Description
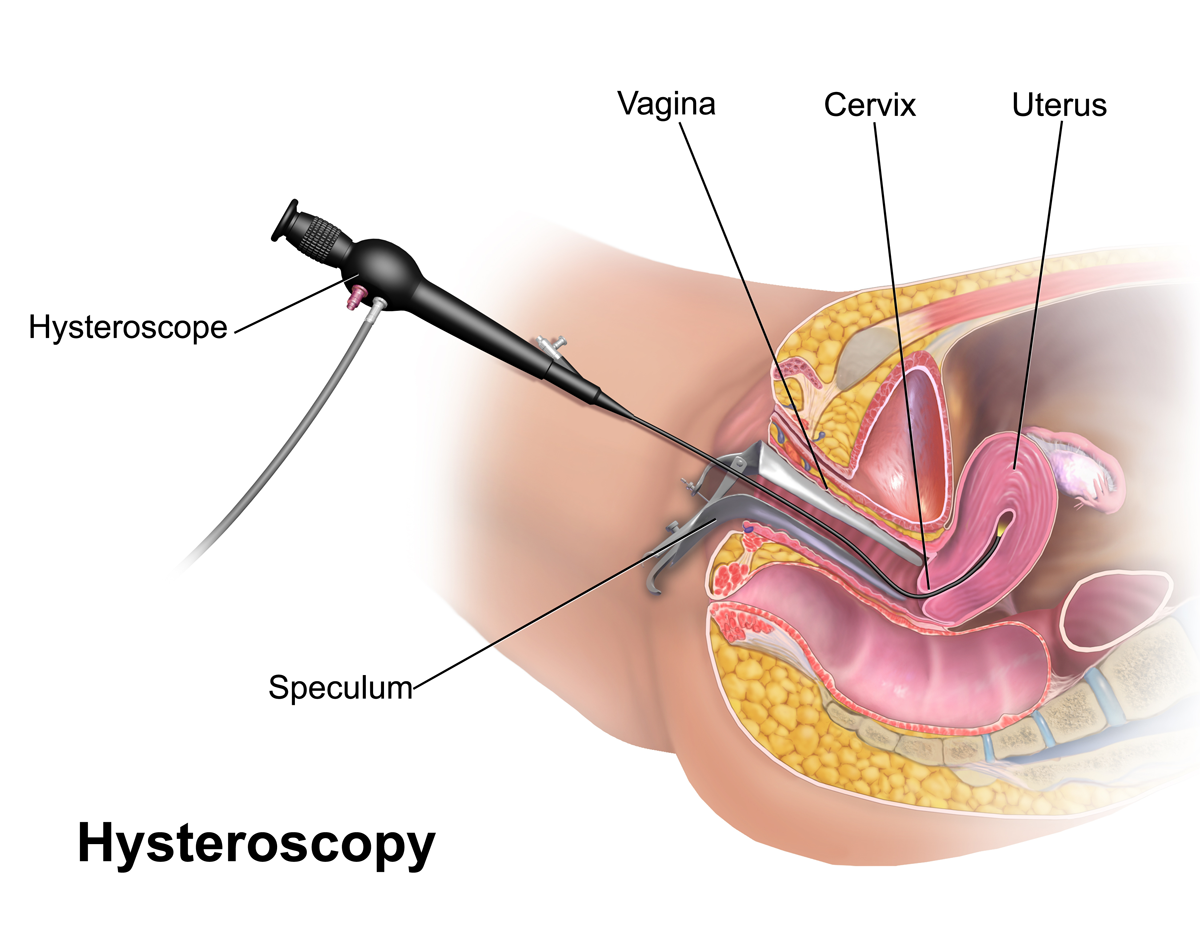
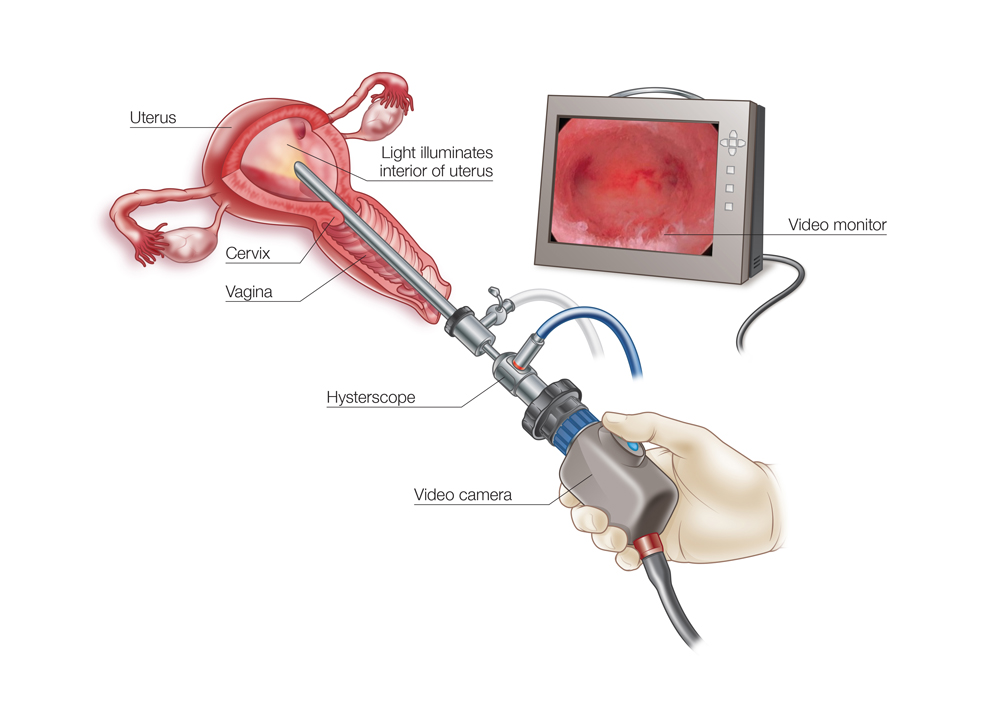
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows a doctor to look inside the uterus using a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope. This procedure can be used for both diagnostic and operative purposes.
Types of Hysteroscopy
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy: Used to diagnose problems of the uterus, such as abnormal bleeding, polyps, fibroids, and structural abnormalities.
- Operative Hysteroscopy: Performed to treat an abnormality detected during a diagnostic hysteroscopy. This can include removing polyps, fibroids, adhesions, or performing endometrial ablation.
Familiarity with Treatment
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that provides a direct view of the uterine cavity, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment of various uterine conditions.
Procedure
- Preparation:
- Blood tests and a pregnancy test may be ordered about a week before the procedure.
- Fasting for a few hours before the procedure if general anesthesia is used.
- Stopping smoking to reduce anesthesia-related risks.
- During the Procedure:
- The patient changes into a hospital gown and lies on an exam table with feet in stirrups.
- A speculum is inserted into the vagina to hold it open, and the vagina and cervix are cleaned with antiseptic.
- The hysteroscope is inserted through the cervix into the uterus, and gas or saline is used to expand the uterus for a clear view.
- The doctor examines the uterine cavity and may perform necessary treatments.
- Duration: The procedure usually takes between 5 to 30 minutes12.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Women with abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Those with suspected uterine abnormalities such as polyps, fibroids, or adhesions.
- Women experiencing infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
- Patients needing confirmation of results from other tests like ultrasound or hysterosalpingography.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Pregnant women.
- Those with active pelvic infections.
- Women with certain medical conditions that contraindicate the use of anesthesia or the procedure itself.
Advantages
- Minimally invasive with a quick recovery time.
- Provides a direct view of the uterine cavity for accurate diagnosis.
- Can treat certain conditions immediately, avoiding the need for additional surgeries.
- Generally safe with a low risk of complications.
Complications
- Infection.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Uterine scarring.
- Side effects from anesthesia.
- Side effects from the gas or fluid used to expand the uterus.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease12.
Previous Care
- Regular gynecological check-ups.
- Discussing the procedure, risks, and benefits with the healthcare provider.
- Following pre-procedure instructions, such as fasting and stopping smoking.
Aftercare
- Monitoring for signs of infection or complications, such as fever, severe abdominal pain, or heavy bleeding.
- Rest and avoiding strenuous activities for a few days.
- Follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider to ensure proper healing.
- Pain management with prescribed medications if necessary.
Hysteroscopy is a valuable tool for diagnosing and treating various uterine conditions with minimal invasiveness.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.