Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
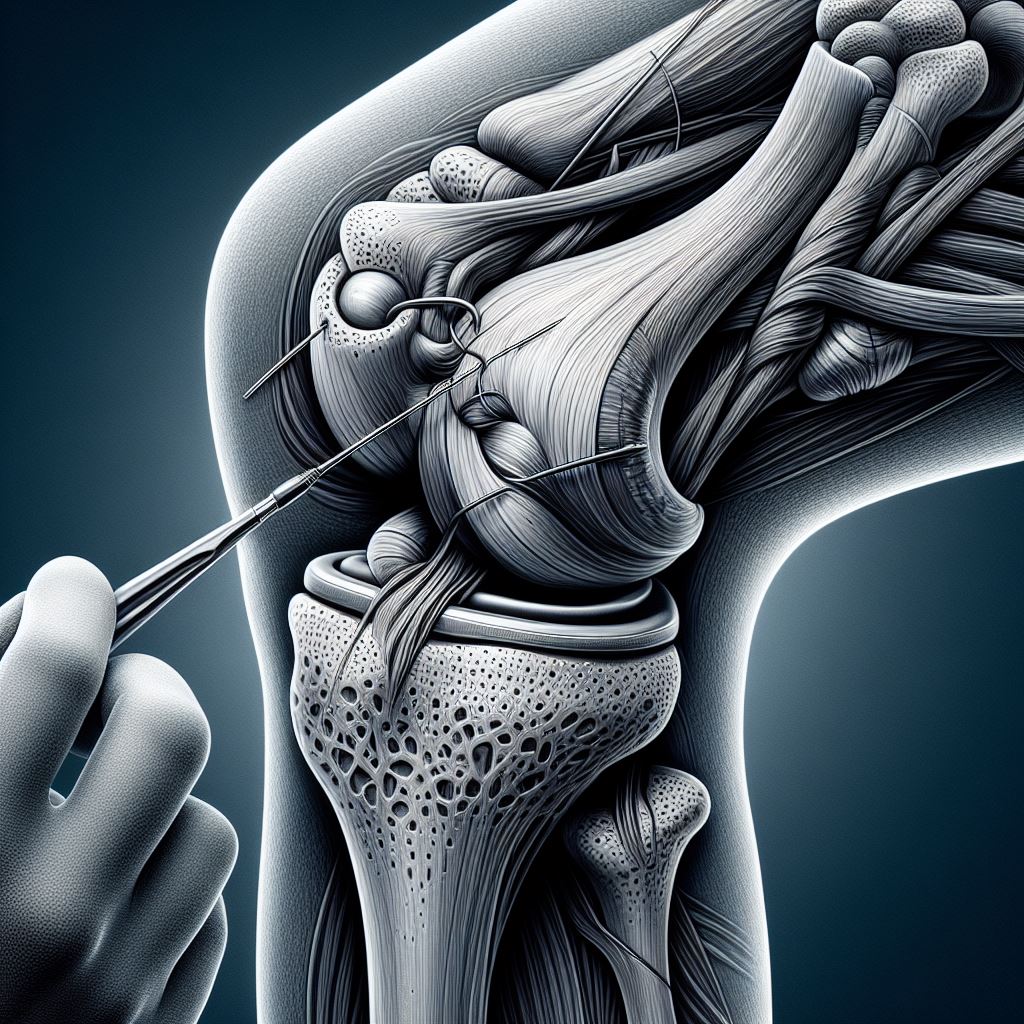
Orthopedic ligament repair is a surgical procedure aimed at fixing a torn ligament and restoring its function. Ligaments are tough, elastic bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and provide stability to joints.
Procedure
The specific procedure for ligament repair can vary depending on the location and severity of the ligament tear. In some cases, the surgeon may be able to sew the torn ends of the ligament together. In other cases, a graft (a piece of tendon from another part of the patient’s body or from a donor) may be used to replace the torn ligament. The surgery is often performed arthroscopically, which involves making small incisions and using a camera to guide the surgery.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthopedic ligament repair is typically suitable for individuals who have experienced a significant ligament tear that is causing pain, instability, or a decrease in function. This can include athletes who have experienced a sports-related injury, as well as individuals who have experienced a traumatic injury to a joint.
Who is it not suitable for?
Orthopedic ligament repair may not be suitable for individuals who are in poor overall health, as the surgery and recovery can be physically demanding. It may also not be suitable for individuals with certain conditions, such as severe arthritis in the joint, which could make the surgery more risky.
Advantages
The main advantage of orthopedic ligament repair is that it can restore stability to a joint and improve function. For athletes, it can often allow them to return to their sport.
Complications
As with any surgery, orthopedic ligament repair carries risks. These can include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and complications from anesthesia. There is also the risk that the surgery will not fully restore function or that the ligament will tear again in the future.
Preoperative care
Preoperative care for orthopedic ligament repair typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as an MRI to assess the damage to the ligament), and possibly blood tests. The patient may also need to stop taking certain medications and to fast for a certain period before the surgery.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care can include pain management, physical therapy, and regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing. The patient may also need to wear a brace and to avoid certain activities for a period of time.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.