Description
Familiarity with Treatment
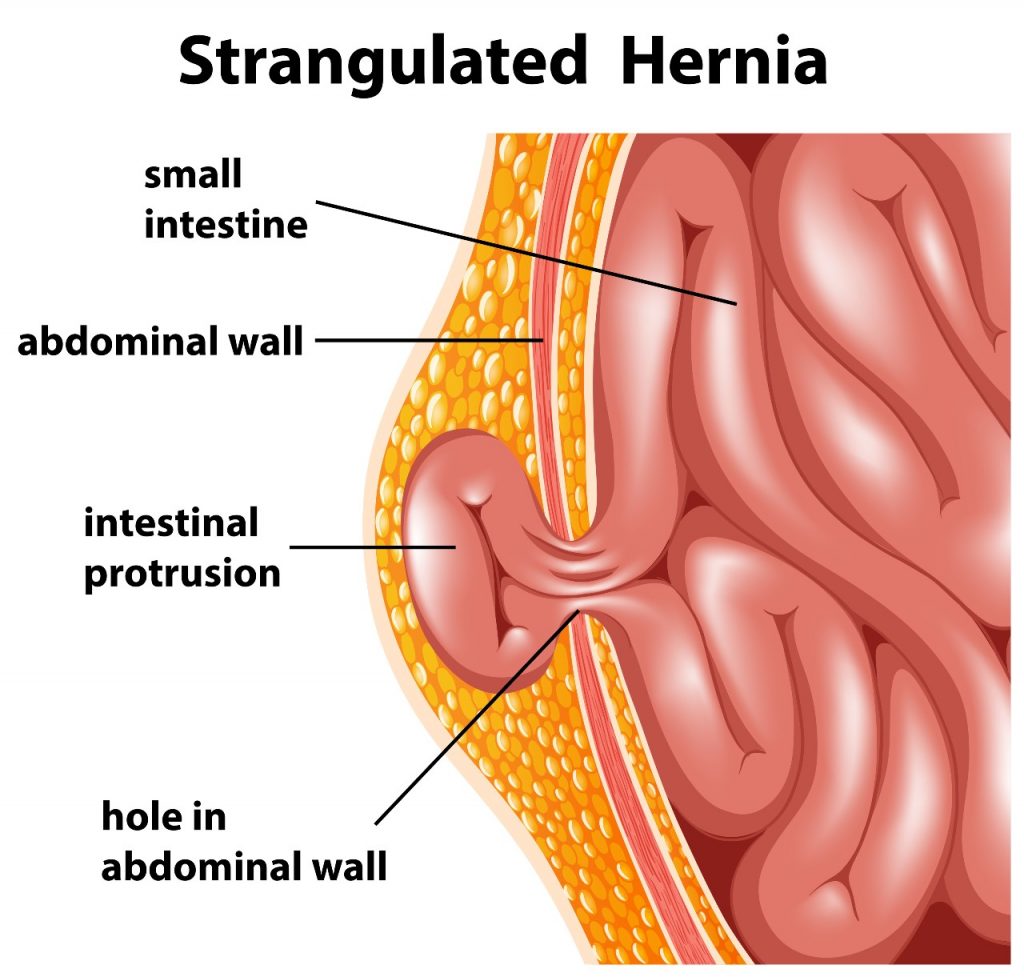
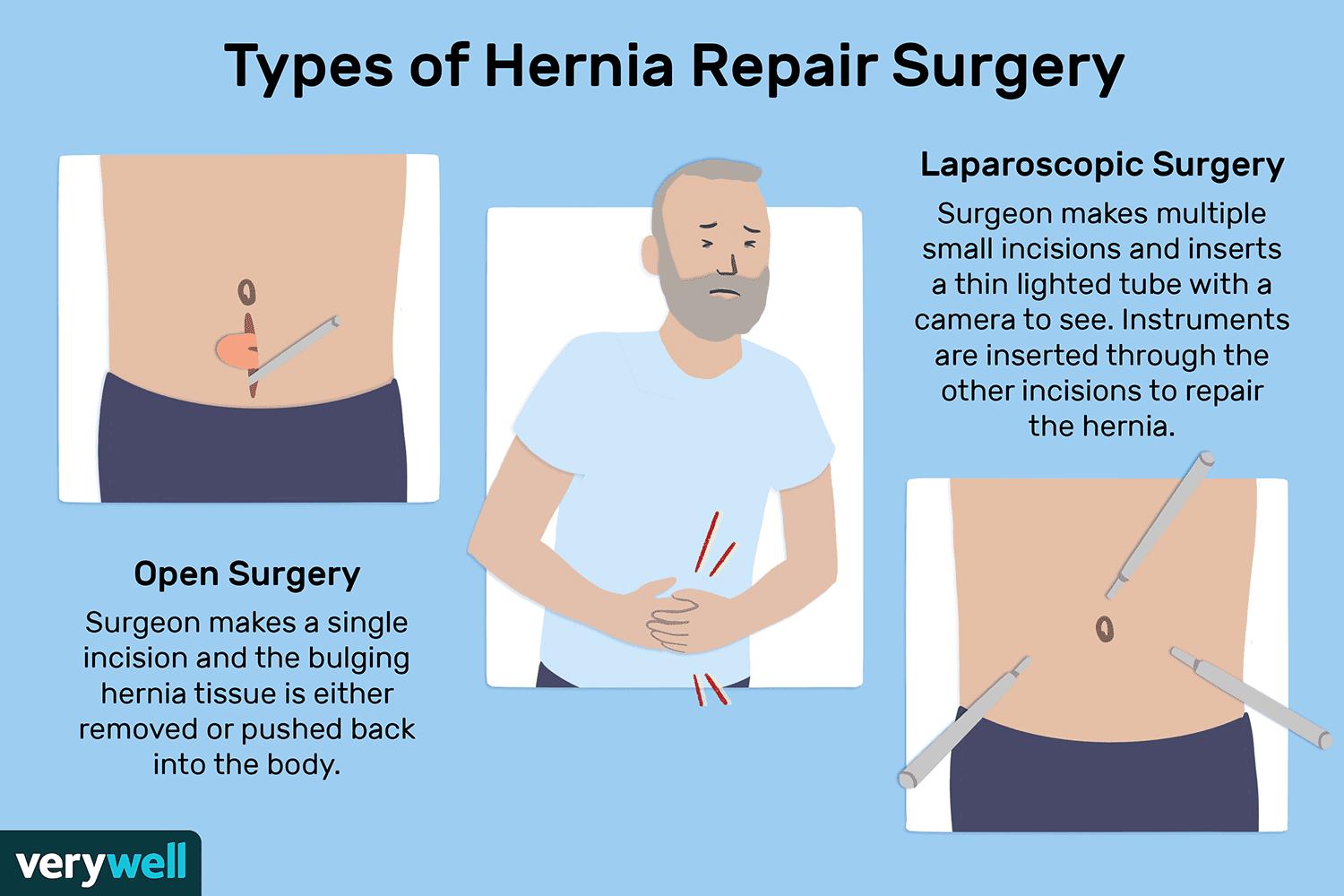
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat various types of hernias. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope and specialized surgical instruments are inserted to repair the hernia. This approach offers the advantage of smaller incisions, reduced postoperative pain, and faster recovery compared to open hernia repair.
Procedure
During laparoscopic hernia repair, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen and inflates it with harmless gas to create space. A laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, is inserted to provide a view of the internal structures. Specialized instruments are used to repair the hernia, often involving the placement of mesh to reinforce the weakened area. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia.
Who is it Suitable For?
Laparoscopic hernia repair is suitable for individuals with different types of hernias, including inguinal, umbilical, and incisional hernias. It is often recommended for individuals who prefer a minimally invasive approach and may be beneficial for those seeking faster recovery and reduced postoperative pain. The suitability of the procedure is determined on a case-by-case basis, considering the individual’s specific condition and overall health.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Laparoscopic hernia repair may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions or contraindications to surgery. The decision to undergo laparoscopic hernia repair is made in consultation with a healthcare provider or surgeon, taking into account the individual’s specific circumstances.
Advantages
The advantages of laparoscopic hernia repair include:
- Minimally invasive approach with smaller incisions.
- Reduced postoperative pain compared to open hernia repair.
- Faster recovery time and earlier return to normal activities.
- Less scarring and reduced risk of wound complications.
- Potential for outpatient treatment, avoiding the need for hospitalization in some cases.
Complications
Complications of laparoscopic hernia repair can include infection, pain, seroma (fluid accumulation), hematoma (blood clot), recurrence of the hernia, and injury to surrounding structures. However, the risk of complications is generally low, and the procedure has been performed successfully in numerous cases.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care for laparoscopic hernia repair involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider to determine the need for surgery and the most appropriate approach. This may include medical risk reduction, diagnostic tests, and discussions about the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care for laparoscopic hernia repair includes pain management, wound care, and monitoring for any signs of complications. Most individuals can expect to return to normal activities within a few weeks. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding diet, activity level, and any necessary follow-up appointments.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.