Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
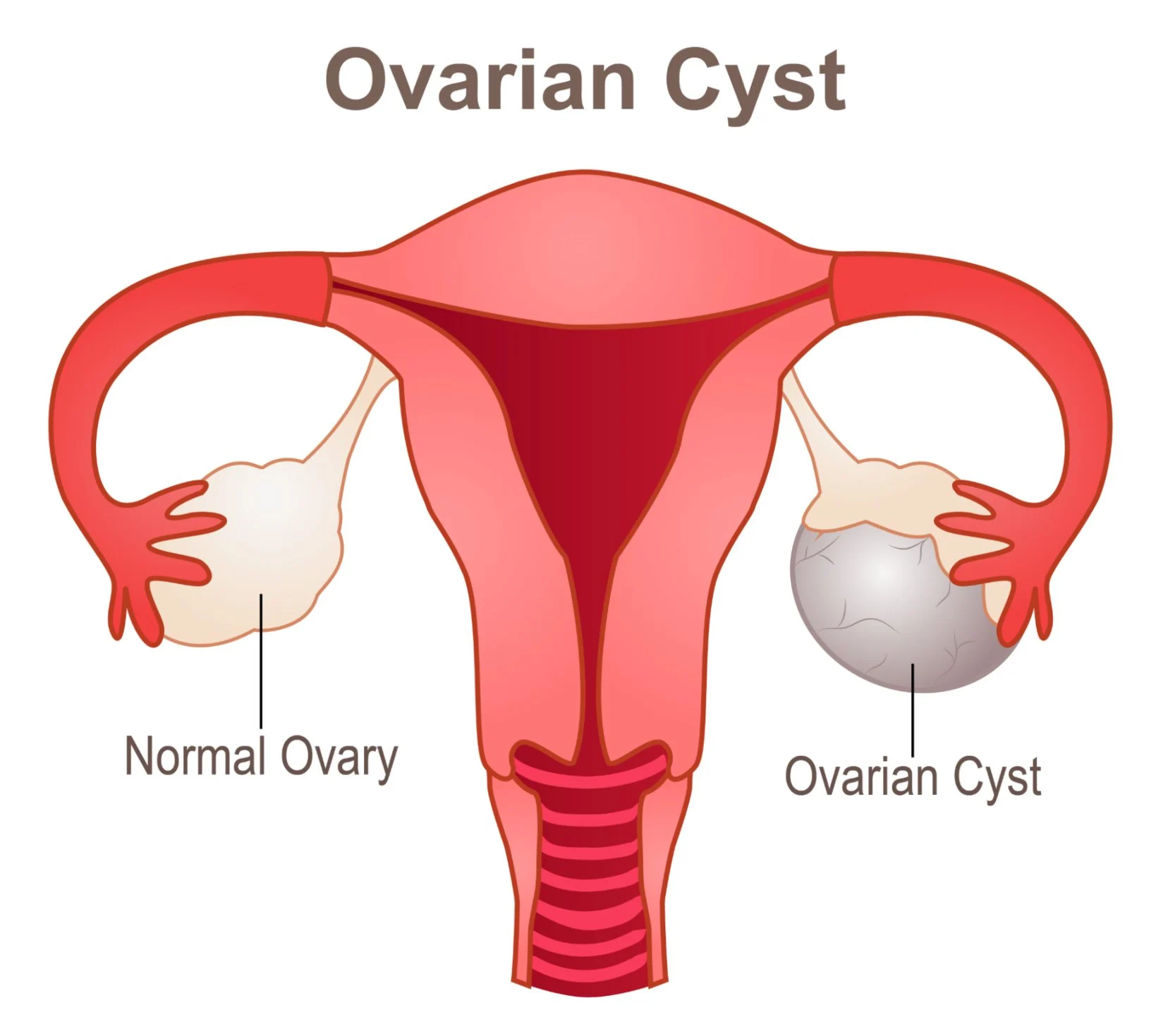
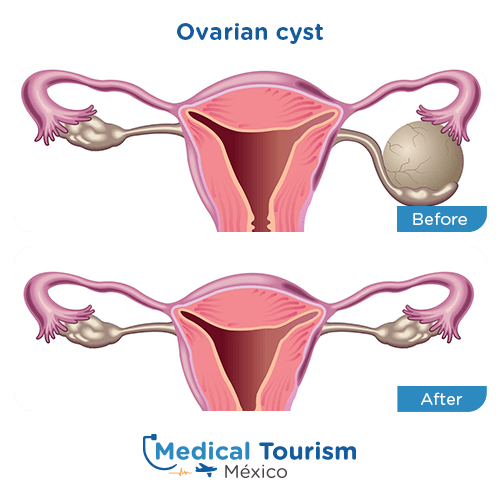
An ovarian cystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove cysts from one or both ovaries. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the ovaries and are often benign. The procedure can be performed using minimally invasive techniques (laparoscopy) or through open surgery (laparotomy) depending on the size and nature of the cyst.
Procedure:
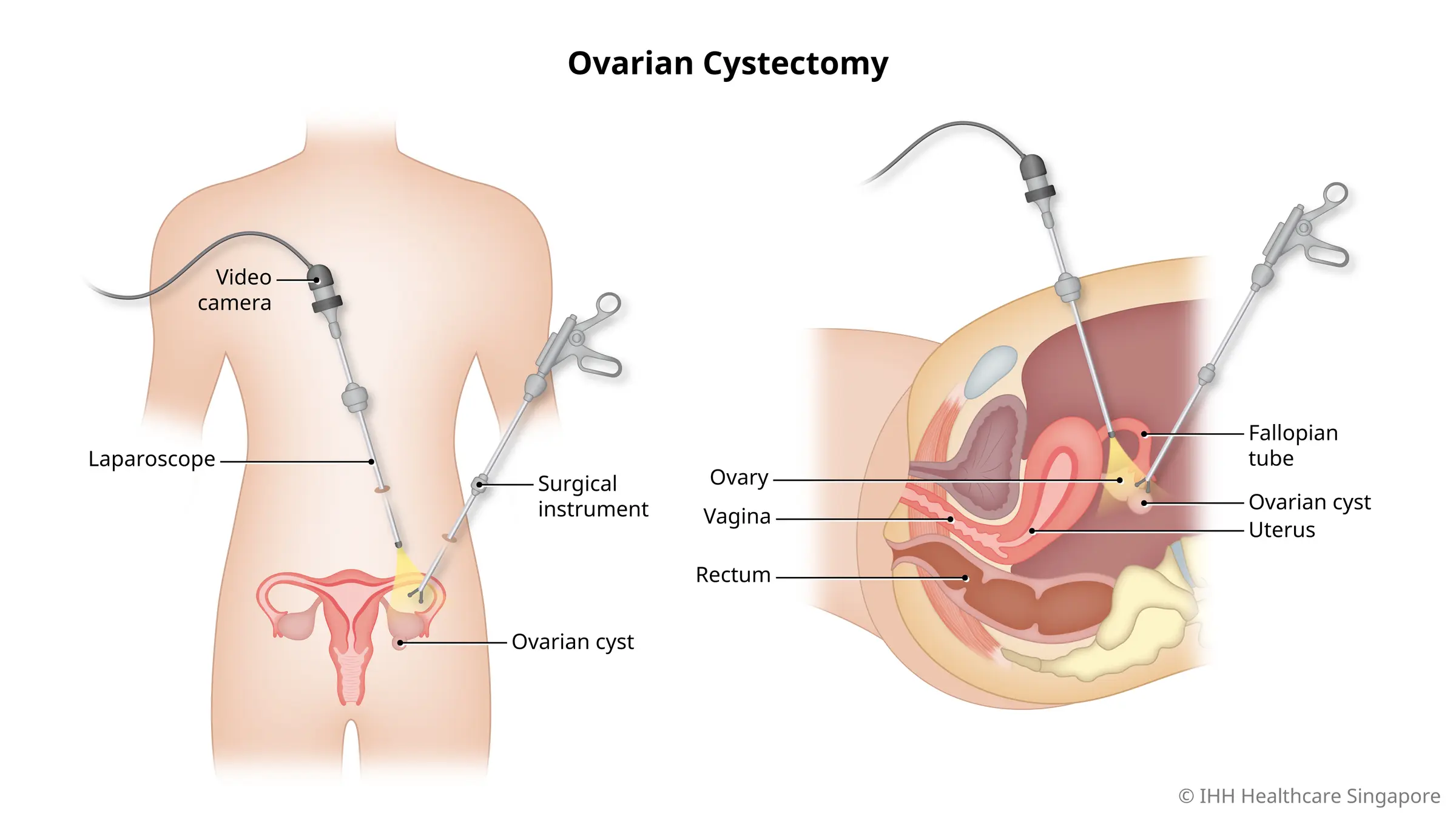
- Laparoscopic Ovarian Cystectomy:
- Preparation: The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Incisions: Small incisions are made in the abdomen.
- Insertion of Instruments: A laparoscope (a small camera) and surgical instruments are inserted through the incisions.
- Removal: The cyst is carefully separated from the ovary and removed.
- Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue.
- Open Ovarian Cystectomy (Laparotomy):
- Preparation: The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Incision: A larger incision is made in the lower abdomen.
- Removal: The cyst is removed through the incision.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures.
Additional Information
Who is it suitable for?
- Individuals with ovarian cysts that are large (typically more than 2.5 to 3 inches in diameter).
- Those experiencing symptoms such as pain, bloating, or discomfort.
- Patients with cysts that do not resolve on their own or grow larger over time.
- Women who wish to preserve their fertility, as the procedure aims to remove the cyst while leaving the ovary intact.
Who is it not suitable for?
- Patients with small, asymptomatic cysts that are likely to resolve on their own.
- Individuals with severe medical conditions that may increase surgical risks.
- Those with cysts that are suspected to be malignant may require a different surgical approach.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive options (laparoscopy) offer quicker recovery times and less postoperative pain.
- Preservation of ovarian tissue, which is important for fertility.
- Effective relief from symptoms caused by the cyst.
Complications:
- Infection at the incision site.
- Bleeding or blood clots.
- Damage to surrounding organs or tissues.
- Recurrence of ovarian cysts.
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Previous Care:
- Preoperative evaluation including imaging tests (ultrasound, MRI) to assess the cyst.
- Blood tests to check overall health and rule out malignancy.
- Discussion of medical history and any medications being taken.
Aftercare:
- Monitoring in the recovery room until anesthesia wears off.
- Pain management with prescribed medications.
- Avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting for a few weeks.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing and ensure no complications.
- Instructions on wound care and signs of infection to watch for.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.