Description
Familiarity with Treatment
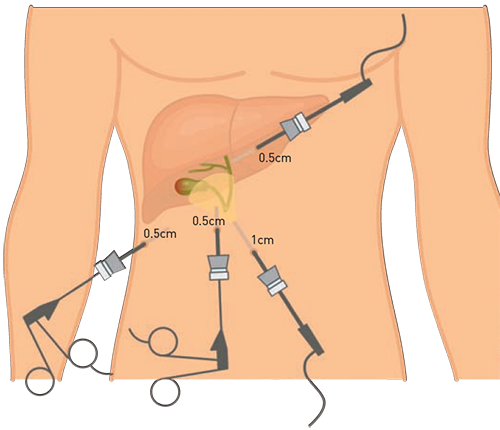
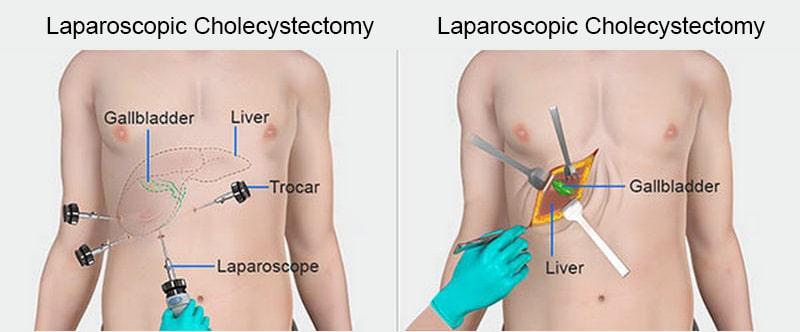
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a widely accepted and commonly performed surgical procedure for the treatment of symptomatic cholelithiasis, or gallstones. It is considered the standard treatment for this condition and has gained popularity due to its minimally invasive nature. The procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder using small incisions and specialized surgical instruments 1.
Procedure
During a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, several small incisions are made in the abdomen. A laparoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and light on the tip, is inserted through one of the incisions to provide a visual image of the gallbladder. Surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions to remove the gallbladder. The surgeon performs the procedure while watching a video monitor that displays the images from the laparoscope 2.
Who is it Suitable For?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is indicated for the treatment of various gallbladder conditions, including symptomatic cholelithiasis, acute or chronic cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, acalculous cholecystitis, gallstone pancreatitis, and gallbladder masses/polyps. It is suitable for a wide range of patients, including young, elderly, thin, and obese individuals 3.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
While laparoscopic cholecystectomy is generally safe and suitable for most patients, there may be certain situations where an open cholecystectomy (traditional surgical procedure) is preferred. This can include cases where there are complications during the laparoscopic procedure, severe scar tissue from previous surgeries, or other factors that make the laparoscopic approach challenging or unsafe 2.
Advantages
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy offers several advantages over open cholecystectomy, including:
- Smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain and scarring.
- Shorter hospital stays, with many patients being discharged on the same day.
- Faster recovery and return to normal activities compared to open surgery.
- Reduced risk of complications such as wound infections and hernias.
Complications
While laparoscopic cholecystectomy is generally safe, there can be potential complications associated with the procedure. These can include bleeding, infection, injury to the bile duct or other nearby structures, liver injury, scars, and a hernia at the incision site. Additionally, there is a small risk of bile duct injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy, although the overall risk is low 1.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for laparoscopic cholecystectomy involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider to determine the need for surgery and the most appropriate approach. This may include medical risk reduction, diagnostic tests, and discussions about the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes 1.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for laparoscopic cholecystectomy includes pain management, wound care, and monitoring for any signs of complications. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days to a week after the procedure. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding diet, activity level, and any necessary follow-up appointments 4.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.