Description
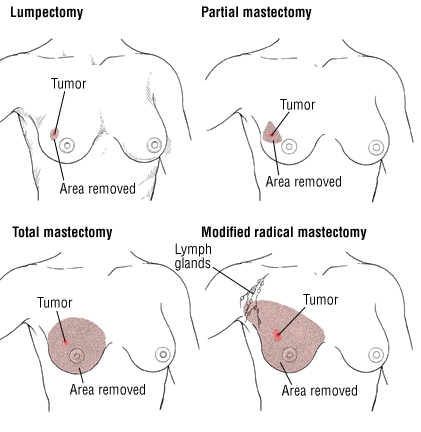
Familiarity with Treatment: A partial mastectomy, also known as a lumpectomy, is a surgical procedure to remove a portion of the breast containing a tumor or abnormal tissue while preserving as much of the healthy breast tissue as possible. This is often referred to as breast-conserving surgery.
Procedure Explanation: During a partial mastectomy, the surgeon removes the tumor along with a margin of surrounding healthy tissue to ensure all cancerous cells are excised. The procedure can be performed under general or local anesthesia. It typically involves making an incision over the tumor site, removing the tumor and some surrounding tissue, and then closing the incision with sutures. The surgery usually takes about 1-2 hours, and patients can often go home the same day.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Patients with early-stage breast cancer (Stage I or II).
- Individuals with a single, small tumor (less than 4 centimeters in diameter).
- Patients who have enough remaining breast tissue to maintain a natural breast shape post-surgery.
- Those who are medically able to undergo surgery and follow-up radiation therapy.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Patients with multiple tumors in different parts of the breast.
- Individuals with large tumors relative to breast size.
- Those who have previously undergone radiation therapy to the same breast.
- Patients with certain medical conditions like scleroderma or lupus, which can complicate healing and radiation therapy.
Advantages:
- Preserves most of the breast tissue, maintaining the natural appearance of the breast.
- Shorter recovery time compared to a full mastectomy.
- Often performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to return home the same day.
- When combined with radiation therapy, it offers similar survival rates to a full mastectomy for early-stage breast cancer.
Complications:
- Risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Potential for changes in breast shape or appearance.
- Possibility of needing additional surgery if cancerous cells are found at the margins.
- Side effects from radiation therapy, such as skin irritation and fatigue.
Previous Care:
- Comprehensive diagnostic imaging (mammogram, ultrasound, MRI) to assess the tumor.
- Biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and plan the extent of surgery.
- Preoperative instructions, including fasting and medication adjustments.
Aftercare:
- Monitoring in the recovery room until the effects of anesthesia wear off.
- Pain management with prescribed medications.
- Instructions on wound care and activity restrictions.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing and discuss any further treatments, such as radiation therapy.
- Regular breast exams and imaging to check for recurrence.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.