Description
Familiarity with Treatment
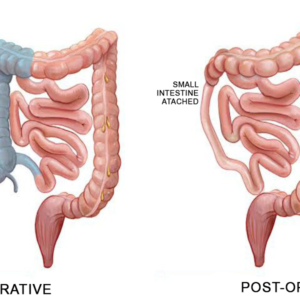
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a less-common weight-loss procedure that involves two major steps. The first step is sleeve gastrectomy, during which about 80 percent of the stomach is removed, leaving a smaller tube-shaped stomach, similar to a banana. The second step bypasses the majority of the intestine by connecting the end portion of the intestine to the duodenum near the stomach. BPD/DS both limits how much you can eat and reduces the absorption of nutrients, including proteins and fats.
Procedure
The initial step of a BPD/DS procedure includes removing a part of the stomach. After creating cuts with the open or laparoscopic method, the surgeon removes a large part of the stomach and structures the remaining parts into a narrow tube. The valve that discharges food to the small intestine, through the pyloric valve, is left intact, alongside a small part of the small intestine that usually connects with the stomach. The second step bypasses the majority of the intestines by associating the end part of the intestines to the duodenum close to the stomach.
Who is it Suitable For?
BPD/DS is generally recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or those with a BMI of 35 or higher with at least one obesity-related comorbidity, such as diabetes mellitus, obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, or severely limiting musculoskeletal issues. Super obese patients with a BMI over 50 should be considered for BPD/DS.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
BPD/DS may not be suitable for individuals with medical contraindications to surgery or those who are unable to follow dietary and other recommendations. It is important to carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of the surgery in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Advantages
- Significant Weight Loss: BPD/DS is associated with significant and lasting weight loss, making it an effective option for individuals with severe obesity.
- Improvement of Comorbidities: The procedure has been shown to improve or resolve obesity-related comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Complications
- Nutritional Deficiencies: BPD/DS is associated with a higher risk of nutritional deficiencies, including those that can be life-threatening if left untreated.
- Perioperative Complications: BPD/DS is associated with a higher risk of perioperative malnutrition and metabolic-related complications compared to other bariatric procedures.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for BPD/DS involves a comprehensive evaluation by the healthcare provider to determine the need for surgery and the most appropriate approach. This may include medical risk reduction and weight loss goals before the surgery.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for BPD/DS includes a strict diet and vitamin supplementation to avoid malnutrition. Patients will need to closely follow their care team’s instructions to avoid complications and ensure a successful recovery. Frequent follow-up care and long-term monitoring are essential for the management of potential complications and nutritional deficiencies.
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a complex weight-loss procedure designed for individuals with severe obesity and related conditions. It is important to carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of the surgery and to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for a successful recovery.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.