Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
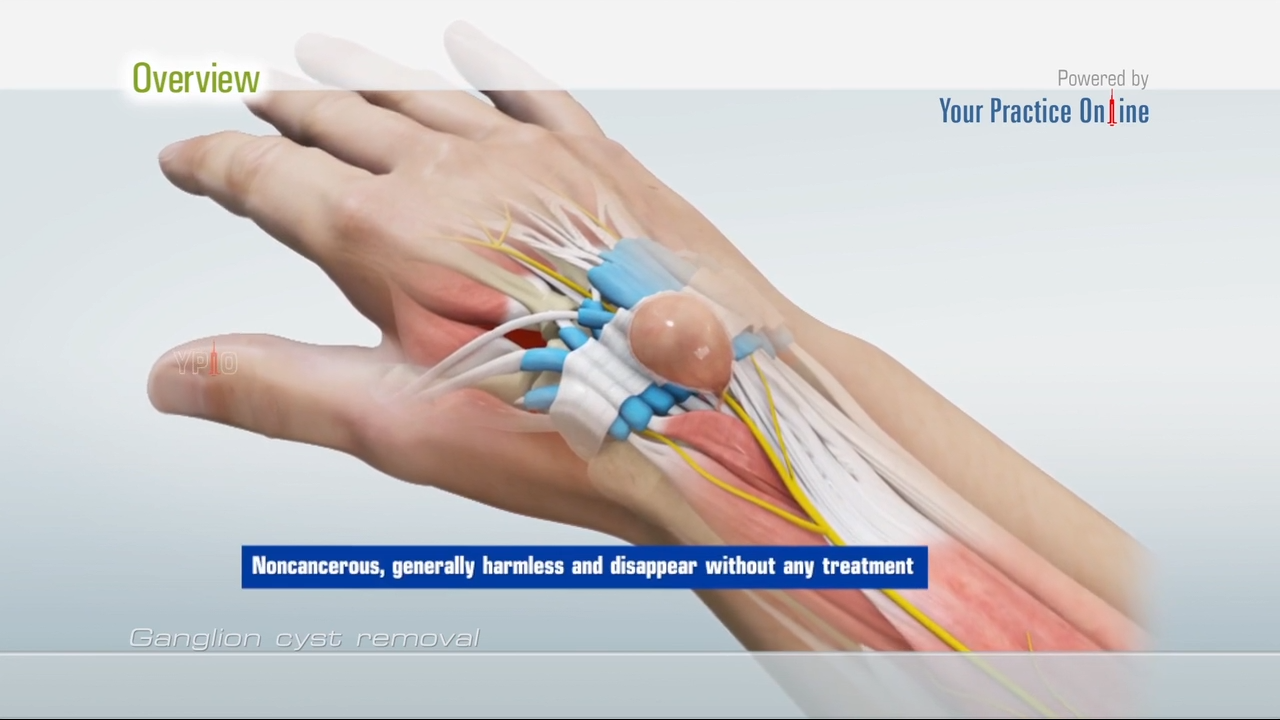
Ganglion cyst removal is a surgical procedure aimed at excising a ganglion cyst, a noncancerous, fluid-filled lump that often develops along the tendons or joints of the wrists or hands. The surgery involves removing the cyst and, in some cases, addressing any underlying joint or tendon issues.
Procedure:
- Incision: An incision is made over the ganglion cyst, allowing the surgeon to access and remove the cyst.
- Exploration and Excision: The surgeon carefully dissects the cyst and its connection to the joint or tendon, ensuring complete removal.
Who is it Suitable for?
Ganglion cyst removal is suitable for individuals with symptomatic ganglion cysts that cause pain, discomfort, or functional impairment, particularly when conservative treatments such as aspiration or immobilization have not provided sufficient relief.
Who is it Not Suitable for?
Ganglion cyst removal may not be suitable for individuals with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic ganglion cysts that do not significantly impair hand function. Additionally, those with certain medical conditions that increase surgical risks may not be good candidates for this procedure.
Advantages:
- Symptom Relief: Ganglion cyst removal surgery aims to alleviate pain, discomfort, and functional limitations associated with the cyst.
- Prevention of Recurrence: Complete excision of the ganglion cyst may reduce the likelihood of its recurrence.
Complications:
- Potential complications of ganglion cyst removal may include surgical site infection, nerve or blood vessel injury, stiffness, recurrence of the cyst, and scarring.
Preoperative Care:
- Comprehensive evaluation of the ganglion cyst, including physical examination and imaging studies, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the need for surgical intervention.
- Patient education regarding the procedure, including potential risks and benefits, as well as expectations for recovery and rehabilitation.
Postoperative Care:
- Immobilization and protection of the surgical site during the initial healing phase.
- Monitoring for signs of infection, impaired healing, or complications.
- Gradual return to normal hand use, avoiding activities that may stress the operated area.
- Rehabilitation exercises, if recommended by the surgeon, to restore hand strength and function.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.