Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
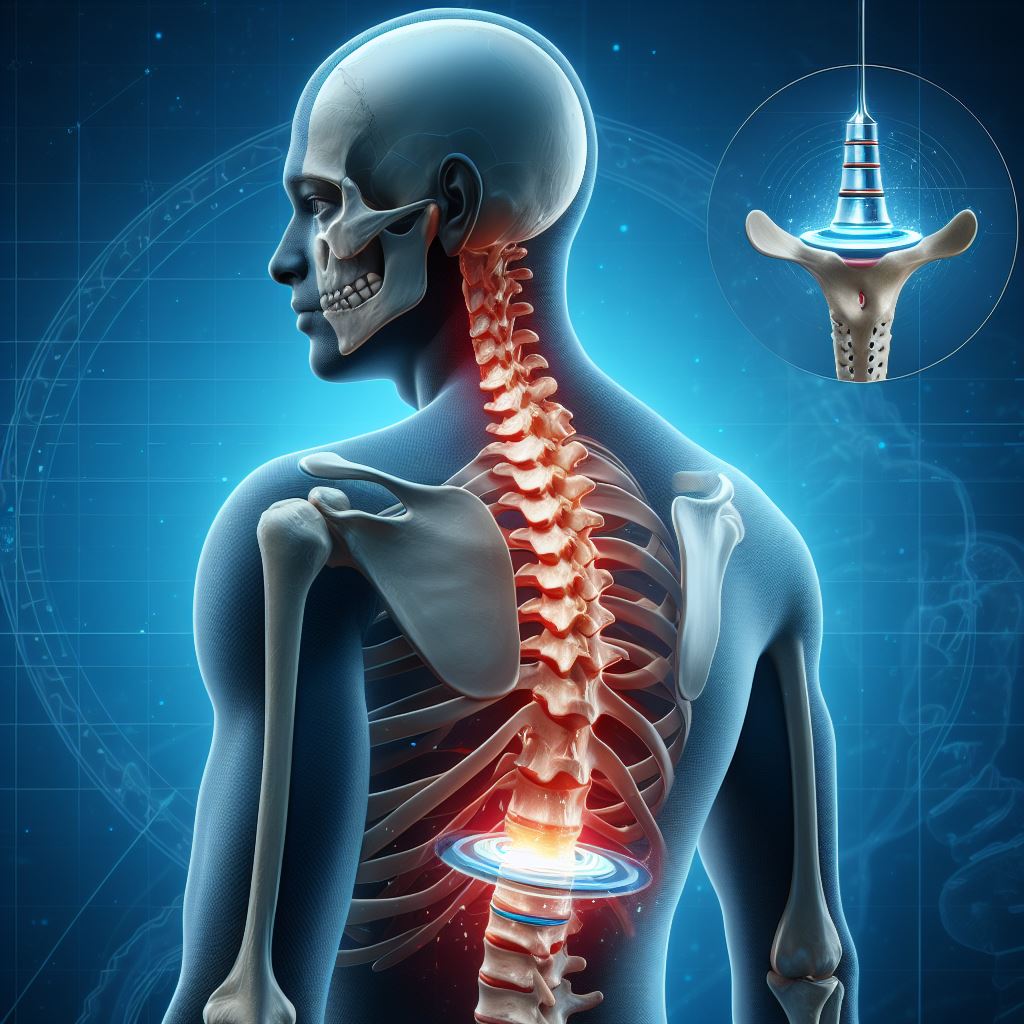
Artificial Disc Replacement (ADR) surgery, also known as total disc replacement, involves the removal of a damaged or degenerated intervertebral disc in the spine and its replacement with an artificial disc device. This procedure aims to maintain spinal motion and function while alleviating pain and other symptoms associated with disc problems.
Procedure: During ADR surgery, the surgeon removes the affected disc and inserts an artificial disc made of metal or a combination of metal and plastic. The prosthetic disc is designed to mimic the function of a natural intervertebral disc, allowing for normal spinal movement and flexibility.
Who Is It Suitable For?
- Individuals with symptomatic degenerative disc disease in the cervical or lumbar spine.
- Patients who have not found relief from conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medications, or injections, and who wish to maintain spinal mobility.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
- Patients with significant spinal instability, severe osteoporosis, or certain types of spinal deformities may not be suitable candidates for ADR surgery.
- Individuals with multiple-level disc degeneration or those with a history of spinal infections may also not be ideal candidates.
Advantages:
- Preservation of spinal motion and flexibility, potentially reducing the risk of adjacent segment degeneration.
- Relief from symptoms associated with degenerated discs, such as pain, numbness, and reduced mobility.
- Shorter recovery time compared to traditional spinal fusion surgery.
Complications:
- Potential complications include infection, implant dislocation, device wear, and adjacent level disc degeneration.
- There is also a risk of injury to nerves or blood vessels during the procedure.
Preoperative Care:
- Patients will undergo a comprehensive evaluation of their medical history and physical condition to assess their suitability for ADR surgery.
- They may have imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to determine the extent of disc degeneration and to help plan the surgical approach.
Postoperative Care:
- After ADR surgery, patients will need to follow specific activity restrictions and physical therapy guidelines to facilitate proper healing and rehabilitation.
- Regular postoperative follow-up appointments and imaging studies may be scheduled to monitor the function and positioning of the artificial disc.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.