Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
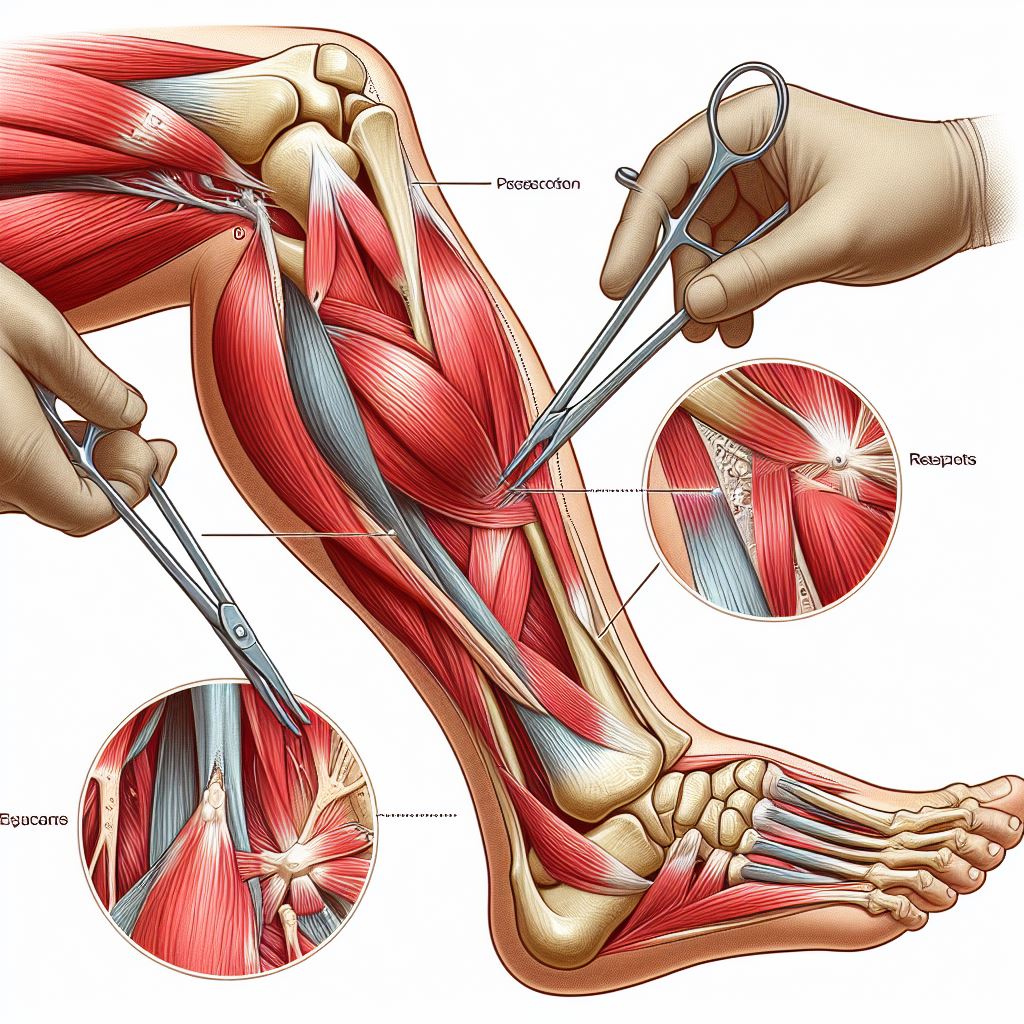
Orthopedic fasciotomy is a surgical procedure performed by orthopedic surgeons to relieve pressure within muscle compartments in the limbs. This procedure is commonly used to treat acute compartment syndrome, a condition where increased pressure within a muscle compartment can lead to tissue damage and impaired blood flow.
Procedure:
Orthopedic fasciotomy involves making one or more incisions in the skin over the affected muscle compartment, then cutting through the fascia to release the pressure buildup. The incisions are typically left open to allow for drainage and reduce the risk of further complications. The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Orthopedic fasciotomy is suitable for individuals who have been diagnosed with acute compartment syndrome or another condition requiring decompression of muscle compartments. It is often performed as an emergency procedure to prevent irreversible damage to muscles and nerves.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
Orthopedic fasciotomy may not be suitable for individuals who are not good candidates for surgery due to underlying medical conditions or those who are unable to undergo general anesthesia. Patients who do not have a clear diagnosis of compartment syndrome may not benefit from this procedure.
Advantages:
The main advantage of orthopedic fasciotomy is the prompt relief of pressure within muscle compartments, which can prevent further damage to muscles and nerves. By decompressing the affected area, orthopedic fasciotomy can restore blood flow and promote healing.
Complications:
Complications of orthopedic fasciotomy may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, compartment syndrome recurrence, and delayed wound healing. It is essential for patients to be monitored closely after surgery to address any potential complications promptly.
Preoperative Care:
Preoperative care for orthopedic fasciotomy may involve diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis, medication management, and patient education. Patients may be advised to stop eating or drinking before surgery and follow their healthcare provider’s instructions to prepare for the procedure.
Postoperative Care:
After orthopedic fasciotomy, patients will require wound care, pain management, physical therapy, and monitoring for any signs of complications. Patients may need to stay in the hospital for observation and rehabilitation before being discharged. Follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon will be necessary to monitor recovery progress and address any concerns.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.