Description
Familiarity with Treatment
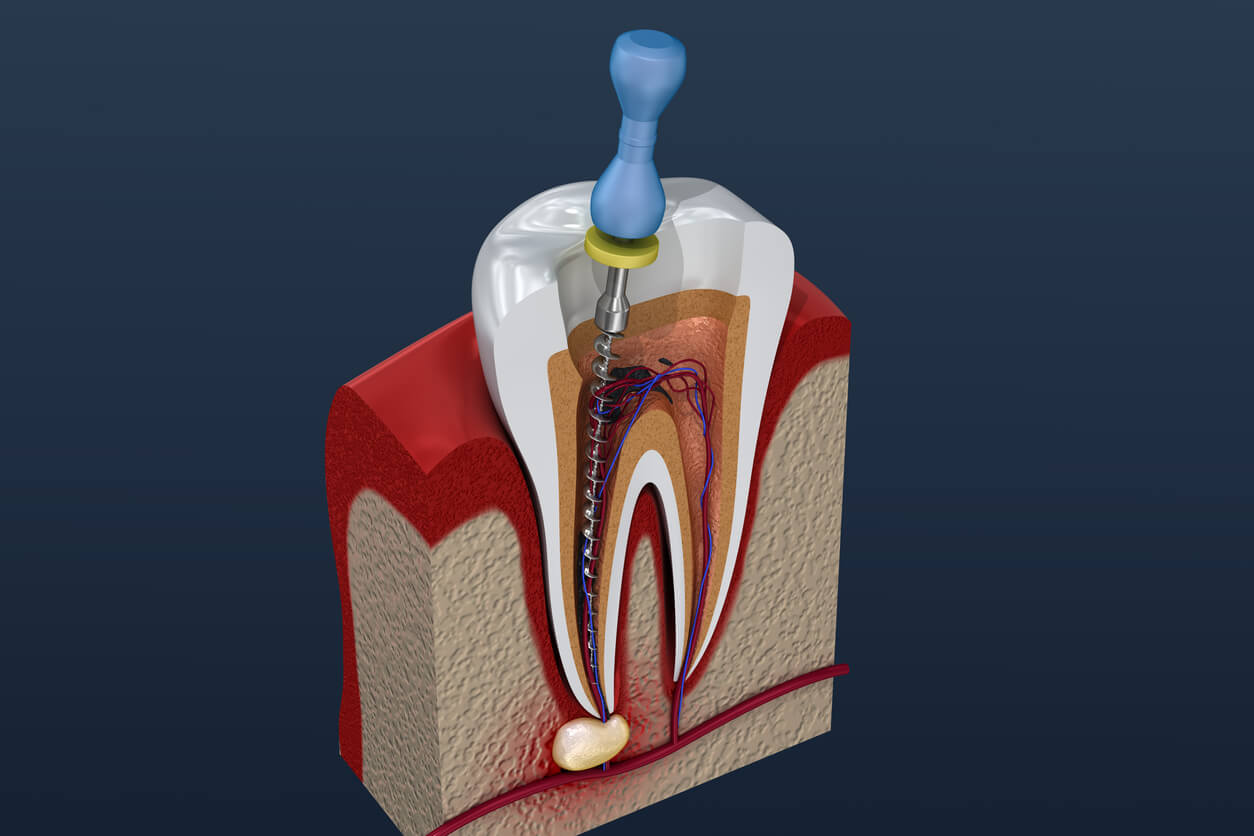
Internal bleaching is a dental procedure performed to lighten the color of a tooth that has undergone root canal treatment and has become discolored from within. It involves the application of a bleaching agent inside the tooth to remove stains and restore a more natural appearance.
Who is it Suitable for?
Internal bleaching is suitable for individuals who have undergone root canal treatment and have a discolored tooth as a result. It is typically recommended when the tooth has become significantly darker or discolored and traditional external teeth whitening methods are not effective in improving its appearance.
Who is it Not Suitable for?
Internal bleaching may not be suitable for individuals with certain dental conditions, such as teeth with extensive decay or structural damage, as well as those with gum disease or active infections. Additionally, individuals with allergies to the bleaching agents used in the procedure may not be suitable candidates.
Advantages
- Restores the natural appearance of a discolored tooth, improving its aesthetic appeal.
- Preserves the natural tooth structure, avoiding the need for more invasive procedures like dental crowns or veneers.
- Typically a less expensive option compared to other cosmetic dental treatments.
Complications
- Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience temporary tooth sensitivity during or after the bleaching process. This sensitivity usually subsides on its own.
- Gum Irritation: Improper application of the bleaching agent can cause irritation to the gums. It is important for the procedure to be performed by a qualified dental professional to minimize this risk.
- Inadequate Results: In some cases, internal bleaching may not achieve the desired level of tooth whitening. This can occur if the tooth has deep or resistant stains.
Preoperative Care
Before undergoing internal bleaching, a comprehensive assessment of the discolored tooth is performed by a dental professional. This may involve a review of the patient’s medical history, evaluation of any existing dental conditions, and the use of imaging techniques (such as X-rays) to assess the tooth’s condition. Preoperative care may also involve discussing the treatment plan, potential risks, and expected outcomes with the dental professional.
Postoperative Care
After internal bleaching, postoperative care may involve managing any tooth sensitivity or gum irritation that may occur. This can be done through the use of desensitizing toothpaste or mouth rinses, as recommended by the dental professional. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices and follow any additional instructions provided by the dentist to ensure the long-term success of the treatment.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.