Description
Familiarity with Treatment
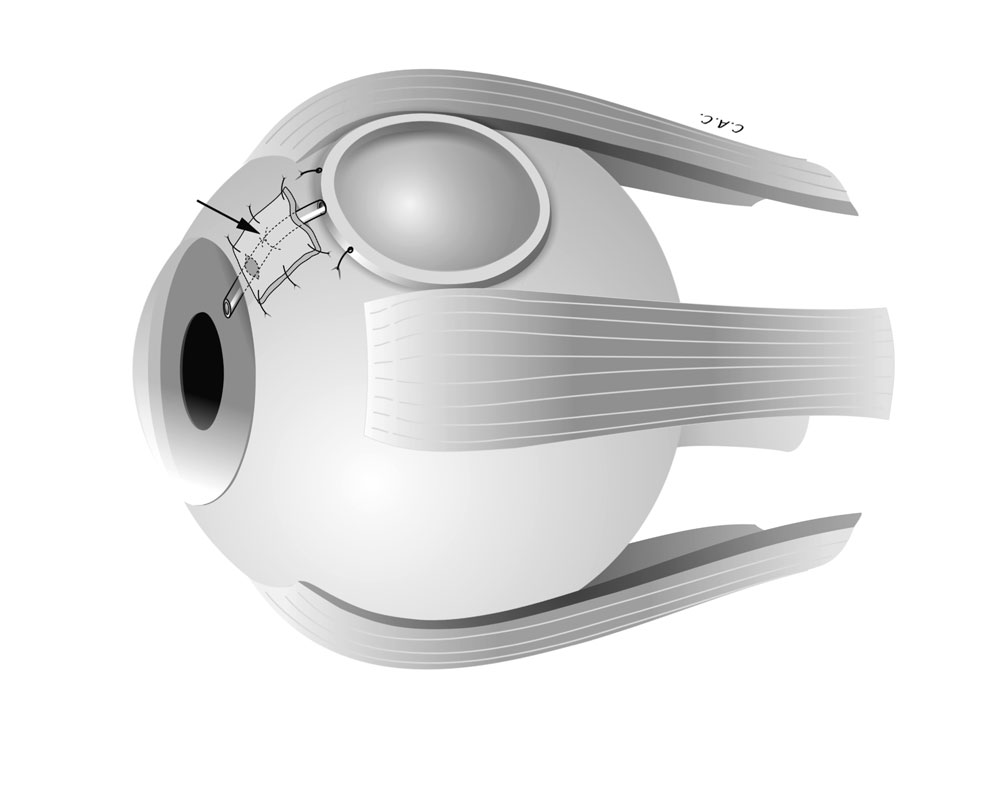
Glaucoma drainage surgery using the Ahmed Valve is a common procedure for managing glaucoma, particularly when other treatments have failed. The Ahmed Valve helps to reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) by providing an alternative drainage pathway for the aqueous humor (fluid inside the eye).
Procedure Explanation
- Anesthesia:
- Local anesthesia is administered to numb the eye.
- Incision:
- A small incision is made in the sclera (white part of the eye).
- Valve Placement:
- The Ahmed Valve is inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye.
- The valve is secured in place, and a small plate is positioned under the conjunctiva (the outer covering of the eye).
- Fluid Drainage:
- The valve regulates the outflow of aqueous humor, reducing IOP by allowing excess fluid to drain into a reservoir under the conjunctiva.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Patients with glaucoma that is not controlled by medications or laser treatments.
- Individuals with secondary glaucoma, such as neovascular glaucoma or uveitic glaucoma.
- Patients who have had previous unsuccessful glaucoma surgeries.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Patients with active eye infections or severe inflammation.
- Individuals with certain types of glaucoma that may not benefit from valve implantation.
- Patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery due to other health conditions.
Advantages
- Effective IOP Reduction: Consistently lowers intraocular pressure.
- Long-Term Solution: Provides a durable method for managing glaucoma.
- Minimally Invasive: Less invasive compared to other surgical options.
- Quick Recovery: Typically involves a shorter recovery period.
Complications
- Infection: Risk of postoperative infection.
- Bleeding: Possible bleeding during or after surgery.
- Hypotony: Excessively low IOP.
- Valve Malfunction: Potential for valve blockage or failure.
- Vision Changes: Possible temporary or permanent changes in vision.
Previous Care
- Preoperative Assessment: Comprehensive eye examination and IOP measurements.
- Medication Review: Adjustments to current medications, especially those affecting IOP.
- Health Evaluation: General health check to ensure suitability for surgery.
Aftercare
- Medications: Use prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and control inflammation.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups to monitor IOP and valve function.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoid strenuous activities and protect the eye from injury.
- Vision Monitoring: Report any changes in vision or discomfort to your ophthalmologist immediately.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.