Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
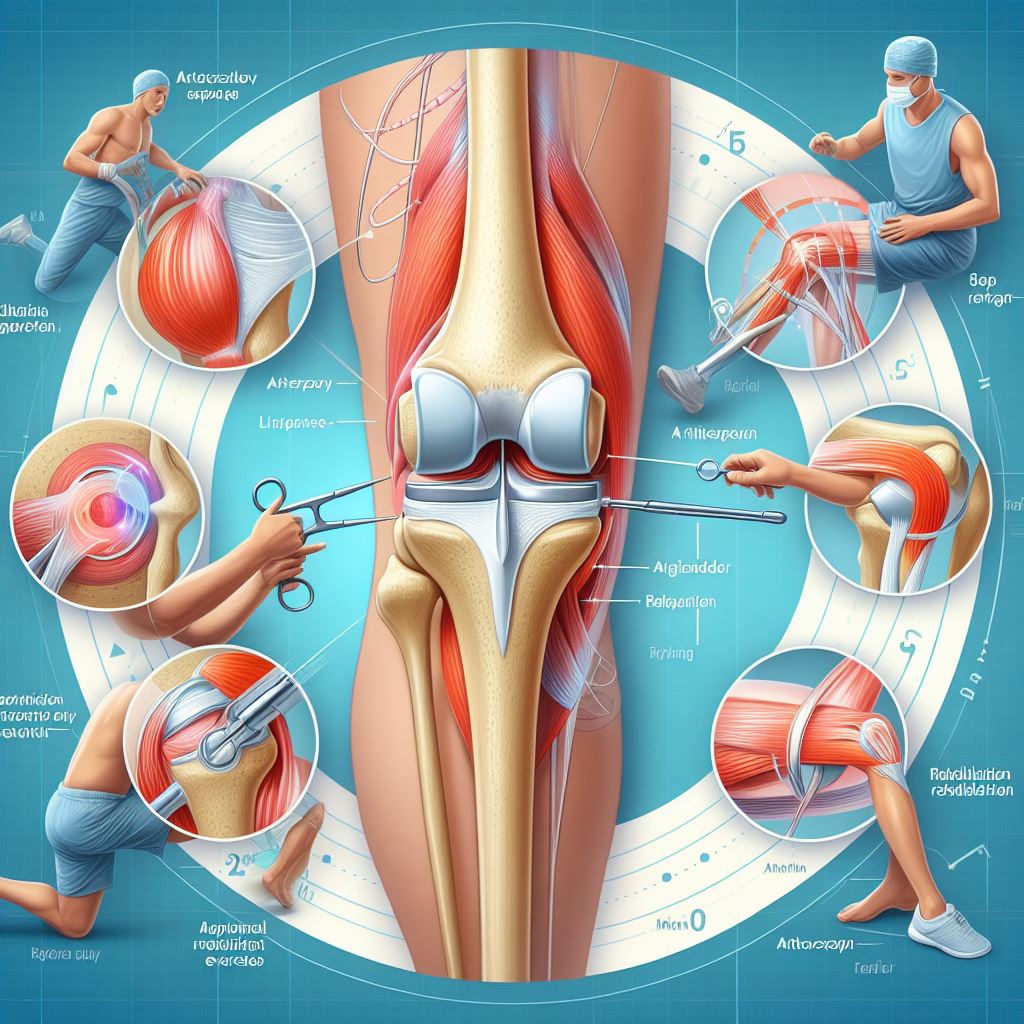
Sports medicine knee surgeries encompass a range of procedures aimed at treating various knee injuries and conditions commonly encountered in athletes and active individuals. These surgeries can address issues such as ligament tears, meniscus injuries, and cartilage damage to restore function and alleviate pain.
Procedure:
Some common knee surgeries in sports medicine include:
- ACL Reconstruction: Involves replacing a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) with a graft to stabilize the knee joint.
- Meniscus Repair: Aims to repair or trim torn meniscal tissue to restore knee function and prevent further damage.
- Cartilage Restoration: Various techniques, such as microfracture, autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI), or osteochondral autograft transfer (OATS), are used to repair damaged knee cartilage.
Who Is It Suitable For?
Sports medicine knee surgeries are suitable for individuals with:
- Acute or chronic knee injuries sustained during athletic activities.
- Ligament tears, meniscus tears, or cartilage damage that cause pain, instability, and limitations in knee function.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
These surgeries may not be suitable for individuals with:
- Severe arthritis or joint degeneration that may require more extensive interventions like total knee replacement.
- Certain medical conditions or factors that increase the risks associated with surgery, such as uncontrolled diabetes or heart disease.
Advantages:
- Restoration of knee stability, function, and range of motion.
- Relief from pain and symptoms associated with knee injuries, allowing individuals to return to sports and physical activities.
- Advancements in surgical techniques and rehabilitation protocols have led to improved outcomes and faster recovery times.
Complications:
Potential complications of sports medicine knee surgeries may include:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Blood clots in the leg or lung.
- Nerve or blood vessel damage.
- Persistent pain or stiffness in the knee.
Preoperative Care:
- Patients will undergo a comprehensive evaluation of their knee injury, medical history, and physical condition to assess their suitability for surgery.
- Preoperative imaging, such as MRI scans, may be used to assess the extent of the knee injury and aid in surgical planning.
Postoperative Care:
- After knee surgery, patients will receive specific instructions regarding pain management, wound care, and rehabilitation exercises.
- Physical therapy and structured rehabilitation programs are often recommended to regain strength, mobility, and function in the knee.
- Gradual return to sports and physical activities will be guided by the surgeon and rehabilitation team to minimize the risk of re-injury.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.