Description
Familiarity with Treatment
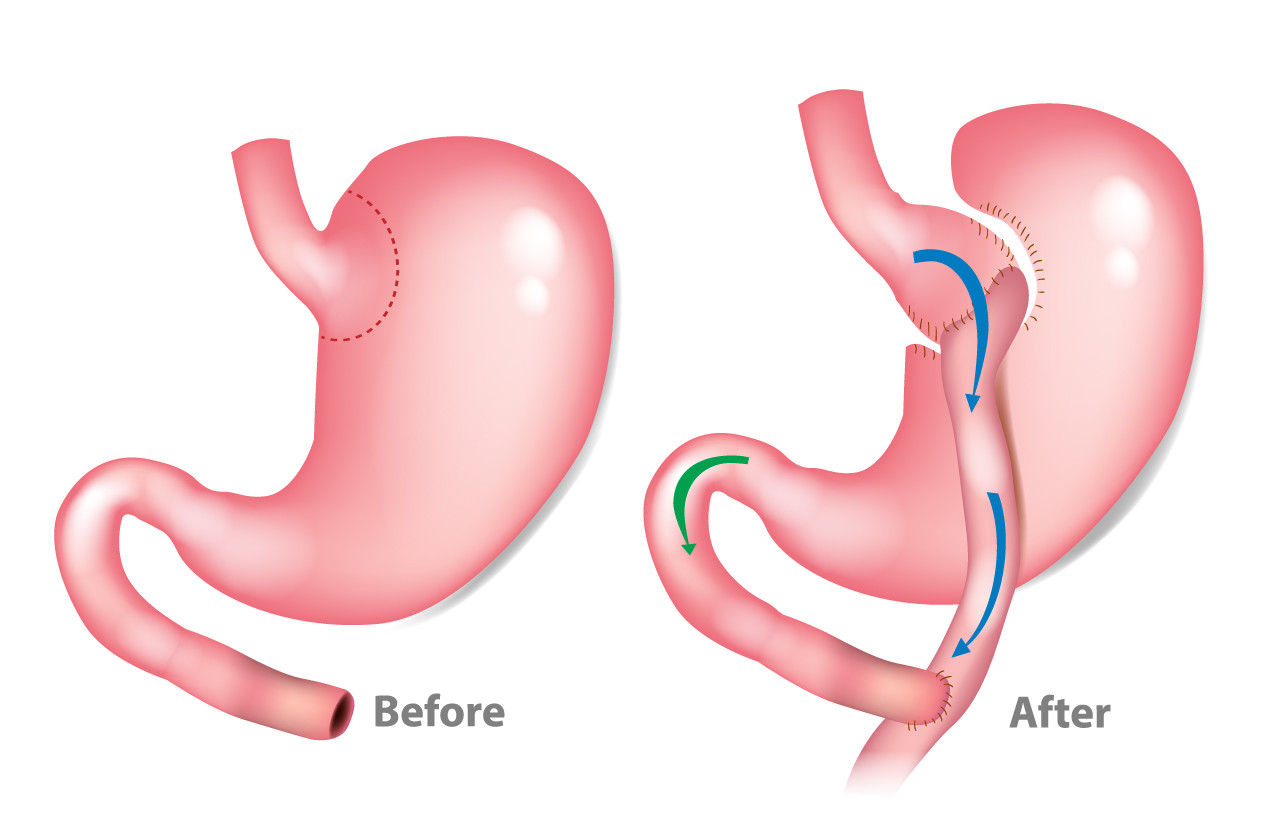
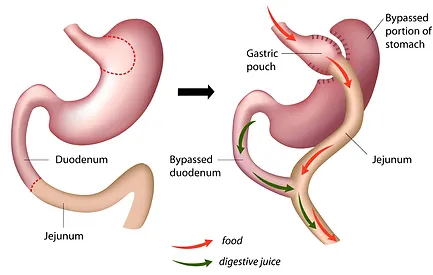
Gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y (roo-en-wy) gastric bypass, is a type of weight-loss surgery that involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting the newly created pouch directly to the small intestine. This surgical procedure is commonly performed to help individuals lose excess weight and reduce the risk of potentially life-threatening weight-related health problems, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obstructive sleep apnea, type 2 diabetes, stroke, cancer, and infertility.
Procedure
During gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon reduces the size of the stomach to create a small pouch about the size of an egg. This pouch is then connected directly to a part of the small intestine called the Roux limb, forming a “Y” shape. As a result, swallowed food bypasses most of the stomach and the first section of the small intestine, leading to reduced calorie absorption and weight loss.
Who is it Suitable For?
Gastric bypass surgery is recommended for individuals who have clinically severe obesity and have not achieved significant weight loss through diet and exercise. It has been shown to help relieve a long list of obesity-related health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (chronic acid reflux).
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Gastric bypass surgery may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who have contraindications to surgery or general anesthesia. The decision to undergo gastric bypass surgery should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, considering the individual’s overall health and specific medical history.
Advantages
- Weight Loss: Gastric bypass surgery can lead to significant and durable weight loss, often resulting in reduced hunger and restricted portions.
- Health Improvement: The procedure has been shown to improve or resolve obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and obstructive sleep apnea.
Complications
- Malnutrition: Gastric bypass surgery limits the types and quantity of food that can be consumed, as well as the nutrients that the body can absorb, potentially leading to malnutrition.
- Stomal Stenosis: This is a potential complication involving the narrowing of the connection between the stomach pouch and the small intestine.
- Dumping Syndrome: Some individuals may experience dumping syndrome, which involves symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and sweating after eating high-sugar or high-fat foods.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for gastric bypass surgery involves a comprehensive evaluation by the healthcare provider to determine the need for surgery and the most appropriate approach. This may include preoperative education, dietary counseling, and psychological evaluation to ensure readiness for the procedure.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for gastric bypass surgery includes monitoring for complications, pain management, wound care, dietary modifications, and long-term follow-up care. Patients will need to make significant lifestyle changes and adhere to a strict dietary plan to support the success of the surgery.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.