Description
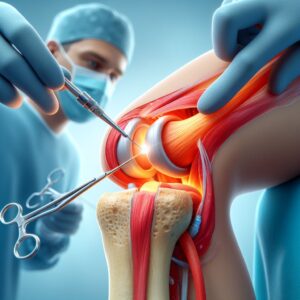
Orthopedic Corrective Surgery is a specialized branch of surgery that deals with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. It is used to correct deformities, restore function, and alleviate pain associated with various musculoskeletal conditions. Here is a detailed overview:
Familiarity with treatment:
Orthopedic Corrective Surgery is a well-established field in medicine. It is commonly used to treat a variety of conditions such as bone deformities, joint issues, sports injuries, and degenerative diseases like arthritis.
Procedure:
The specific procedure for Orthopedic Corrective Surgery depends on the condition being treated. It may involve realigning bones, repairing or replacing joints, correcting deformities, or removing diseased or damaged tissue. The surgery can be performed using traditional open surgery methods or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the complexity of the condition.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthopedic Corrective Surgery is suitable for individuals suffering from musculoskeletal conditions that cause pain, limit mobility, or affect quality of life. This includes conditions like arthritis, scoliosis, fractures, sports injuries, and congenital deformities.
Who is it not suitable for?
Orthopedic Corrective Surgery may not be suitable for individuals with certain health conditions that increase surgical risks, such as heart disease, uncontrolled diabetes, or severe obesity. It may also not be suitable for those who have not responded well to less invasive treatments or for whom the risks of surgery outweigh the potential benefits.
Advantages:
The advantages of Orthopedic Corrective Surgery include improved mobility, reduced pain, and enhanced quality of life. It can also prevent further deterioration of the condition and improve physical appearance in cases of visible deformities.
Complications:
As with any surgery, Orthopedic Corrective Surgery carries risks. These can include infection, bleeding, anesthesia complications, damage to surrounding tissues, and the potential for the issue to recur or for new issues to arise. There may also be a risk of non-union (where the bones do not heal properly) or malunion (where the bones heal in an incorrect position).
Preoperative care:
Preoperative care for Orthopedic Corrective Surgery typically involves a thorough medical evaluation to assess the patient’s health and readiness for surgery. The patient may need to stop taking certain medications or to follow specific dietary guidelines. They may also need to undergo certain tests or procedures in preparation for surgery.
Postoperative care:
Postoperative care can include pain management, wound care, physical therapy or rehabilitation, and regular follow-up appointments to monitor the patient’s recovery. The patient may also need to take certain medications or to follow specific lifestyle or dietary guidelines to support healing and recovery.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.