Description
Familiarity with Treatment
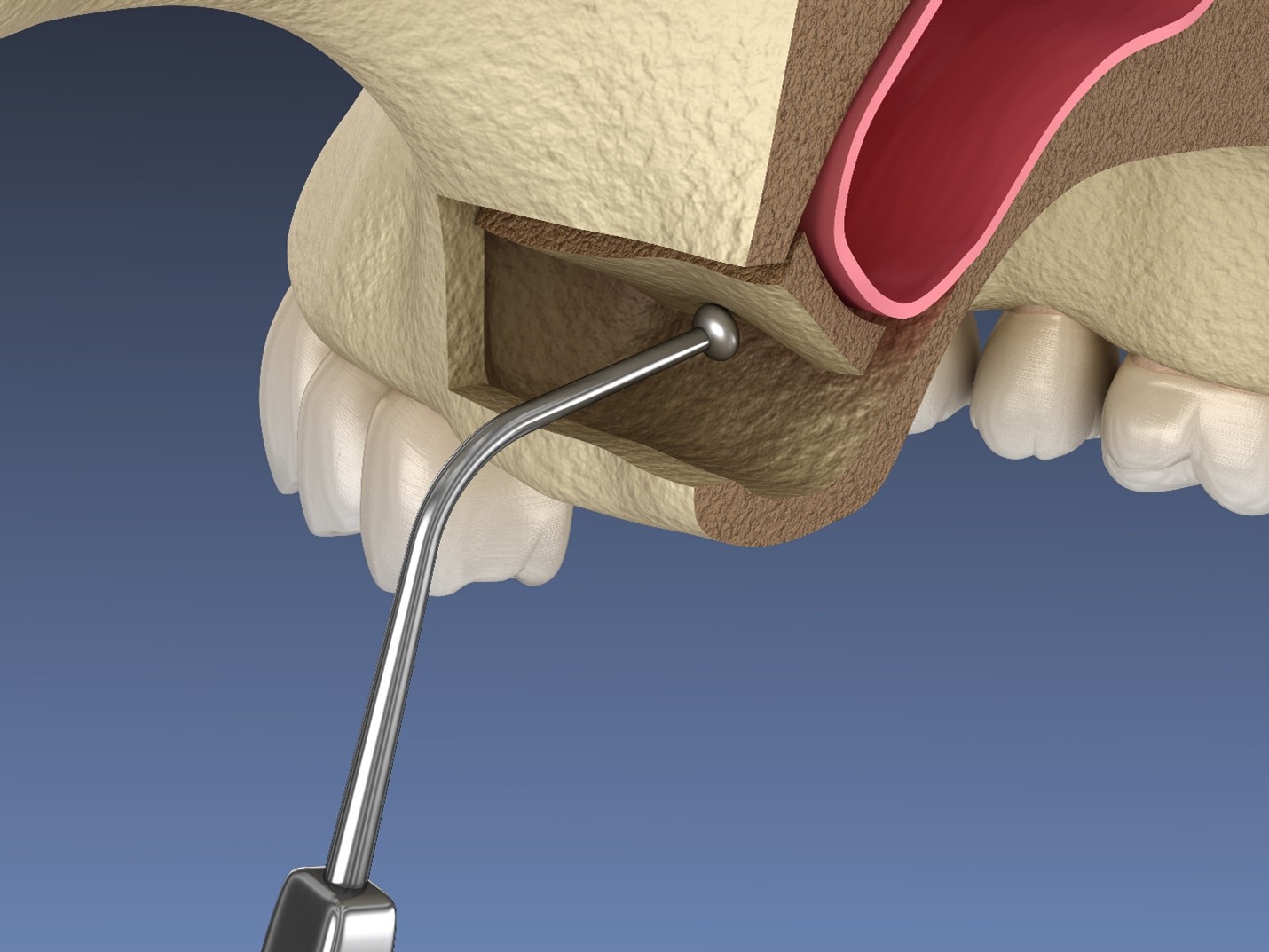
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves the transplantation of bone tissue to repair and rebuild diseased or damaged bones. It is a versatile procedure used to address a wide range of conditions, including fractures, infections, spinal fusion, and joint problems. The bone tissue used for grafting can be obtained from the patient’s own body, a donor, or synthetic sources.
Procedure
The procedure involves the transplantation of bone tissue to the affected area, where it acts as a filler or scaffold for new bone growth. The bone graft material can be obtained from various sources, including the patient’s hips, legs, ribs, or from synthetic bone substitutes. Over time, the graft material integrates with the surrounding bone tissue, promoting the regeneration and healing of the affected area.
Who is it Suitable For?
Bone grafting is suitable for individuals with conditions such as fractures, bone defects, infections, trauma, joint problems, and spinal fusion. It is also used to address birth abnormalities and benign tumors and cysts. The type of bone graft used depends on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual circumstances.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Bone grafting may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who may not be suitable candidates for surgical procedures. Specific considerations and contraindications should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances.
Advantages
- Bone Regeneration: Bone grafting promotes the regeneration and healing of diseased or damaged bones, helping to restore bone structure and function.
- Versatility: The procedure can be used to address a wide range of conditions, making it a versatile treatment option for various bone-related issues.
Complications
- Infection: There is a risk of infection following bone grafting, which requires careful monitoring and management to prevent complications.
- Nerve Damage: Nerve damage is a potential complication of the procedure, and individuals should be aware of the associated risks and symptoms.
Preoperative Care
Before undergoing bone grafting, individuals should discuss the choice of bone source with their healthcare provider, whether it is from their own body, a donor, or a synthetic source. Preoperative care may also involve discussions about potential risks, preoperative preparations, and the choice of anesthesia.
Postoperative Care
Following bone grafting, individuals should adhere to postoperative care instructions provided by their healthcare provider. This may include guidelines for managing discomfort, monitoring the healing process, and attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper recovery and the effectiveness of the procedure. It is important to follow any specific instructions related to the type of bone graft used and the expected recovery timeline.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.