Description
Familiarity with treatment
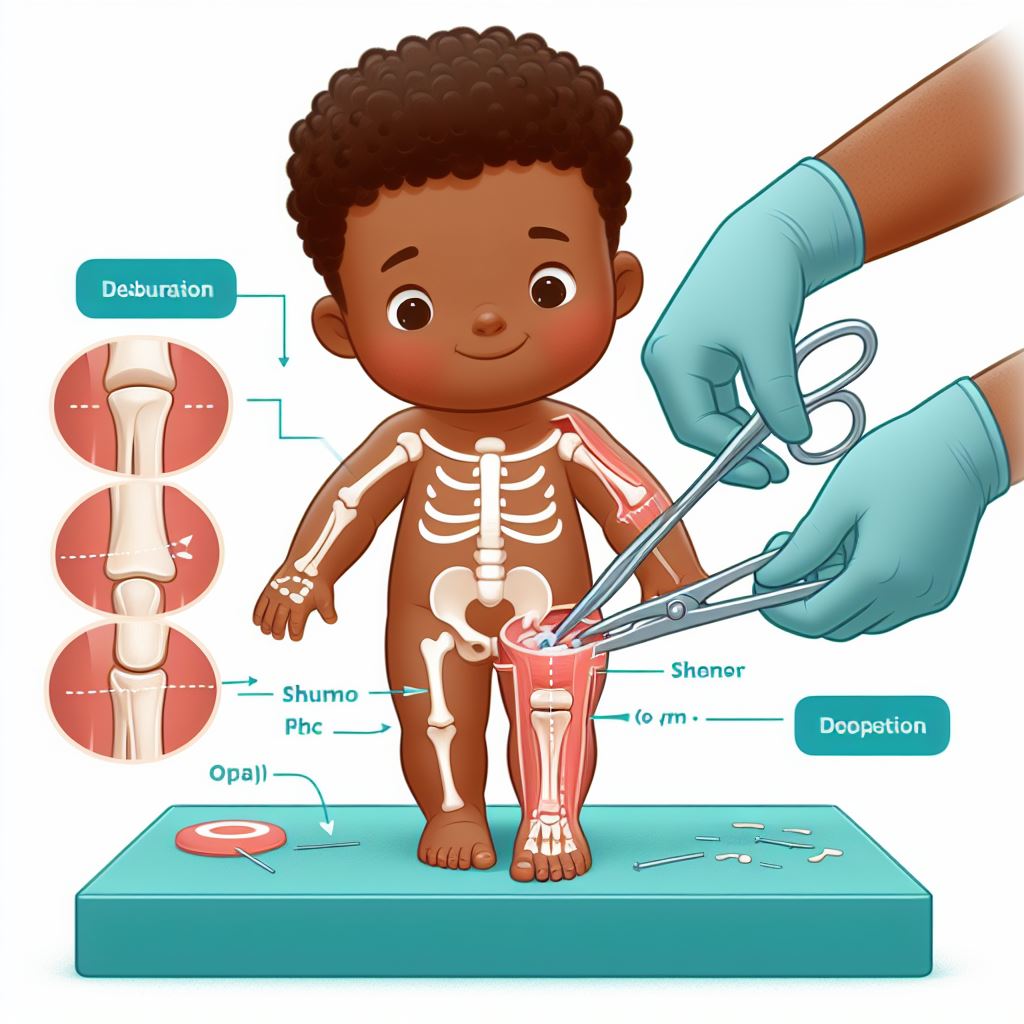
Pediatric osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and reshaping of a bone to correct deformities, improve alignment, or address growth-related issues in children. This procedure is utilized to treat various orthopedic conditions, including limb deformities, hip dysplasia, and angular deformities of the knees or ankles.
Procedure
The surgical procedure for pediatric osteotomy involves making precise cuts in the bone to allow for realignment or correction of the deformity. The bone may be fixed with plates, screws, or external fixators to maintain the corrected position during healing. The specific technique and approach depend on the type and location of the deformity being addressed.
Who is it suitable for?
Pediatric osteotomy is suitable for children who have:
- Angular or rotational deformities of the limbs that are impacting their mobility, function, or causing pain
- Growth-related issues such as leg length inequality or abnormal joint development
- Specific orthopedic conditions such as hip dysplasia, Blount’s disease, or other bone deformities that can benefit from realignment or correction
Who is it not suitable for?
Pediatric osteotomy may not be suitable for children who:
- Have mild deformities that can be effectively managed with non-surgical methods
- Have medical conditions that pose a high risk for surgery and recovery
- Have reached skeletal maturity, limiting the potential for growth-related corrections
Advantages
- Correction of deformities or malalignment, potentially improving function and mobility
- Prevention of further progression of the deformity and associated complications
- Restoration of more normal bone and joint mechanics
Complications
Complications associated with pediatric osteotomy can include:
- Infection
- Delayed or non-union of the bone
- Nerve or blood vessel injury
- Overcorrection or undercorrection of the deformity
- Implant-related issues
Preoperative care
Preoperative care for pediatric osteotomy involves comprehensive evaluation, including imaging studies to assess the nature and severity of the bone deformity. It also involves optimizing the child’s overall health and addressing any specific medical conditions to prepare for surgery.
Postoperative care
After pediatric osteotomy, close monitoring is required to manage the healing process, including assessment of bone union and alignment. Physical therapy and exercises are crucial to aid in the child’s recovery and to promote mobility and strength. Long-term follow-up care is essential to monitor bone healing, assess function and mobility, and address any potential complications or issues related to the surgery.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.