Description
Familiarity with treatment
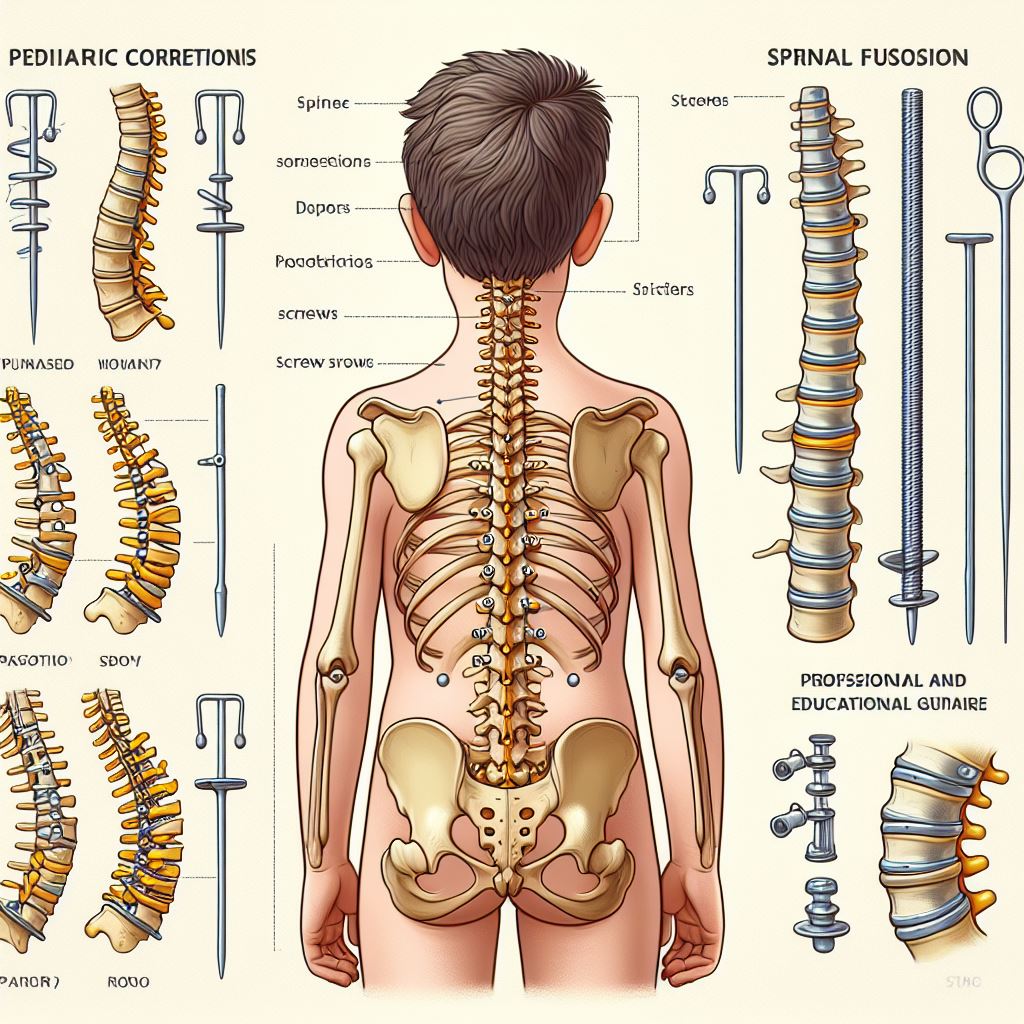
Pediatric scoliosis correction involves surgical procedures aimed at correcting abnormal curvature of the spine in children. Scoliosis is characterized by a sideways curvature of the spine, and when conservative treatments such as bracing and physical therapy are ineffective in halting the progression of the curve, surgery may be considered.
Procedure
The surgical procedure for pediatric scoliosis correction typically involves spinal instrumentation and fusion. During the procedure, the surgeon realigns the spine using rods, screws, and other implants to correct the curvature. Bone grafts may be used to fuse the vertebrae together, stabilizing the spine in the corrected position.
Who is it suitable for?
Pediatric scoliosis correction is suitable for children who have:
- Moderate to severe spinal curvature that is progressing despite non-surgical interventions
- Significant spinal deformity that poses a risk to the child’s health, lung function, or quality of life
- Skeletally immature spines with a high risk of progression into adulthood
Who is it not suitable for?
Pediatric scoliosis correction may not be suitable for children who:
- Have mild spinal curvature that can be effectively managed with non-surgical methods
- Have medical conditions that pose a high risk for surgery and recovery
- Are not skeletally mature and may benefit from non-fusion techniques such as growth-friendly implants
Advantages
- Correction of spinal deformity, potentially preventing progression and associated health issues
- Improved spinal alignment and potential for improved lung function and overall quality of life
- Aesthetic improvement in some cases
Complications
Complications associated with pediatric scoliosis correction can include:
- Infection
- Implant failure
- Pseudarthrosis (failure of the bone to fuse)
- Neurological deficits
- Potential impact on spinal growth and development
Preoperative care
Preoperative care for pediatric scoliosis correction involves comprehensive evaluation, including imaging studies to assess the severity and characteristics of the spinal curvature. It also involves optimizing the child’s overall health and addressing any specific medical conditions to prepare for surgery.
Postoperative care
After pediatric scoliosis correction, close monitoring for wound healing, pain management, and rehabilitation is essential. Physical therapy and exercises are crucial to aid in the child’s recovery and to promote spinal mobility and strength. Long-term follow-up care is essential to monitor spinal fusion, assess spinal growth and development, and address any potential complications or issues related to the surgery.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.