Description
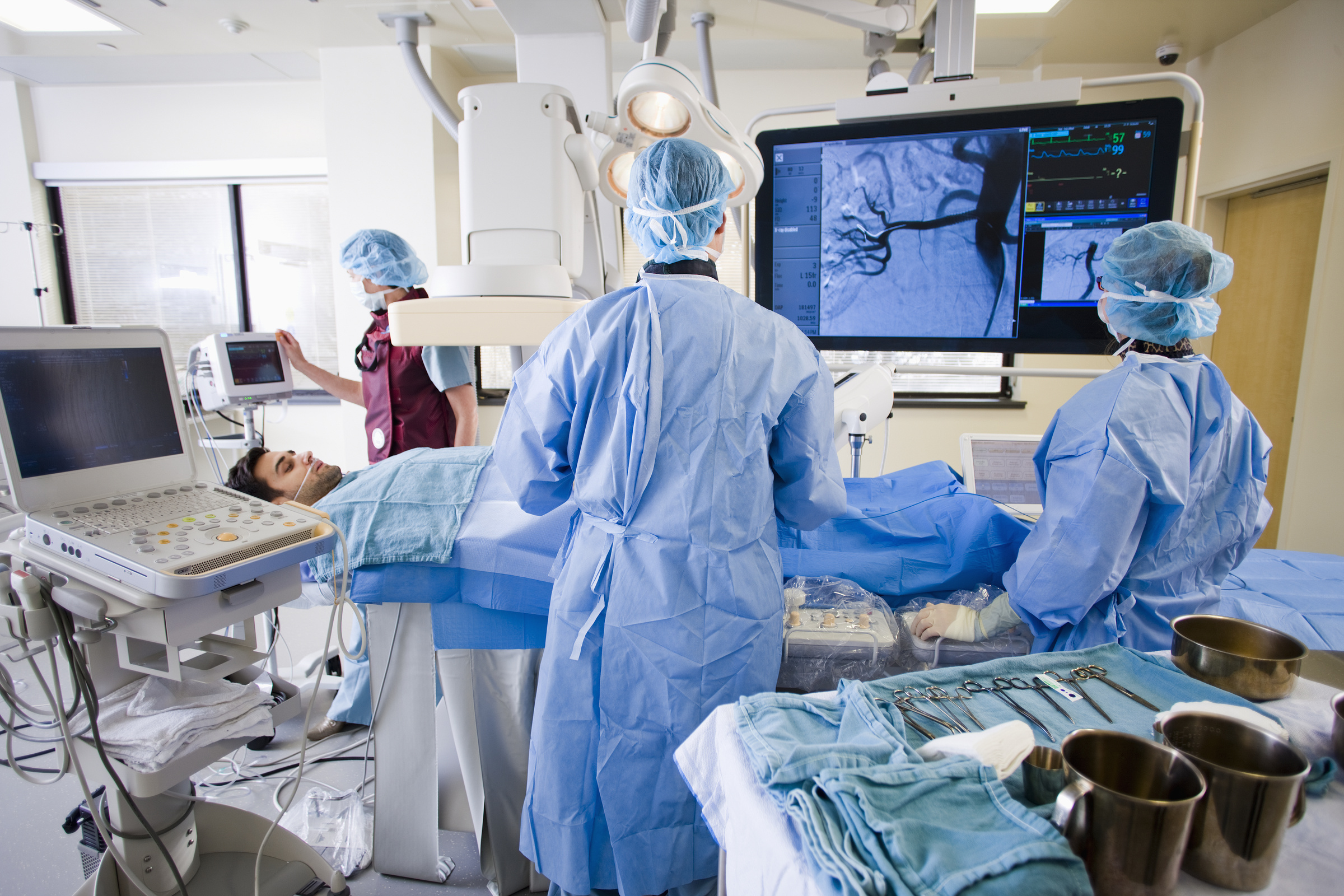
Left main angioplasty is a procedure used to open a narrowed or blocked left main coronary artery, which supplies a significant portion of blood to the heart. This procedure often involves the use of a stent to keep the artery open.
Types of Left Main Angioplasty
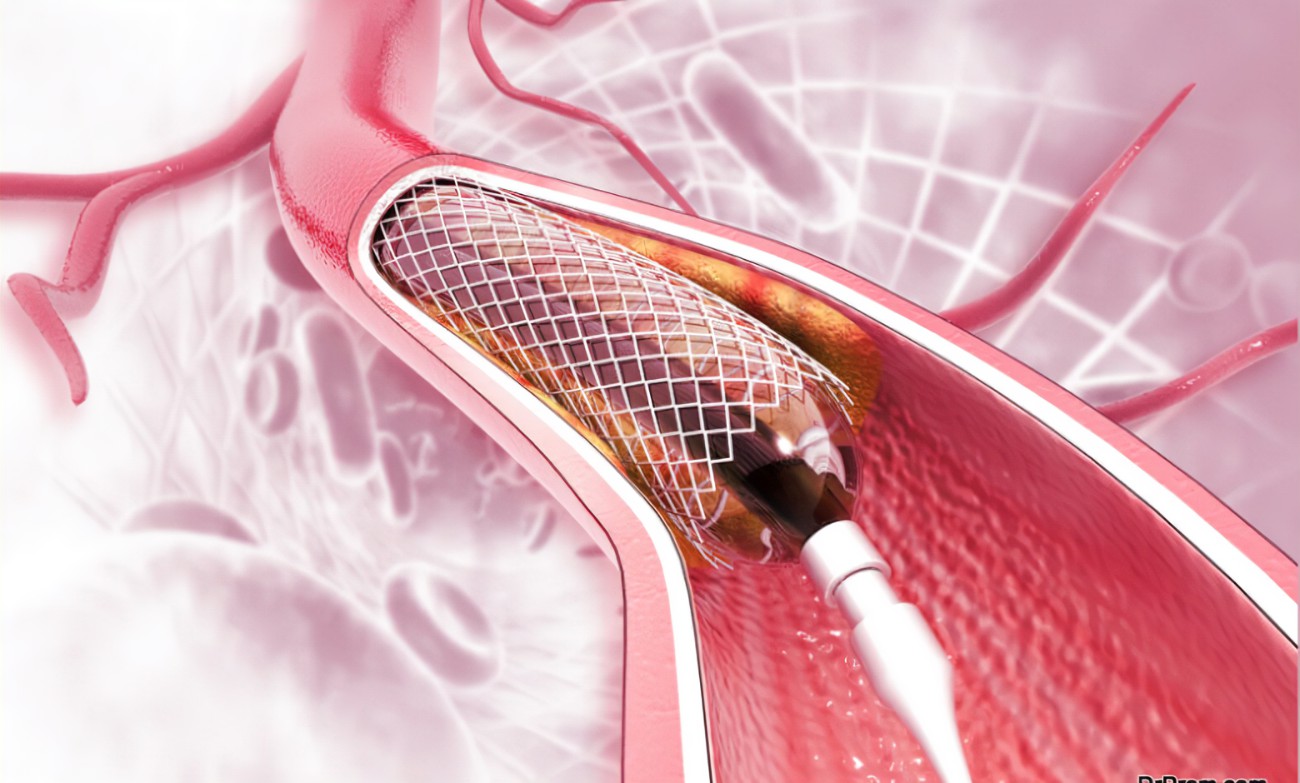
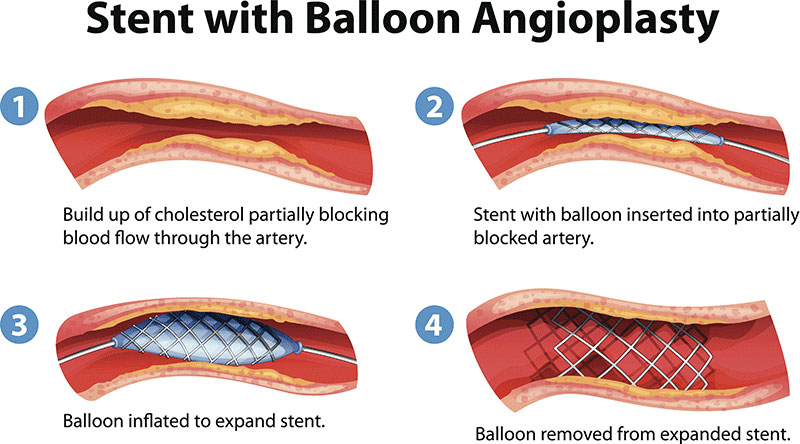
- Balloon Angioplasty: A small balloon at the tip of a catheter is inflated to widen the artery.
- Stent Placement: A stent (a small wire mesh tube) is placed in the artery to keep it open after balloon angioplasty.
- Drug-Eluting Stent: A stent coated with medication to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
Familiarity with Treatment
Left main angioplasty is a critical procedure for patients with significant blockages in the left main coronary artery. This artery is crucial as it supplies blood to a large portion of the heart muscle. Blockages here can lead to severe heart attacks or other serious cardiac events.
Procedure
- Preparation:
- Pre-procedure tests such as blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECG), and imaging studies.
- Fasting for several hours before the procedure.
- Stopping certain medications as advised by the healthcare provider.
- During the Procedure:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is used at the catheter insertion site, usually in the groin or wrist.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is threaded through the blood vessels to the blocked artery.
- Balloon Inflation: The balloon at the catheter’s tip is inflated to widen the artery.
- Stent Placement: A stent is placed to keep the artery open.
- Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of heart function and blood flow.
- Duration: The procedure typically takes 1 to 2 hours12.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Patients with significant blockages in the left main coronary artery.
- Those experiencing severe chest pain (angina) or other symptoms of coronary artery disease.
- Patients who are not suitable candidates for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Patients with very complex coronary artery disease that may be better treated with CABG.
- Those with certain medical conditions that contraindicate the use of angioplasty or stenting.
Advantages
- Minimally invasive with a shorter recovery time compared to open-heart surgery.
- Immediate improvement in blood flow to the heart.
- Reduced symptoms of chest pain and improved quality of life.
- Lower risk of complications compared to more invasive procedures12.
Complications
- Re-narrowing of the artery (restenosis).
- Blood clots forming within the stent.
- Bleeding or infection at the catheter insertion site.
- Rare risks include heart attack, stroke, or damage to the coronary artery12.
Previous Care
- Regular check-ups and monitoring of heart health.
- Lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Medications to manage cholesterol, blood pressure, and other risk factors.
Aftercare
- Monitoring for signs of complications, such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Medications to prevent blood clots and manage heart health.
- Follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider to monitor recovery.
- Gradual return to normal activities, avoiding strenuous exercise initially.
- Lifestyle changes to maintain heart health and prevent future blockages.
Left main angioplasty is a vital procedure for patients with significant coronary artery disease, offering a less invasive option with a quicker recovery time.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.