Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
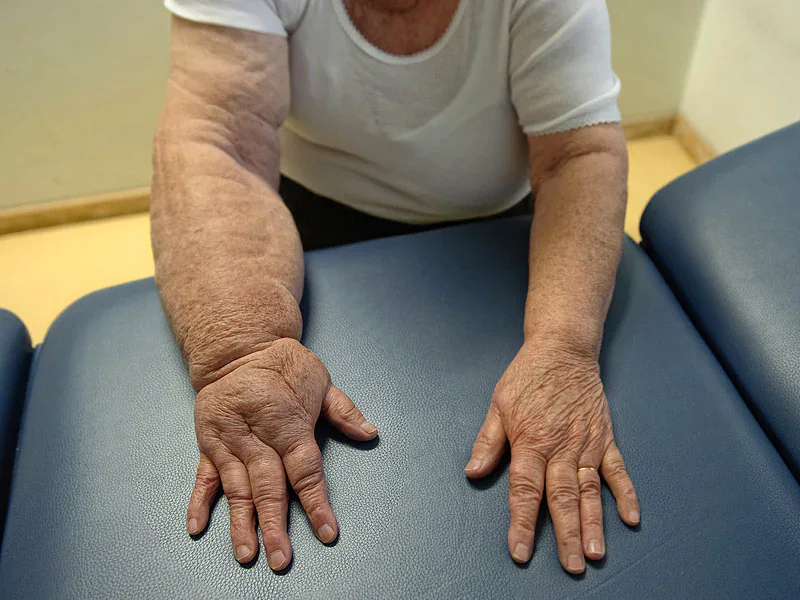
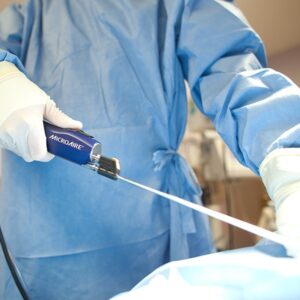
Lymphatic surgery encompasses a range of surgical procedures designed to address lymphatic system disorders, such as lymphedema. These procedures aim to improve lymphatic drainage, reduce swelling, and enhance overall lymphatic function.
Procedure:
- Lymphaticovenous Anastomosis (LVA): Involves the direct connection of lymphatic vessels to nearby veins, allowing excess lymphatic fluid to drain into the venous system.
- Vascularized Lymph Node Transfer (VLNT): In this procedure, healthy lymph nodes, along with their connecting blood vessels, are transferred to the affected area to improve lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling.
- Lymphatic Bypass Surgery: A surgical bypass is created to redirect lymphatic fluid from blocked or damaged vessels to alternative pathways, facilitating drainage.
Who is it Suitable for?
Lymphatic surgery is suitable for individuals with lymphatic system disorders, such as lymphedema, which may result from cancer treatment, trauma, or other causes. It is often considered for patients experiencing persistent swelling and impaired lymphatic function.
Who is it Not Suitable for?
Lymphatic surgery may not be suitable for individuals with certain advanced medical conditions that may pose significant surgical risks, as well as those with minimal or manageable lymphatic swelling that does not warrant surgical intervention.
Advantages:
- Reduction of Swelling: Lymphatic surgery can help reduce persistent swelling associated with lymphatic system disorders, potentially improving mobility and comfort for patients.
- Improved Lymphatic Function: These procedures aim to enhance the overall function of the lymphatic system, leading to better fluid balance and reduced complications.
Complications:
- Potential complications of lymphatic surgery may include surgical site infection, impaired wound healing, persistent or recurrent swelling, and the risk of damage to nearby structures.
Preoperative Care:
- Comprehensive evaluation of the lymphatic disorder and the patient’s symptoms to determine the need for lymphatic surgery
- Assessment of the patient’s general health and medical history
- Patient education regarding the procedure, potential outcomes, and postoperative care
Postoperative Care:
- Monitoring for signs of infection or impaired wound healing at the surgical site
- Compression therapy and elevation of the affected limb to manage swelling
- Rehabilitation and physical therapy to optimize function and mobility
- Regular follow-up appointments to assess healing and lymphatic function


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.