Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
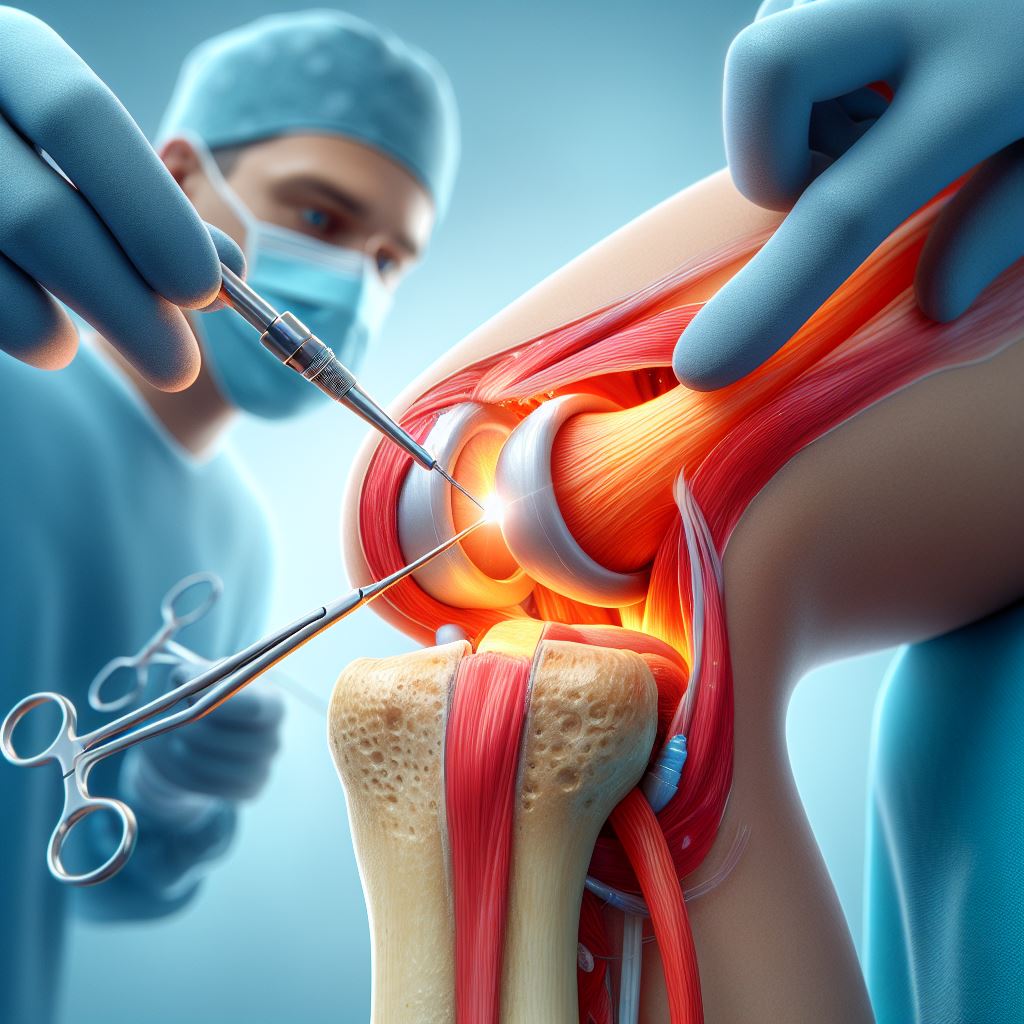
Arthroscopic surgery, commonly used in sports medicine, involves the use of a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat joint problems. This minimally invasive approach allows surgeons to visualize, diagnose, and treat a variety of joint conditions with smaller incisions and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
Procedure:
During arthroscopic surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions near the joint and inserts the arthroscope to view the internal structures of the joint on a monitor. Depending on the specific condition, the surgeon can then use small instruments to repair or remove damaged tissues, such as torn ligaments, cartilage, or inflamed synovial tissue.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Arthroscopic surgery is suitable for individuals with various joint conditions, including:
- Ligament tears, such as anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears in the knee.
- Meniscus tears in the knee.
- Rotator cuff tears and labral tears in the shoulder.
- Loose bodies or damaged cartilage in the joint.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
Arthroscopic surgery may not be suitable for individuals with:
- Advanced arthritis or joint degeneration that requires more extensive surgical intervention, such as joint replacement.
- Certain medical conditions that increase the risks associated with surgery, such as uncontrolled diabetes or heart disease.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive approach leading to smaller incisions, less tissue damage, and potentially faster recovery times.
- Reduced risk of complications such as infection and blood loss compared to traditional open surgery.
- Can often be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing for shorter hospital stays and quicker return to activity.
Complications:
Potential complications of arthroscopic surgery may include:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Nerve or blood vessel damage.
- Formation of blood clots.
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Preoperative Care:
- Patients will undergo a comprehensive evaluation of their medical history and physical condition to assess their suitability for arthroscopic surgery.
- They may be advised to discontinue certain medications or supplements that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Postoperative Care:
- After arthroscopic surgery, patients will be given specific instructions on wound care, pain management, and physical therapy protocols.
- Rehabilitation may include exercises to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joint.
- Patients will be advised on activity restrictions and gradual return to normal activities.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.