Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
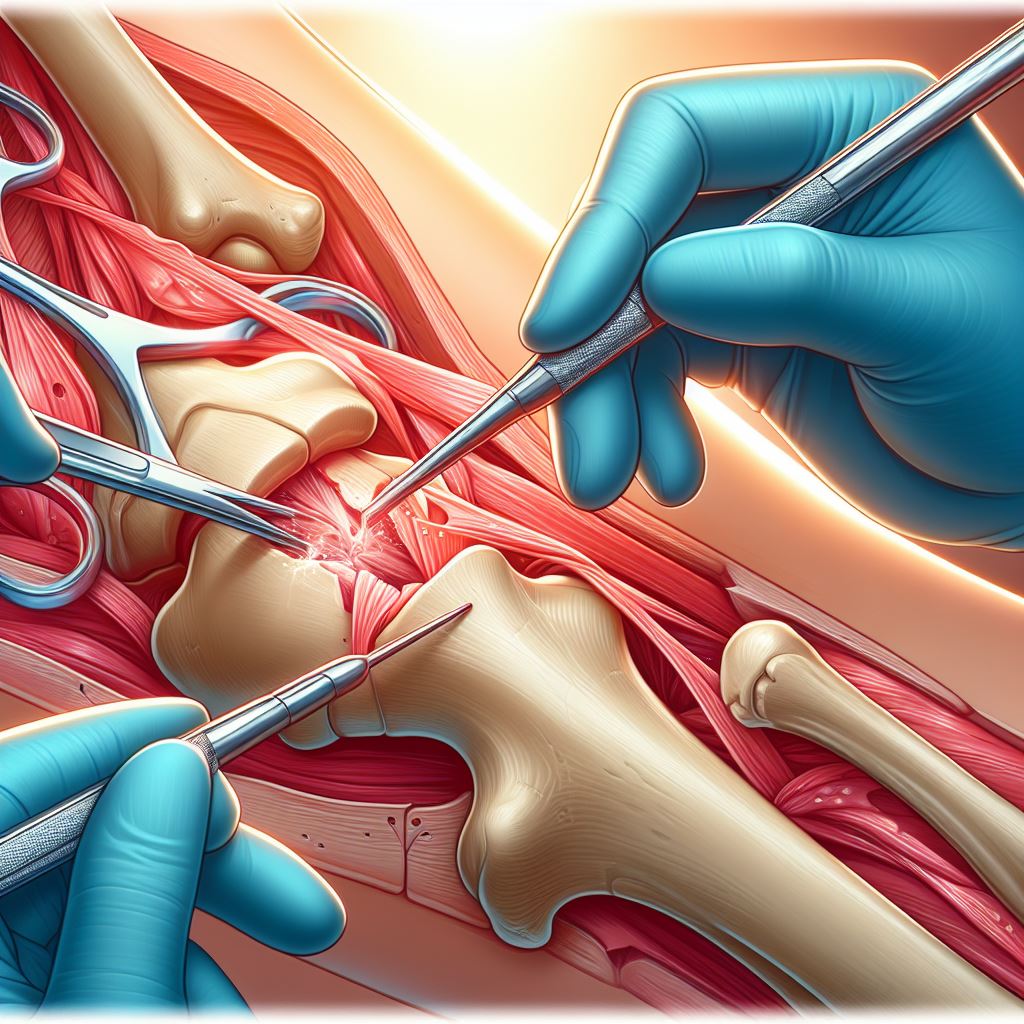
Orthopedic debridement is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of damaged, infected, or nonviable tissue from the musculoskeletal system. This procedure aims to clean the wound, reduce infection, and promote healing.
Procedure:
1. Surgical debridement: The surgeon makes an incision over the affected area to access the damaged tissue. They carefully remove the nonviable tissue, such as dead skin, muscle, or bone, using various surgical instruments like scalpels, forceps, or scissors.
2. Sharp debridement: This method involves using sharp instruments to remove necrotic tissue more effectively, especially in deep wounds or infections.
3. Conservative debridement: In this method, the surgeon removes only the most obviously damaged tissue, leaving healthier tissue intact.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthopedic debridement is suitable for patients with:
1. Open fractures: When a bone breaks through the skin, debridement is necessary to remove contaminants and reduce the risk of infection.
2. Infected wounds or osteomyelitis: Debridement helps eliminate infected tissue and promote healing in cases of severe infection or bone infection.
3. Chronic non-healing wounds: Debridement can remove dead tissue and stimulate the growth of healthy tissue in long-standing wounds.
Who is it not suitable for?
Orthopedic debridement may not be suitable for patients with severe medical conditions that make them high-risk candidates for surgery or those who cannot tolerate anesthesia. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if debridement is appropriate for your specific situation.
Advantages:
1. Reduces infection and promotes healing
2. Removes nonviable tissue and contaminants from the wound
3. Helps prevent complications like sepsis or further tissue damage
4. May be necessary before other orthopedic procedures or implantations
Complications:
Like any surgical procedure, orthopedic debridement carries potential risks and complications, including:
1. Infection
2. Bleeding
3. Blood clots
4. Nerve damage
5. Wound breakdown or dehiscence
6. Pain and discomfort
7. Limited mobility or stiffness
Preoperative Care:
Before the surgery, your healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and necessary imaging studies. They may also adjust your current medications or ask you to stop taking certain ones temporarily. It is essential to follow any specific preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare team, such as fasting guidelines and avoiding certain medications or substances.
Postoperative Care:
After the surgery, you will be closely monitored in a hospital or surgical facility. You may experience pain, swelling, and discomfort, for which your healthcare team will provide appropriate pain management. Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be necessary to regain mobility and function, depending on the extent of the debridement and the affected area. Your healthcare provider will also provide wound care instructions and follow-up appointments to monitor your healing progress.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.