Description
Familiarity with Treatment
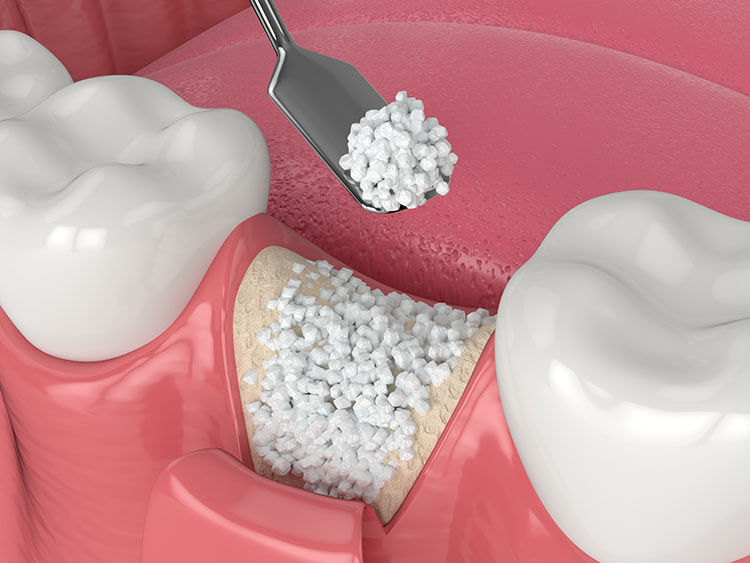
Connective tissue grafting is a leading treatment for gum recession, offering benefits such as high success rates and a relatively quick recovery. This procedure involves the replacement and regeneration of lost gum tissue, commonly using tissue from the palate and occasionally substitute grafting materials from licensed bone and tissue banks. Different gum grafting techniques and materials are available, and the specific approach can be explained in detail during a consultation with a dentist or periodontist.
Procedure
During a connective tissue graft surgery, a flap of skin is cut at the roof of the mouth (palate), and tissue from under the flap, known as subepithelial connective tissue, is removed and then stitched to the gum tissue surrounding the exposed root. The procedure involves the removal of connective tissue from under the palatal flap, followed by stitching the flap back down. This technique aims to address gum recession and provide support for the exposed roots of the teeth.
Who is it Suitable For?
Connective tissue grafting is suitable for individuals with gum recession, where the roots of the teeth become exposed. It is a common method used to treat root exposure and can effectively replace lost gum tissue, providing support and protection for the teeth.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Individuals who may not be suitable candidates for connective tissue grafting include those with specific oral health conditions or medical histories that may pose risks or complications during the procedure. It is important for individuals to consult with a dentist or periodontist to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on their individual circumstances.
Advantages
- Effective Treatment: Connective tissue grafting is considered the gold standard for the treatment of gum recession, offering high success rates and the potential for significant improvement in gum tissue support.
- Regeneration of Lost Tissue: The procedure aims to replace and regenerate lost gum tissue, providing essential support for the teeth and addressing the consequences of gum recession.
- Customized Approach: Different techniques and materials are available, allowing for a tailored treatment approach based on the individual’s specific case and oral health history.
Complications
- Donor Site Complications: Complications can arise at the donor site, particularly when harvesting connective tissue grafts from the palate. The harvesting technique can influence these complications, and it is important to consider the potential risks and challenges associated with the procedure.
- Postoperative Healing: The healing process following connective tissue grafting may involve temporary discomfort, swelling, and the need for careful postoperative care to ensure proper recovery.
Preoperative Care
Before undergoing connective tissue grafting, individuals should receive a comprehensive evaluation by a dental professional to assess their suitability for the procedure. This evaluation may include discussions about treatment goals, potential risks, and preoperative preparations.
Postoperative Care
Following connective tissue grafting, individuals should adhere to postoperative care instructions provided by the dental professional. This may include guidelines for oral hygiene, managing discomfort, monitoring the healing process, and attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper recovery and the effectiveness of the procedure.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.