Description
Familiarity with treatment
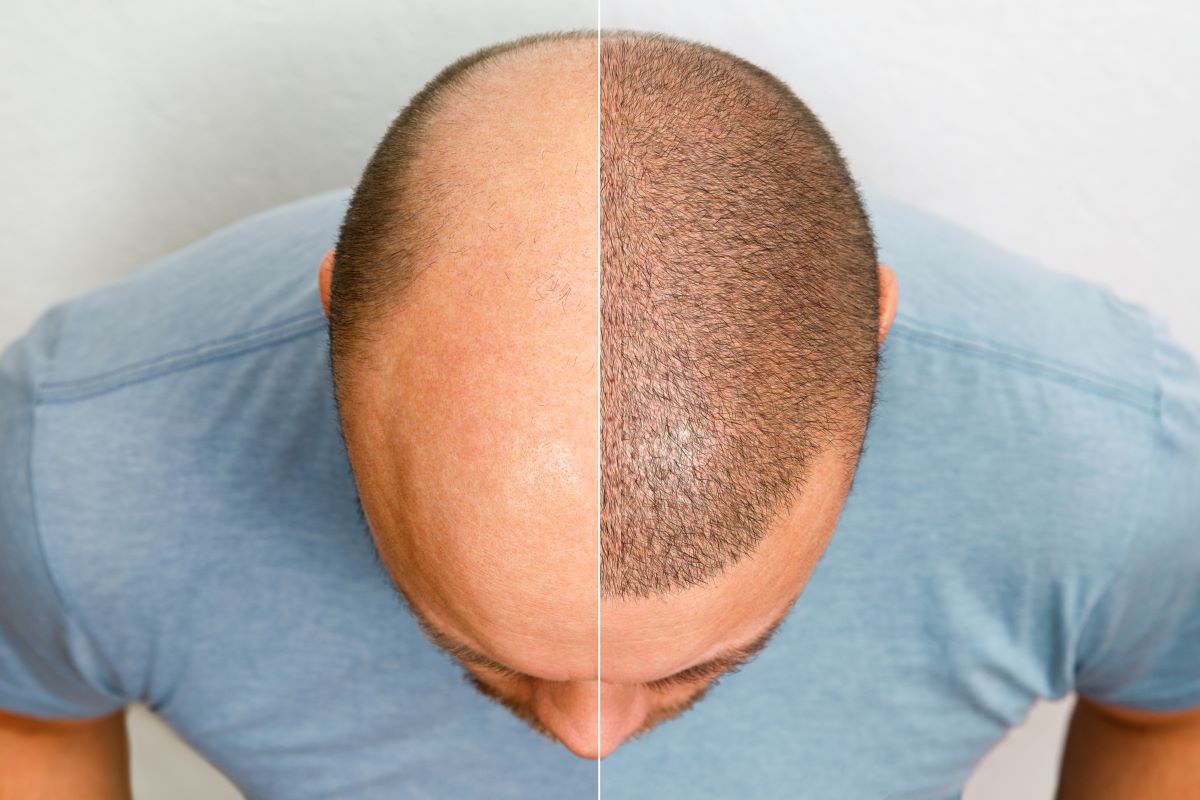
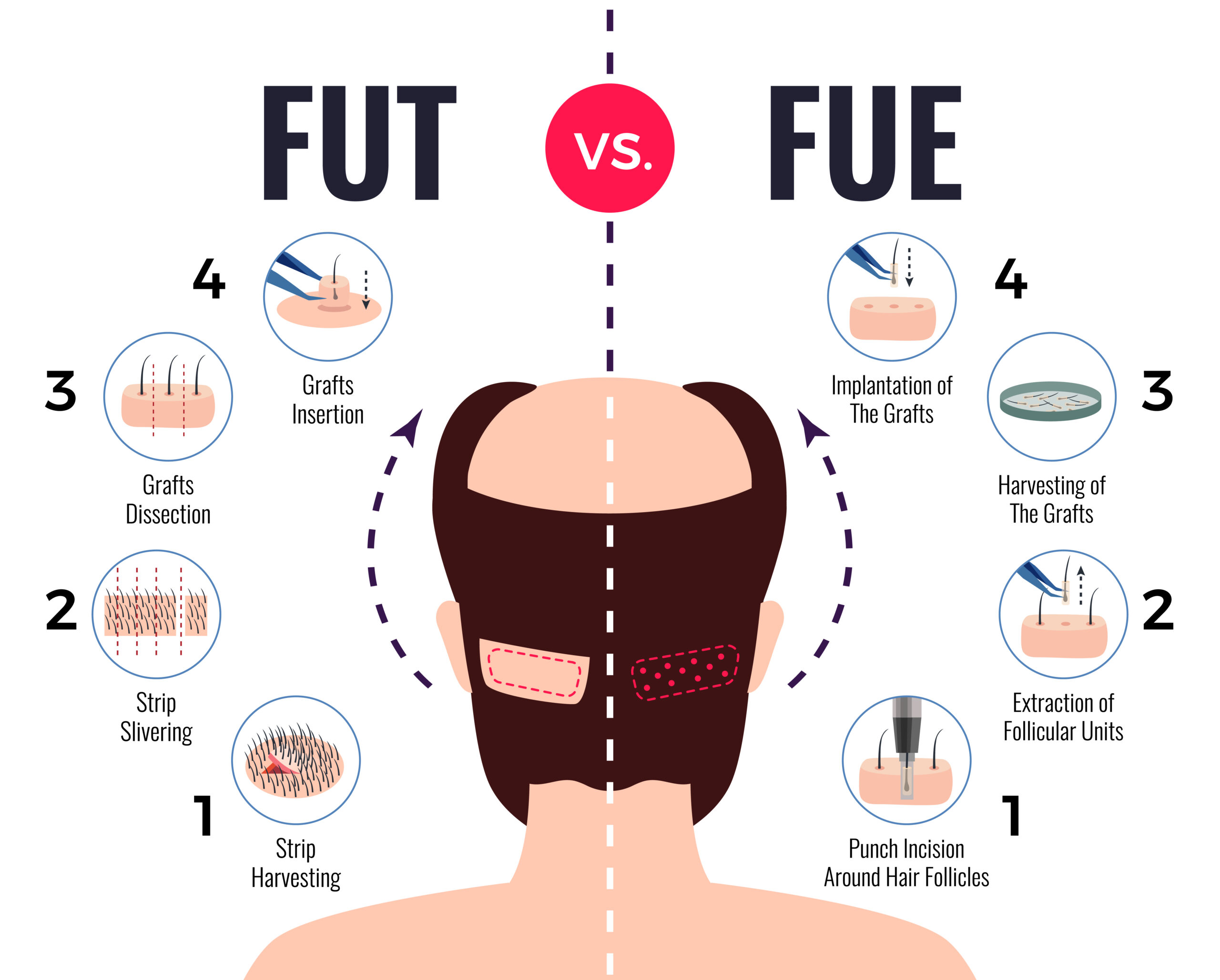
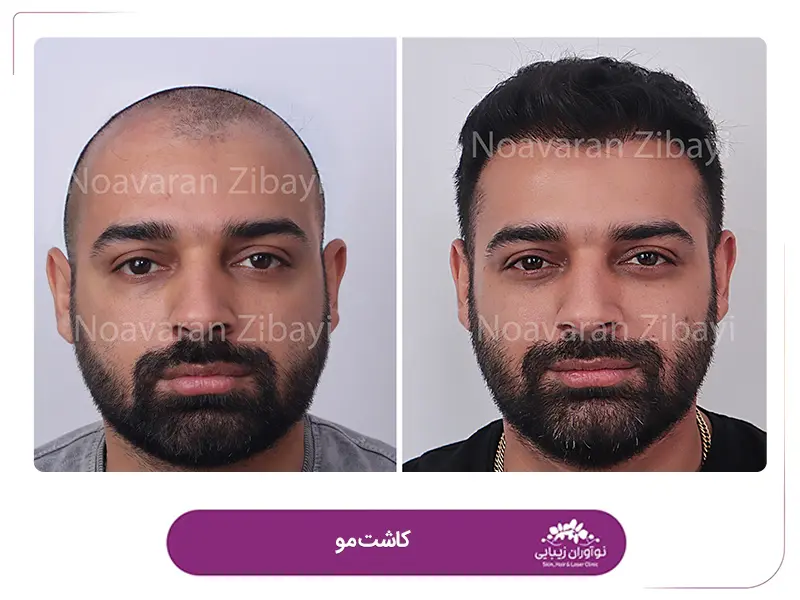
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is a hair restoration technique that involves transplanting hair in naturally occurring groups of 1 to 4 hairs, known as follicular units. FUT is also referred to as the strip procedure because it involves removing a strip of skin from the back or sides of the scalp, which is then dissected into individual grafts. These grafts, consisting of follicular units, are then transplanted into the bald or thinning areas of the scalp.
The advantages of FUT include the ability to transplant thousands of grafts in a single session, maximizing the cosmetic impact of the procedure. FUT is considered an advancement over older hair transplantation methods that used larger grafts, which often resulted in a pluggy and unnatural appearance. When properly performed, FUT results in a natural-looking hair growth pattern that is undetectable as a hair transplant.
The FUT procedure typically involves the following steps:
Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient’s scalp is cleaned, and the donor and recipient areas are marked.
Donor area harvesting: A strip of skin, usually from the back or sides of the scalp, is surgically removed. The size of the strip depends on the number of grafts needed. The incision is then closed with sutures or staples.
Graft dissection: The strip of skin is carefully dissected under a microscope to separate it into individual follicular units. Each unit contains one to four hairs, along with sebaceous glands, nerves, small muscles, and occasional fine vellus hairs.
Recipient site creation: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area, where the grafts will be transplanted. The surgeon strategically places the incisions to ensure a natural-looking hairline and overall distribution.
Graft transplantation: The dissected follicular units are then transplanted into the recipient sites using specialized instruments. The surgeon ensures proper angulation, direction, and density to achieve a natural appearance.
Postoperative care: After the procedure, the patient may experience some discomfort, swelling, and scabbing in both the donor and recipient areas. Pain medication and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor progress and provide guidance on postoperative care.
Who is it suitable for?
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is suitable for individuals experiencing male pattern baldness or other types of hair loss. It is particularly effective for those looking to restore a receding hairline or fill in balding areas. FUT works best for individuals who have a sufficient donor area, which is typically the back or sides of the scalp, where hair follicles are not influenced by the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), responsible for most hair loss.
During the FUT procedure, a surgeon cuts a strip of skin from the donor area, usually from the back of the head. This strip is then dissected into individual follicular units, which are small groups of hair follicles. These follicular units are then transplanted into the balding or thinning areas of the scalp.
Who is it not suitable for?
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) may not be suitable for everyone. Here are some factors that may make FUT less appropriate:
Limited donor hair: FUT requires a sufficient amount of donor hair, typically from the back or sides of the scalp, to transplant into the bald or thinning areas. If a person has limited donor hair or has already undergone multiple hair transplant procedures, FUT may not be feasible.
Desire to wear short hairstyles: FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which can be covered by surrounding hair. However, if a person prefers to wear very short hairstyles that expose the donor area, FUT may not be the best option. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or other hair restoration methods that do not leave a linear scar may be more suitable.
Tight scalp or scalp laxity issues: FUT requires the surgeon to remove a strip of skin from the scalp. If a person has a tight scalp or scalp laxity issues, it may affect the ability to safely remove the strip and close the incision properly.
Preference for minimal scarring: While FUT can provide excellent results, it does leave a linear scar at the donor site. If a person is concerned about visible scarring or prefers a minimally invasive approach, they may consider other hair transplant methods like FUE or robotic hair transplantation.
Medical conditions or contraindications: Certain medical conditions or medications may affect the suitability of FUT. It is important to consult with a qualified surgeon who can evaluate your specific circumstances and determine if FUT is appropriate for you.
Advantages
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) offers several advantages for individuals considering hair restoration. Here are some key benefits of FUT:
Maximizes graft yield: FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session. The strip of skin harvested during FUT contains a higher number of follicular units compared to other methods, maximizing the number of grafts available for transplantation. This can result in a more significant cosmetic impact and improved hair density.
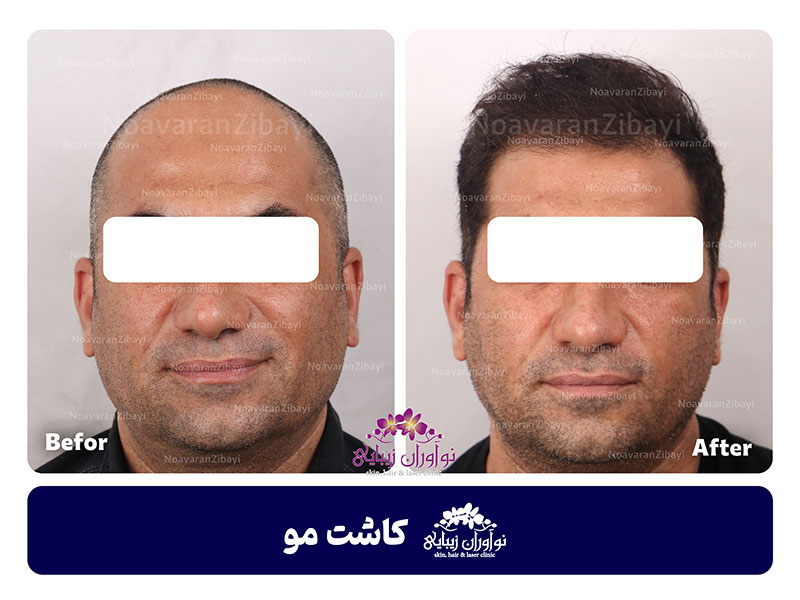
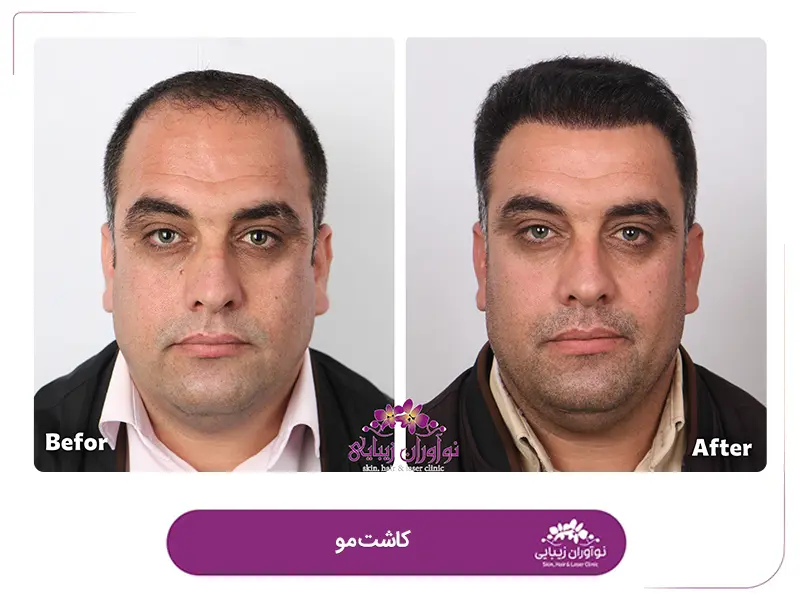
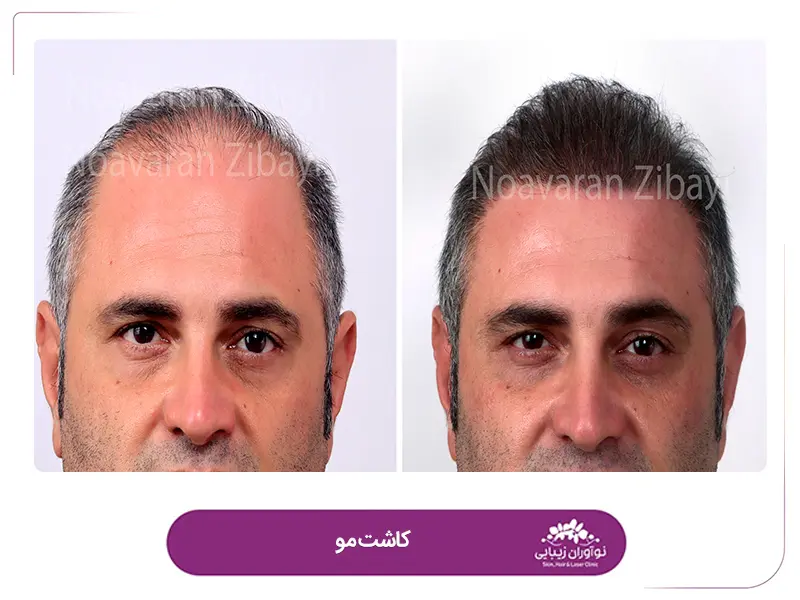
Natural-looking results: FUT is known for producing natural-looking results. The use of follicular units, which consist of 1 to 4 hairs, mimics the way hair grows naturally. The surgeon strategically places the grafts to create a hairline and overall distribution that blends seamlessly with the existing hair.
Suitable for extensive hair loss: FUT is particularly suitable for individuals with extensive hair loss or larger areas of baldness. The ability to transplant a higher number of grafts in a single session makes FUT an effective option for covering larger areas of the scalp.
Cost-effective: FUT can be a cost-effective option compared to other hair transplant methods. Since a larger number of grafts can be transplanted in a single session, fewer sessions may be required to achieve the desired results, reducing overall costs.
Long-term viability: The transplanted hair follicles in FUT are typically resistant to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is responsible for most hair loss. This means that the transplanted hair is less likely to fall out over time, providing long-term viability and a lasting solution for hair restoration.
Complications
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is generally a safe and effective procedure for hair restoration. However, like any surgical procedure, there are potential complications and risks associated with FUT. Here are some of the possible complications:
Scarring: FUT involves the removal of a strip of skin from the donor area, which results in a linear scar. The visibility of the scar can vary depending on factors such as the individual’s healing ability, the skill of the surgeon in closing the incision, and the length of the hair surrounding the scar. Although efforts are made to minimize scarring, it is important to consider the potential for a visible scar when opting for FUT.
Numbness and Sensation Changes: Some individuals may experience temporary or permanent numbness or changes in sensation in the donor or recipient areas. This can occur due to nerve damage during the procedure. In most cases, sensation returns to normal over time, but it is important to discuss this potential risk with your surgeon.
Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection. Following proper postoperative care instructions and taking prescribed antibiotics can help minimize this risk.
Bleeding: Bleeding is a potential complication during and after the FUT procedure. Surgeons take precautions to control bleeding during the surgery, and patients are advised to avoid activities that may increase blood flow to the scalp immediately after the procedure.
Delayed Healing: Some individuals may experience delayed healing of the incision site or the transplanted grafts. Factors such as poor wound care, underlying medical conditions, or individual healing responses can contribute to delayed healing.
Unnatural-looking Results: While FUT is known for producing natural-looking results, there is a possibility of the transplanted hair appearing unnatural if not properly placed or if the hairline design is not well-executed. Choosing an experienced and skilled surgeon can help minimize this risk.
preoperative care
Preoperative care for Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is an essential part of ensuring a successful procedure and optimal results. Here are some key aspects of preoperative care:
Consultation and Evaluation: The first step in the preoperative process is to schedule a consultation with a qualified hair transplant surgeon. During this consultation, the surgeon will evaluate your hair loss pattern, assess the donor area, discuss your goals and expectations, and determine if you are a suitable candidate for FUT.
Medical History and Medication Review: It is important to provide your surgeon with a comprehensive medical history, including any underlying medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are currently taking. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued before the procedure.
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke or consume alcohol, your surgeon may advise you to refrain from these activities for a certain period before the surgery. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair healing and increase the risk of complications.
Avoid Blood-Thinning Substances: Your surgeon may instruct you to avoid blood-thinning substances, such as aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and herbal supplements, as they can increase the risk of bleeding during and after the procedure.
Hair Care: It is generally recommended to avoid cutting or shaving your hair too short before the procedure. Having some length to the hair in the donor area can help conceal the linear scar that may result from FUT.
Preoperative Instructions: Your surgeon will provide you with specific preoperative instructions to follow. These may include guidelines on when to stop eating and drinking before the surgery, what to wear on the day of the procedure, and any specific hair care instructions.
Arrange Transportation: Since FUT is performed under local anesthesia, you may not require general anesthesia. However, it is still advisable to arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure, as you may experience some postoperative discomfort or drowsiness.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care is crucial for ensuring proper healing and optimal results after Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). Here are some key aspects of postoperative care:
Follow Surgeon’s Instructions: It is important to carefully follow the postoperative instructions provided by your surgeon. These instructions may include guidelines on medication usage, wound care, and activities to avoid during the recovery period.
Medication and Wound Care: Your surgeon may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection and pain medication to manage any discomfort. It is important to take these medications as directed. Additionally, you may be instructed to keep the surgical area clean and apply any recommended topical ointments or dressings.
Avoid Physical Activity: It is generally advised to avoid strenuous physical activities, heavy lifting, and exercise for a certain period after the procedure. This helps prevent excessive sweating, which can interfere with the healing process.
Protect the Transplanted Area: It is important to protect the transplanted area from direct sunlight, extreme temperatures, and trauma. Wearing a hat or using sunscreen with a high SPF can help shield the scalp from harmful UV rays.
Gentle Hair Washing: Your surgeon will provide specific instructions on when and how to wash your hair after the procedure. Typically, a gentle shampoo is recommended, and you should avoid rubbing or scratching the transplanted area.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair the healing process. It is advisable to avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake during the recovery period.
Follow-up Appointments: Your surgeon will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and assess the healing of the transplanted hair. It is important to attend these appointments and discuss any concerns or questions you may have.


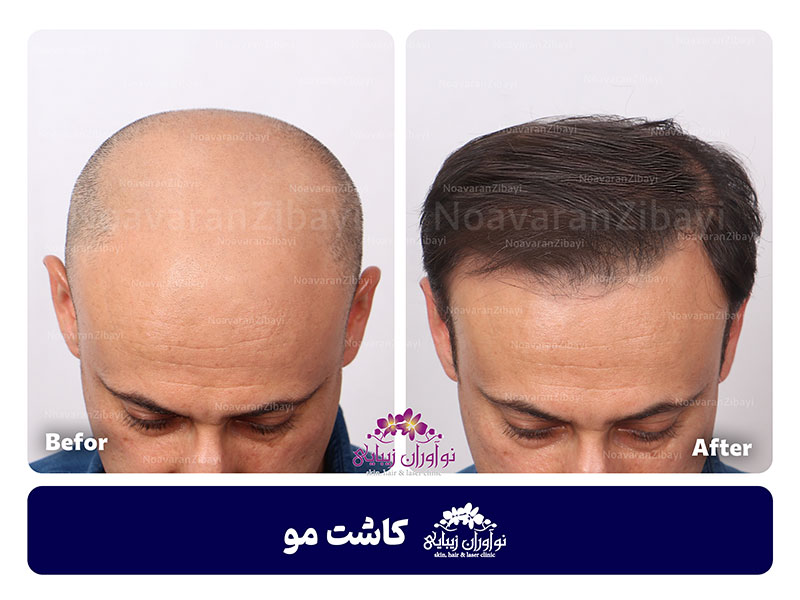

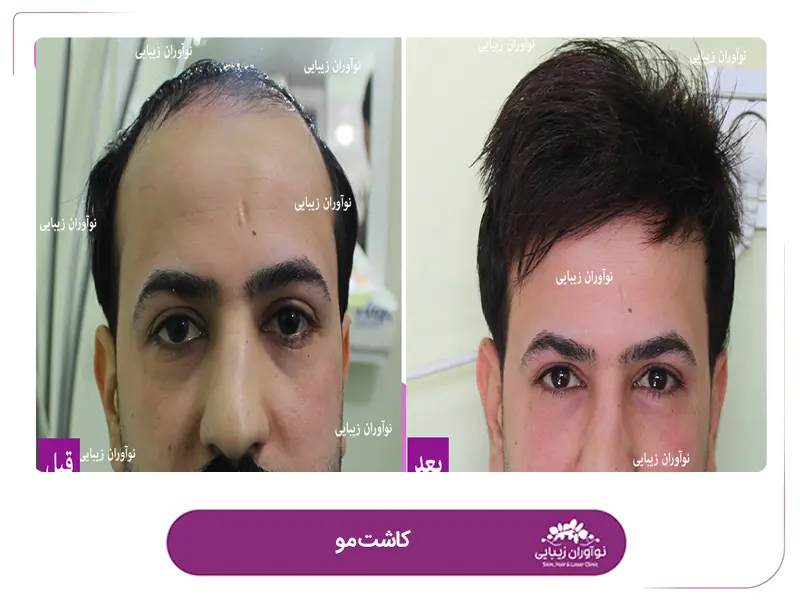

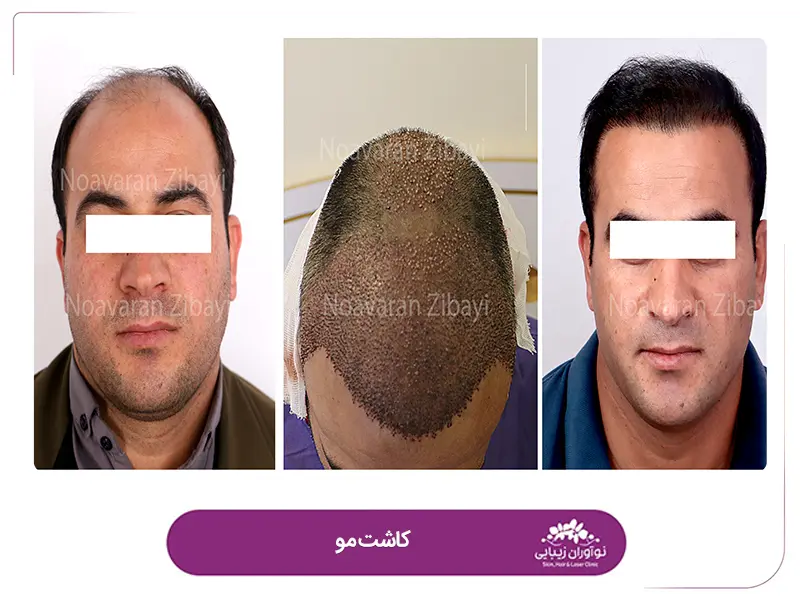






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.