Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
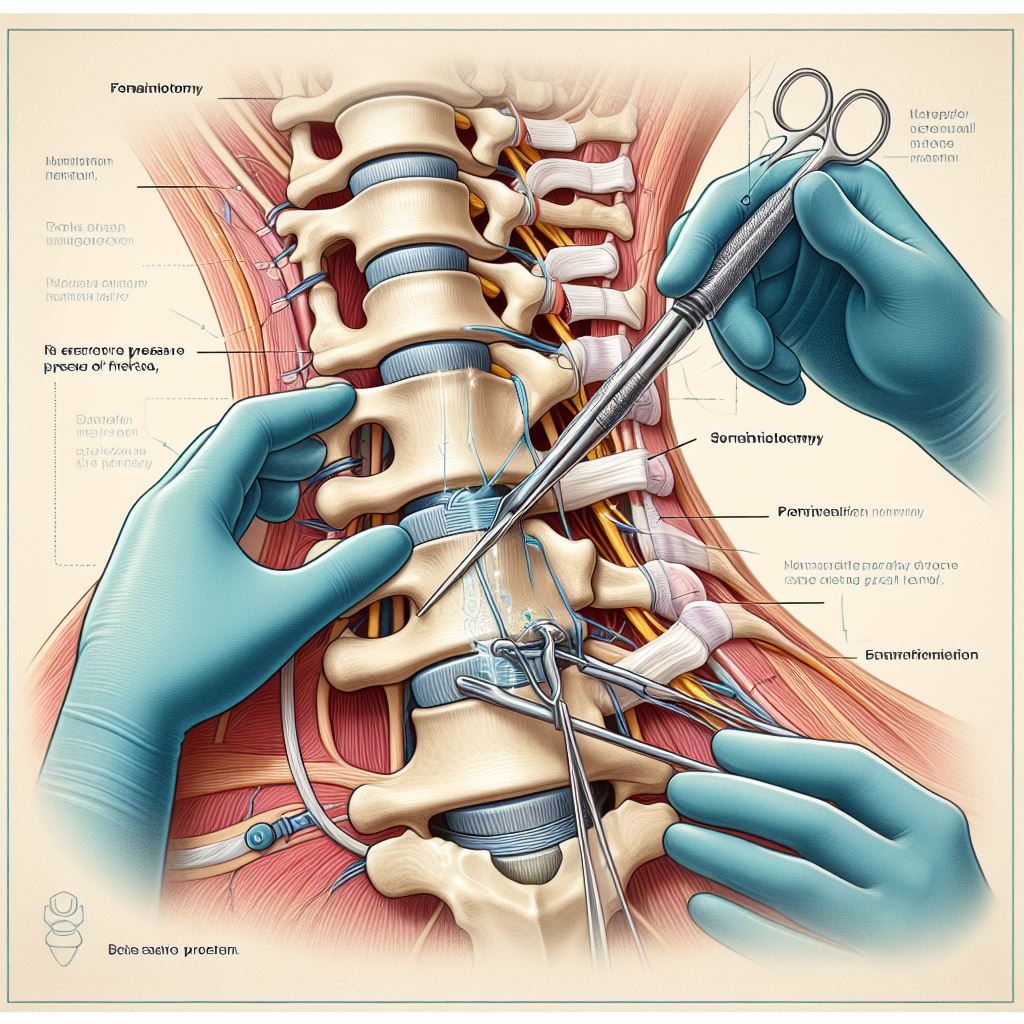
Foraminotomy is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving pressure on a spinal nerve by enlarging the neural foramen, the opening through which the nerve root exits the spinal canal. This surgery is commonly performed to address conditions such as foraminal stenosis or a herniated disc that is compressing a nerve in the spinal column.
Procedure: During a foraminotomy, the surgeon makes an incision in the back and then removes a portion of bone or tissue that is encroaching upon the nerve, thereby widening the neural foramen and alleviating the pressure on the affected nerve.
Who Is It Suitable For?
- Individuals experiencing symptoms such as arm or leg pain, weakness, or numbness due to nerve compression in the spinal column.
- Those who have not found relief from conservative treatments and whose symptoms significantly impact their quality of life.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
- Patients with mild or manageable symptoms that do not significantly impact daily life.
- Individuals with spinal conditions that are better treated through alternative methods or who are not good candidates for surgery due to underlying health concerns.
Advantages:
- Alleviation of symptoms caused by nerve compression, such as pain, numbness, and weakness.
- Potential improvement in mobility and overall quality of life for individuals affected by severe nerve compression.
Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks of bleeding, infection, nerve damage, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- There is also a small risk of recurrent nerve compression, spinal instability, or incomplete relief of symptoms.
Preoperative Care:
- Patients will undergo a comprehensive evaluation of their medical history and physical condition to assess their suitability for surgery.
- They may be advised to discontinue certain medications or supplements that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Postoperative Care:
- After surgery, patients will need to limit activities that put stress on the back while the surgical site heals.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be recommended to aid in recovery and restore strength and flexibility.
- Patients will be advised on proper lifting techniques and instructed on how to gradually resume normal activities.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.