Description
Familiarity with Treatment
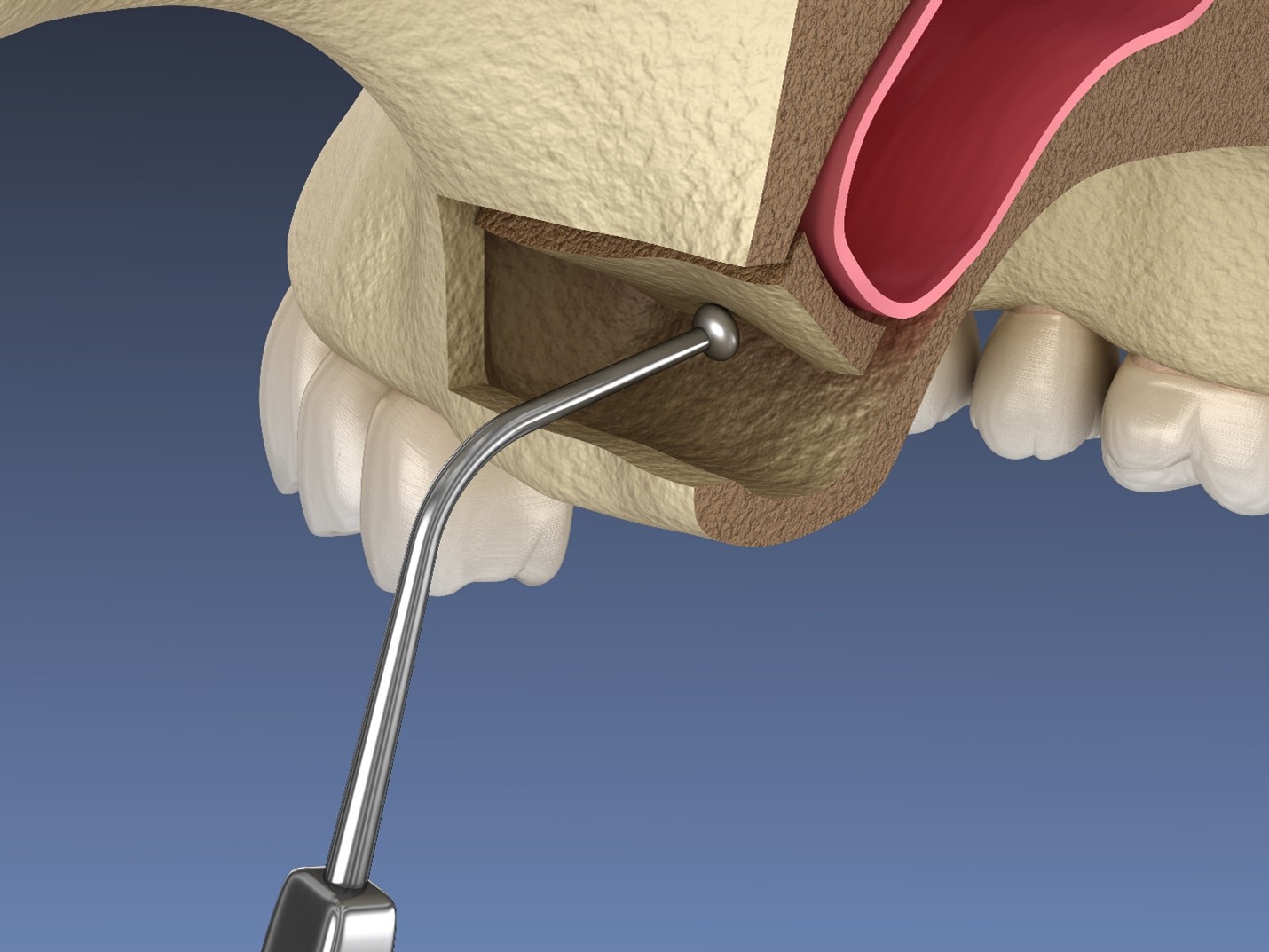
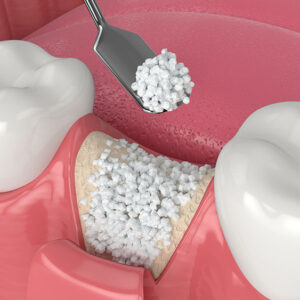
Gingival grafts, also known as gum grafts, are surgical procedures used to address gum recession and improve the health and aesthetics of the gums. The procedure involves the transplantation of gum tissue from one area of the mouth to another, typically to cover exposed tooth roots and increase the width of the attached gingiva.
Procedure
There are several types of gingival grafts, including free gingival grafts, connective tissue grafts, and pedicle (lateral) grafts. In a free gingival graft, a small layer of tissue is removed from the palate of the patient’s mouth and then relocated to the site of gum recession. It is sutured into place and serves to protect the exposed root as living tissue. Connective tissue grafts involve the removal of tissue from the roof of the mouth and its attachment to the existing gum tissue to cover the exposed tooth root. Pedicle grafts involve grafting tissue from the gum area near the recession site.
Who is it Suitable For?
Gingival grafts are suitable for individuals with gum recession, thin gum tissue, or inadequate attached gingiva. It is also used to address root exposure, improve oral health, and enhance the aesthetics of the smile.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Gingival grafts may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who may not be suitable candidates for surgical procedures. Specific considerations and contraindications should be discussed with a dental professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances.
Advantages
- Improved Gum Health: Gingival grafts can improve gum health by covering exposed tooth roots and increasing the width of the attached gingiva.
- Aesthetic Enhancement: The procedure can enhance the aesthetics of the smile by addressing gum recession and creating a more harmonious gum line.
Complications
- Donor Site Morbidity: Donor site morbidity, especially for free gingival grafts, is not infrequent, and patients should be advised appropriately about potential postoperative symptoms and complications.
- Mismatch in Color: Free gingival grafts may result in a mismatch in color between the donor tissue and the recipient site, leading to postoperative discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
Preoperative Care
Before undergoing gingival grafts, individuals should receive a comprehensive evaluation by a dental professional to assess their suitability for the procedure. This evaluation may include discussions about treatment goals, potential risks, and preoperative preparations.
Postoperative Care
Following gingival grafts, individuals should closely follow postoperative care instructions provided by the dental professional. This may include guidelines for oral hygiene, managing discomfort, monitoring the healing process, and attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper recovery and the effectiveness of the procedure. Proper postoperative care is essential for minimizing complications and ensuring optimal outcomes.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.