Description
Familiarity with Treatment
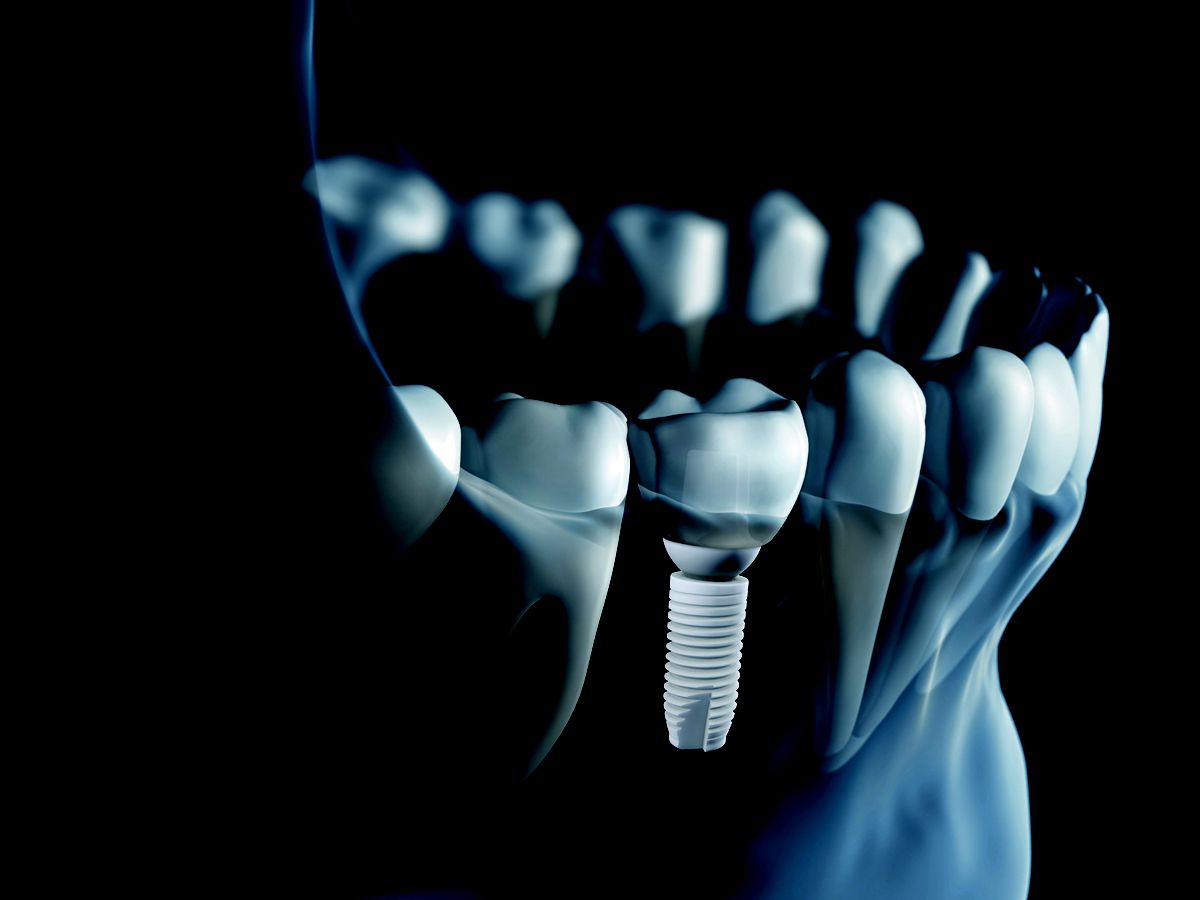
A dental implant is a surgical component that is placed into the jawbone to support a dental prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or denture. It serves as an artificial tooth root, providing a stable foundation for the replacement tooth.
Procedure
The procedure for dental implants typically involves the following steps:
- Evaluation and Planning: A comprehensive evaluation is conducted to assess the patient’s oral health, bone density, and suitability for the procedure. This may include imaging studies and a thorough examination of the oral and jaw structures.
- Implant Placement: The dental implant, usually made of titanium, is surgically placed into the jawbone. The implant is then left to integrate with the bone through a process called osseointegration, which typically takes several months.
- Abutment Placement: Once osseointegration is complete, an abutment is attached to the implant. The abutment serves as a connector between the implant and the dental prosthesis.
- Prosthesis Attachment: Finally, a dental prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or denture, is attached to the abutment, providing a functional and natural-looking replacement tooth.
Who is it Suitable For?
Dental implants are suitable for individuals who have lost one or more teeth and are looking for a permanent and stable solution for tooth replacement. They are generally recommended for individuals with good oral health and sufficient bone density to support the implant.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Dental implants may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or insufficient bone density to support the implant. A comprehensive evaluation by a dental professional is necessary to determine suitability for the procedure.
Advantages
- Natural Appearance: Dental implants provide a natural appearance, as they are designed to look and function like natural teeth.
- Improved Chewing and Speech: With dental implants, individuals can regain the ability to chew and speak properly, enhancing their overall quality of life.
- Longevity: Dental implants are a long-lasting solution for tooth replacement, with proper care and maintenance.
Complications
- Surgical Risks: As with any surgical procedure, there are inherent risks associated with implant placement, including infection, bleeding, and potential damage to surrounding structures.
- Osseointegration Issues: In some cases, the implant may fail to integrate with the jawbone, leading to implant failure. This can occur due to factors such as poor oral hygiene, smoking, or certain medical conditions.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for dental implants involves a comprehensive evaluation by a dental professional to assess the patient’s oral health, bone density, and suitability for the procedure. This may include imaging studies and a thorough examination of the oral and jaw structures.
Postoperative Care
Following the placement of dental implants, individuals should adhere to postoperative instructions provided by their dental professional. This may include guidelines for oral hygiene, dietary restrictions, and follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and ensure the success of the implants.
Dental implants offer a natural appearance, improved functionality, and longevity as a solution for tooth replacement.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.