Description
Familiarity with Treatment
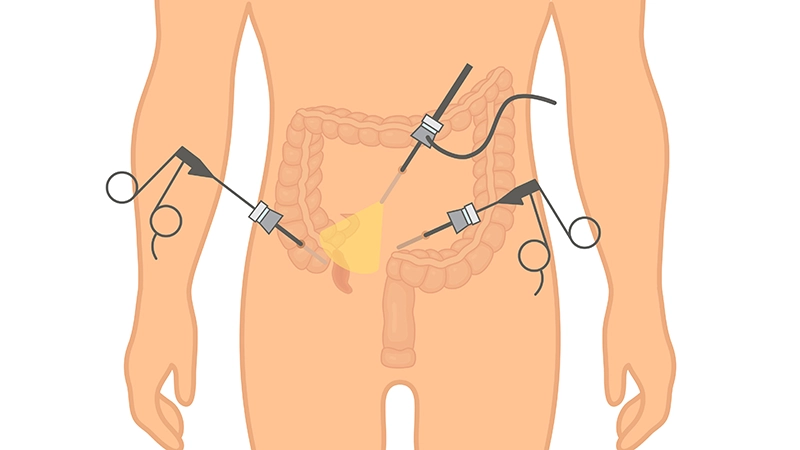
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the appendix. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon uses these instruments to remove the appendix, guided by a camera that provides a view inside the abdomen.
Procedure
During a laparoscopic appendectomy, from 1 to 3 tiny cuts are made in the abdomen. A long, thin tube called a laparoscope, which has a tiny video camera and surgical tools, is inserted through one of the incisions. The surgeon uses the camera to guide the tools and remove the appendix through one of the incisions. In some cases, if the appendix has burst and infection has spread, the surgeon may need to switch to an open appendectomy.
Who is it Suitable For?
Laparoscopic appendectomy is suitable for individuals diagnosed with appendicitis, particularly those with uncomplicated cases. It is often preferred due to its minimally invasive nature, resulting in less pain, smaller scars, and a faster recovery time compared to open appendectomy.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Laparoscopic appendectomy may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those who have contraindications to general anesthesia. Additionally, if the surgeon encounters complications during the laparoscopic procedure, they may need to switch to an open appendectomy for the patient’s safety.
Advantages
- Less Invasive: Laparoscopic appendectomy is less invasive than open appendectomy, resulting in smaller incisions, less pain, and a faster recovery time.
- Lower Infection Rates: Laparoscopic appendectomy is associated with a lower risk of incision site infection compared to open appendectomy.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy typically have a shorter hospital stay compared to open appendectomy.
Complications
- Intra-abdominal and Pelvic Infection: While laparoscopic appendectomy is associated with a lower risk of incision site infection, it carries a higher risk of intra-abdominal and pelvic infection compared to open appendectomy.
- Postoperative Complications: Complications of laparoscopic appendectomy may include bleeding, infection in the surgery area, hernias, blood clots, and heart problems.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for laparoscopic appendectomy involves a comprehensive evaluation by the healthcare provider to determine the need for surgery and the most appropriate approach. Preoperative antibiotics and appropriate wound scrubbing may be used to minimize the risk of postoperative wound infections.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for laparoscopic appendectomy includes monitoring for complications, pain management, wound care, and follow-up visits with the doctor. The recovery time for laparoscopic appendectomy is typically shorter compared to open appendectomy, with full recovery taking 1 to 2 weeks.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.