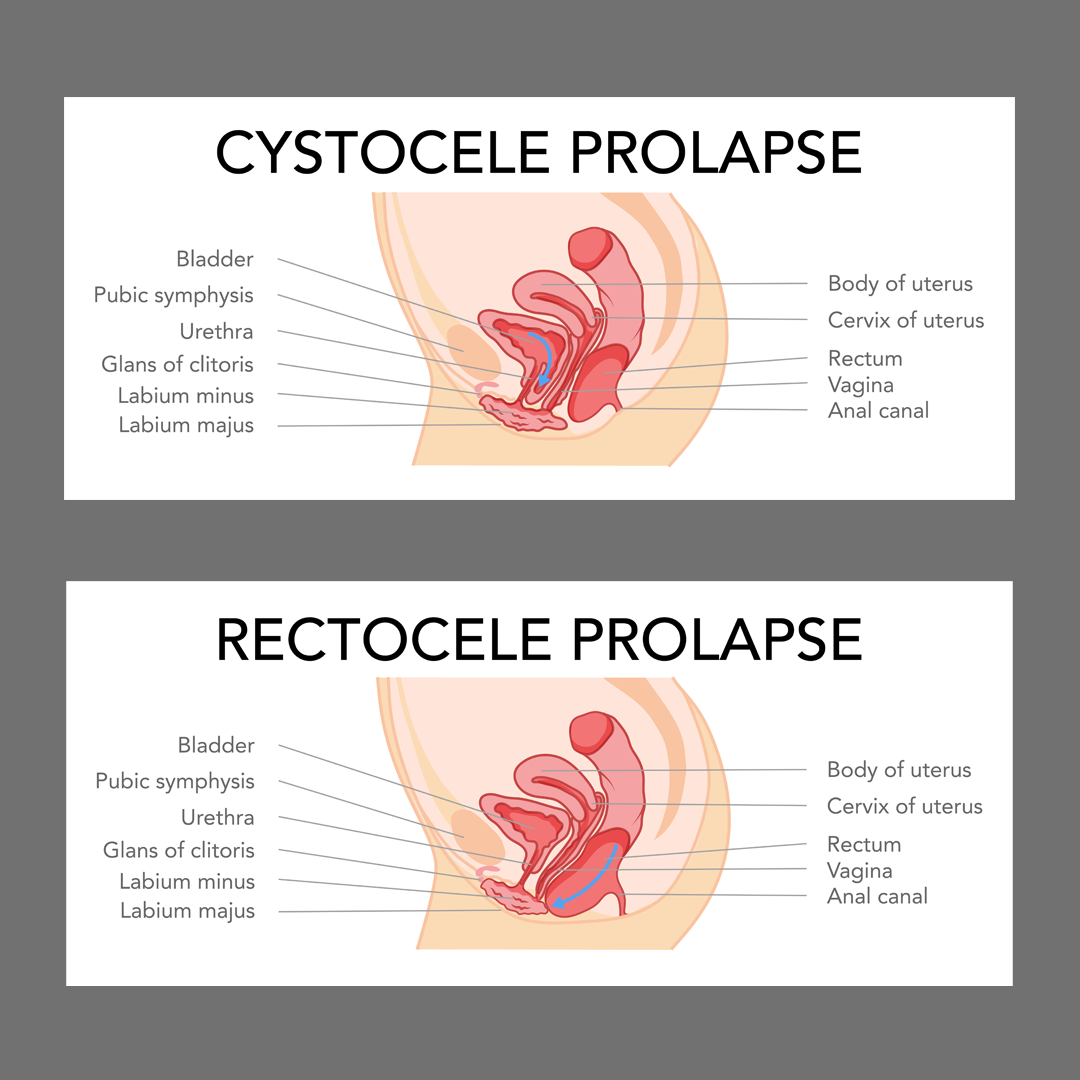
Familiarity with Treatment: Anterior and posterior colporrhaphy are surgical procedures used to repair pelvic organ prolapse (POP). Anterior colporrhaphy addresses cystocele (bladder prolapse), while posterior colporrhaphy addresses rectocele (rectum prolapse).
Procedure:
- Anterior Colporrhaphy (Cystocele Repair): The surgeon makes an incision in the front wall of the vagina to access and tighten the weakened muscles between the bladder and vagina. This helps to lift and support the bladder.
- Posterior Colporrhaphy (Rectocele Repair): The surgeon makes an incision in the back wall of the vagina to access and tighten the weakened muscles between the rectum and vagina. This helps to lift and support the rectum.
Who is it suitable for?
- Individuals with moderate to severe symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse that interfere with daily activities and quality of life.
- Those who have not found relief from conservative treatments such as pelvic floor exercises, pessaries, or hormone therapy.
Who is it not suitable for?
- Individuals with mild prolapse symptoms that do not significantly impact daily life.
- Those who can manage their symptoms effectively with non-surgical treatments.
- Patients with certain medical conditions that may increase surgical risks.
Advantages:
- Provides long-term relief from symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse.
- Improves quality of life by addressing issues such as urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and painful intercourse.
- Less invasive compared to other reconstructive surgeries that require abdominal incisions.
Complications:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding or blood clots.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Recurrence of prolapse.
- Injury to surrounding organs such as the bladder or rectum.
Previous Care:
- Preoperative evaluation including blood and urine tests.
- Fasting for 6-8 hours before the procedure.
- Stopping certain medications as advised by the healthcare provider.
Aftercare:
- Hospital stay for at least one night.
- Pain management with prescribed medications.
- Avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks.
- Following up with the healthcare provider for postoperative check-ups.
- Performing pelvic floor exercises as recommended to strengthen the pelvic muscles.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.