Description
What is Blepharospasm?
Blepharospasm is a neurological condition characterized by involuntary eyelid twitching or blinking. These spasms can be frequent and forceful, causing difficulty keeping the eyes open and significantly impacting daily life.
Botox Injections: A Targeted Approach
Botox (botulinum toxin A) injections offer a minimally invasive treatment option for blepharospasm. Botox works by temporarily blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscles to contract. By inhibiting this signal, Botox relaxes the overactive muscles around the eyes, reducing involuntary eyelid twitching.
Procedure:
- Preparation: An anesthetic cream may be applied to numb the injection area.
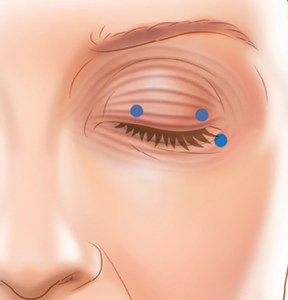
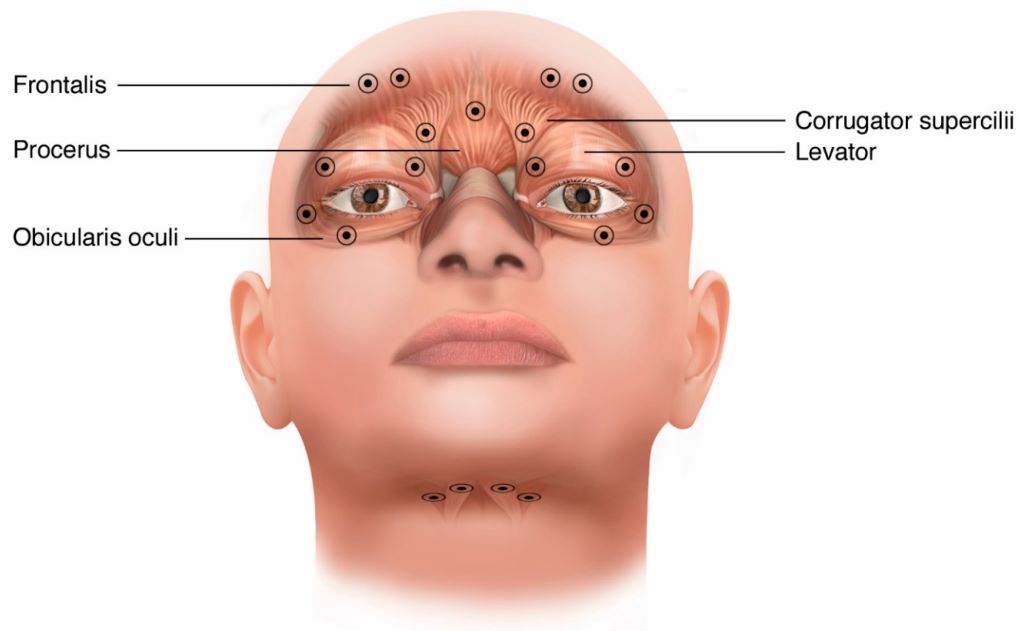
- Marking Injection Sites: The ophthalmologist carefully marks specific injection points around the eyes, targeting the muscles responsible for eyelid closure.
- Precise Injections: Using a very thin needle, small amounts of Botox are injected into the marked areas.
Who is Suitable for Botox Injections?
Individuals diagnosed with blepharospasm experiencing:
- Frequent and forceful eyelid twitching or blinking
- Difficulty keeping the eyes open
- Significant disruption to daily activities due to blepharospasm
- Unsatisfactory results with other treatments like eyelid lubricants or medications.
Who is Not Suitable?
Botox injections may not be suitable for everyone with blepharospasm. They are generally not recommended for:
- Patients with a history of allergic reactions to Botox
- Individuals with neuromuscular disorders affecting muscle function
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People with active eye infections
Advantages:
- Effective Relief: Botox injections can significantly reduce eyelid twitching and improve eye opening, enhancing daily activities.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is quick and relatively painless.
- Outpatient Procedure: Botox injections are typically performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home the same day.
- Temporary Treatment: The effects of Botox wear off over time (usually 3-4 months), allowing for repeat injections if needed.
Complications:
- Drooping Eyelid (Ptosis): This is the most common temporary side effect, usually resolving within a few weeks.
- Bruising or Swelling: Minor bruising or swelling at the injection site may occur, but typically fades quickly.
- Dry Eyes: Some patients may experience temporary dry eyes after injections.
- Headache: Mild headaches can sometimes occur after the procedure.
- Corneal Exposure: In rare cases, excessive ptosis can lead to difficulty blinking and expose the cornea, requiring lubricating eye drops or ointment.
Preoperative Care:
- Comprehensive eye exam to confirm the diagnosis of blepharospasm and rule out other causes of eyelid twitching.
- Discussion of risks and benefits of Botox injections with your ophthalmologist.
- Discontinuing certain medications that may increase bleeding risk.
Postoperative Care:
- Using artificial tears or lubricating eye drops as needed to address dry eyes.
- Avoiding strenuous activity for a short period.
- Following up with your ophthalmologist at scheduled intervals to monitor the effects of the injections and determine if repeat treatments are necessary.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.