Description
Familiarity with Treatment
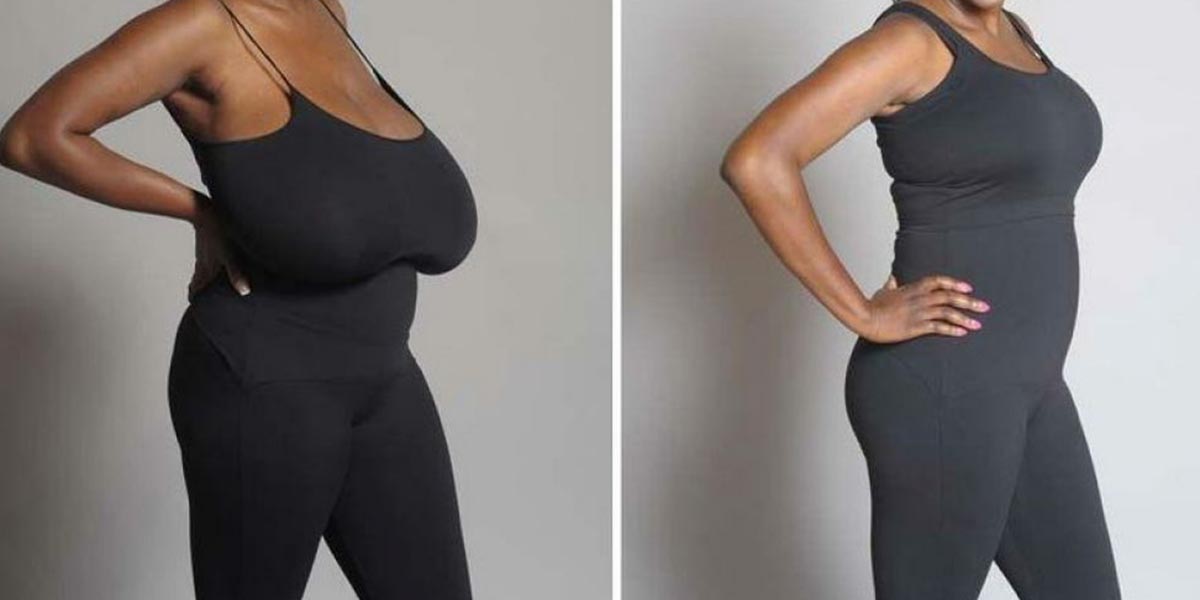
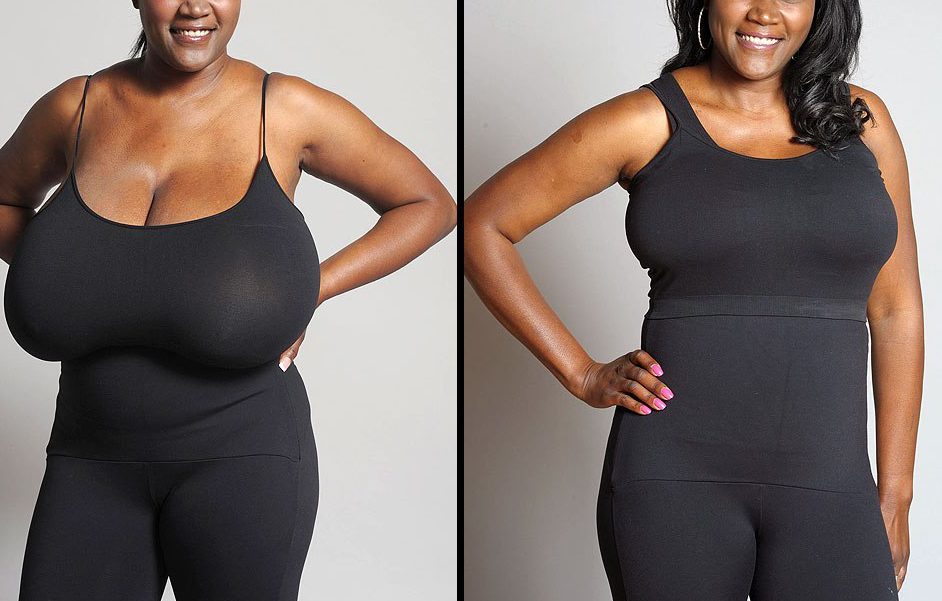
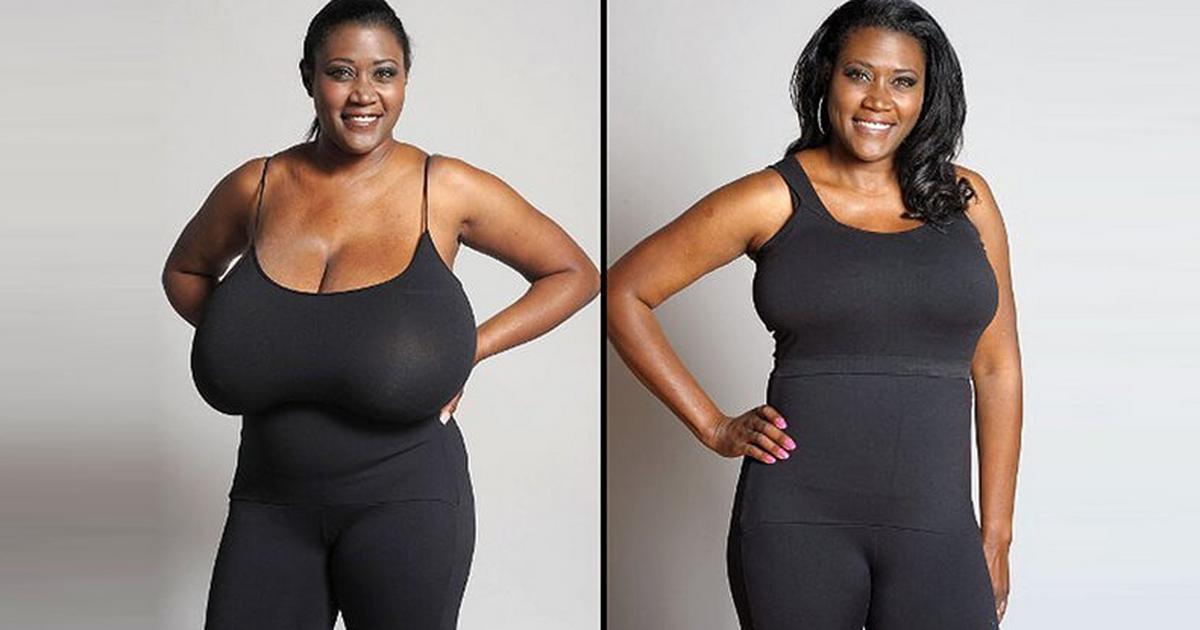
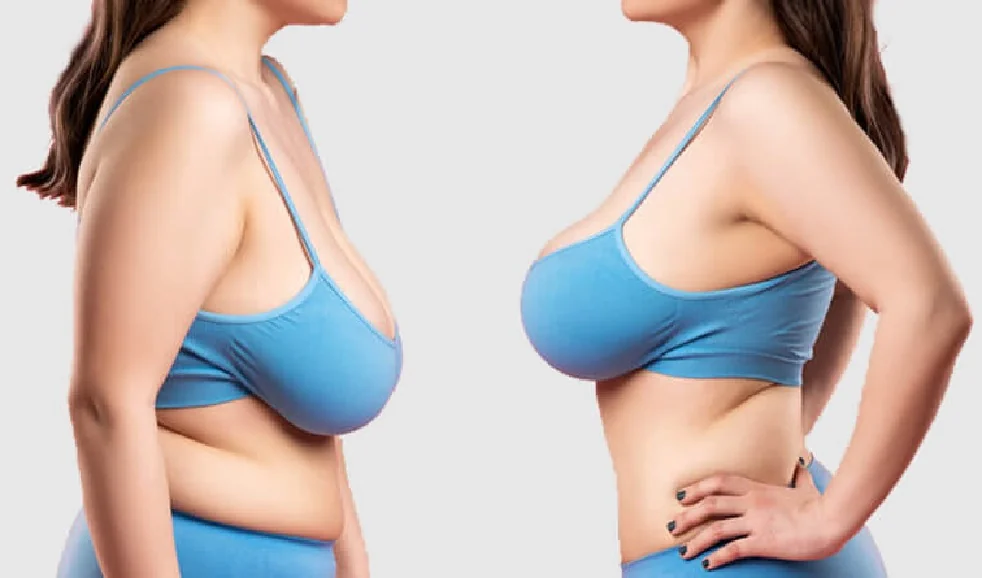
Mammoplasty refers to surgical procedures aimed at altering the size, shape, or position of the breasts. It includes:
- Breast Reduction (Reduction Mammoplasty): Reducing breast size by removing excess tissue and skin.
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy): Lifting and reshaping sagging breasts.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Breast Reduction: Ideal for those experiencing physical discomfort (back, neck, or shoulder pain) due to overly large breasts, or those seeking a more proportionate breast size.
- Breast Lift: Best for individuals with sagging breasts due to aging, pregnancy, breastfeeding, or significant weight loss, who want to improve breast contour without significantly changing size.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Individuals with certain medical conditions that may impair healing (e.g., uncontrolled diabetes, severe cardiovascular issues).
- Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Individuals with unrealistic expectations about the outcomes of the surgery.
- People who smoke heavily, as smoking can interfere with the healing process.
Advantages
- Breast Reduction: Relief from physical discomfort, improved ability to engage in physical activities, better-fitting clothing.
- Breast Lift: Improved breast contour and firmness, more youthful appearance.
Complications
- General Risks: Infection, bleeding, adverse reaction to anesthesia, scarring.
- Specific to Augmentation: Implant rupture or leakage, capsular contracture (scar tissue forming around the implant), changes in nipple or breast sensation.
- Specific to Reduction: Potential for asymmetry, changes in nipple or breast sensation, difficulty breastfeeding.
- Specific to Lift: Similar to reduction, with additional risk of changes in breast shape over time.
Previous Care (Preoperative Care)
- Consultation: Detailed discussion with a board-certified plastic surgeon to understand goals, options, and potential risks.
- Medical Evaluation: Comprehensive health assessment, including medical history and physical examination.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Quitting smoking, avoiding certain medications (e.g., blood thinners), and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Preparation: Arranging for post-surgery care and support, planning for recovery time.
Aftercare (Postoperative Care)
- Immediate Care: Monitoring in a recovery area, managing pain and swelling with prescribed medications, wearing a surgical bra or compression garment.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups with the surgeon to monitor healing and address any concerns.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks, gradually resuming normal activities as advised by the surgeon.
- Long-Term Care: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring for any changes or complications, and attending annual check-ups.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.