Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
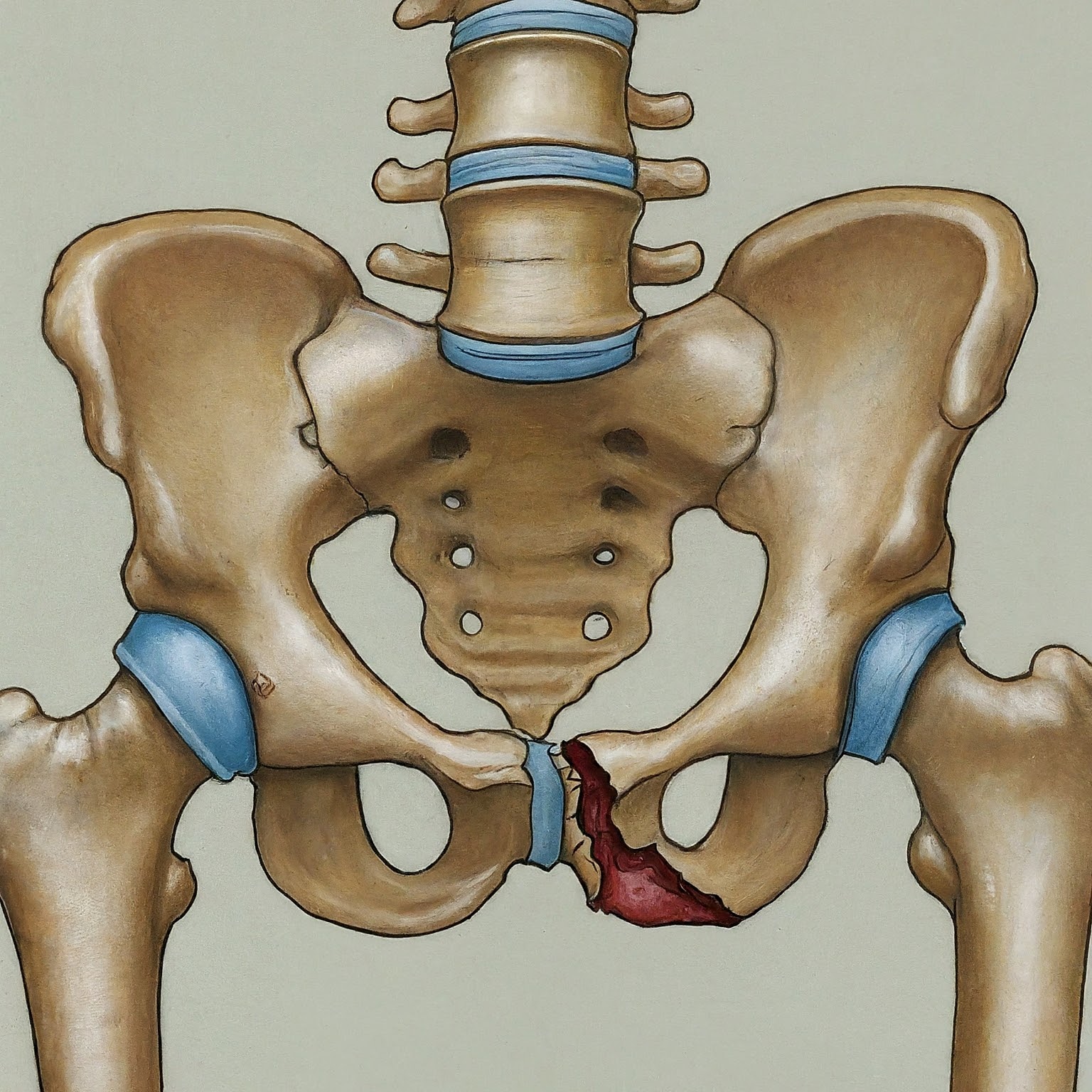
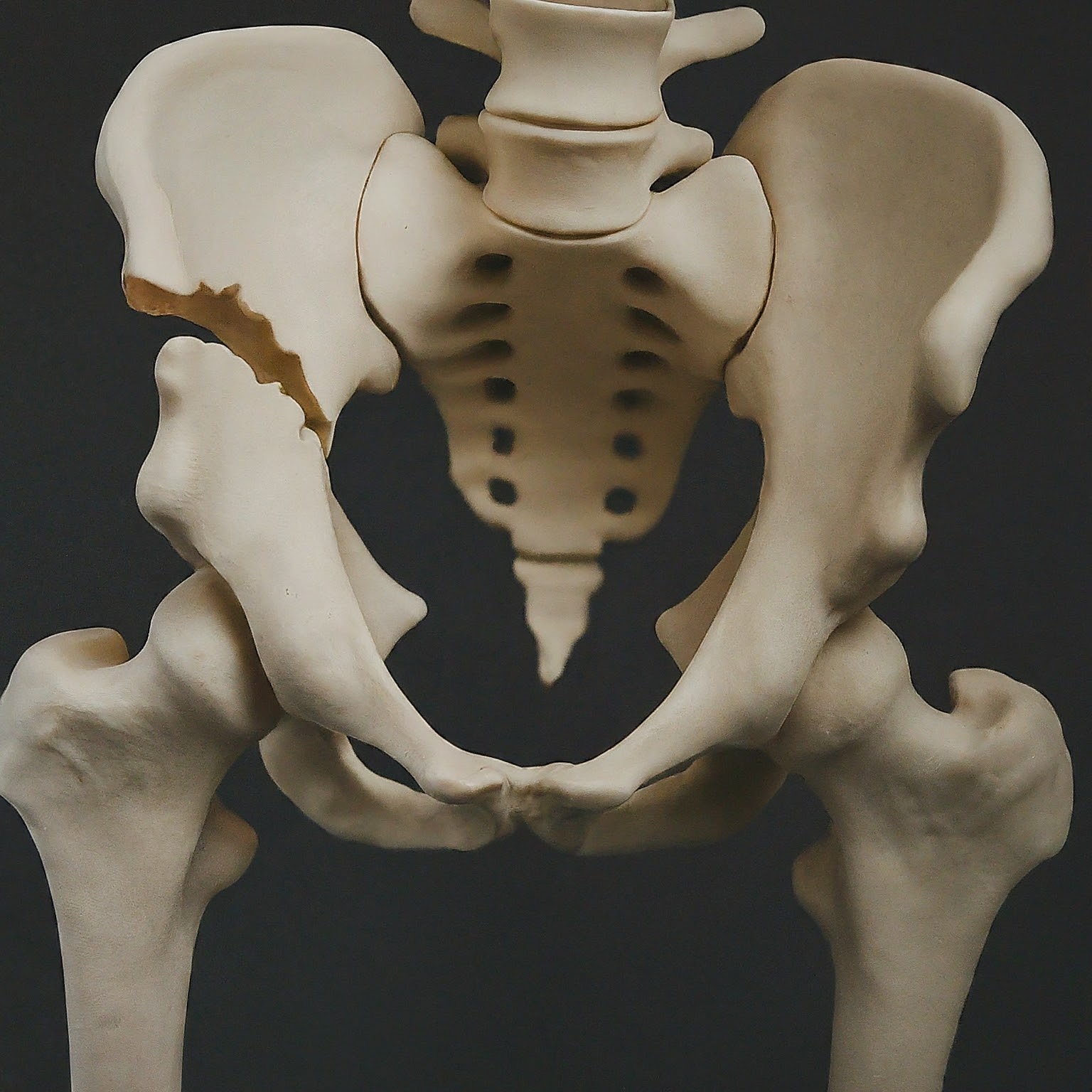
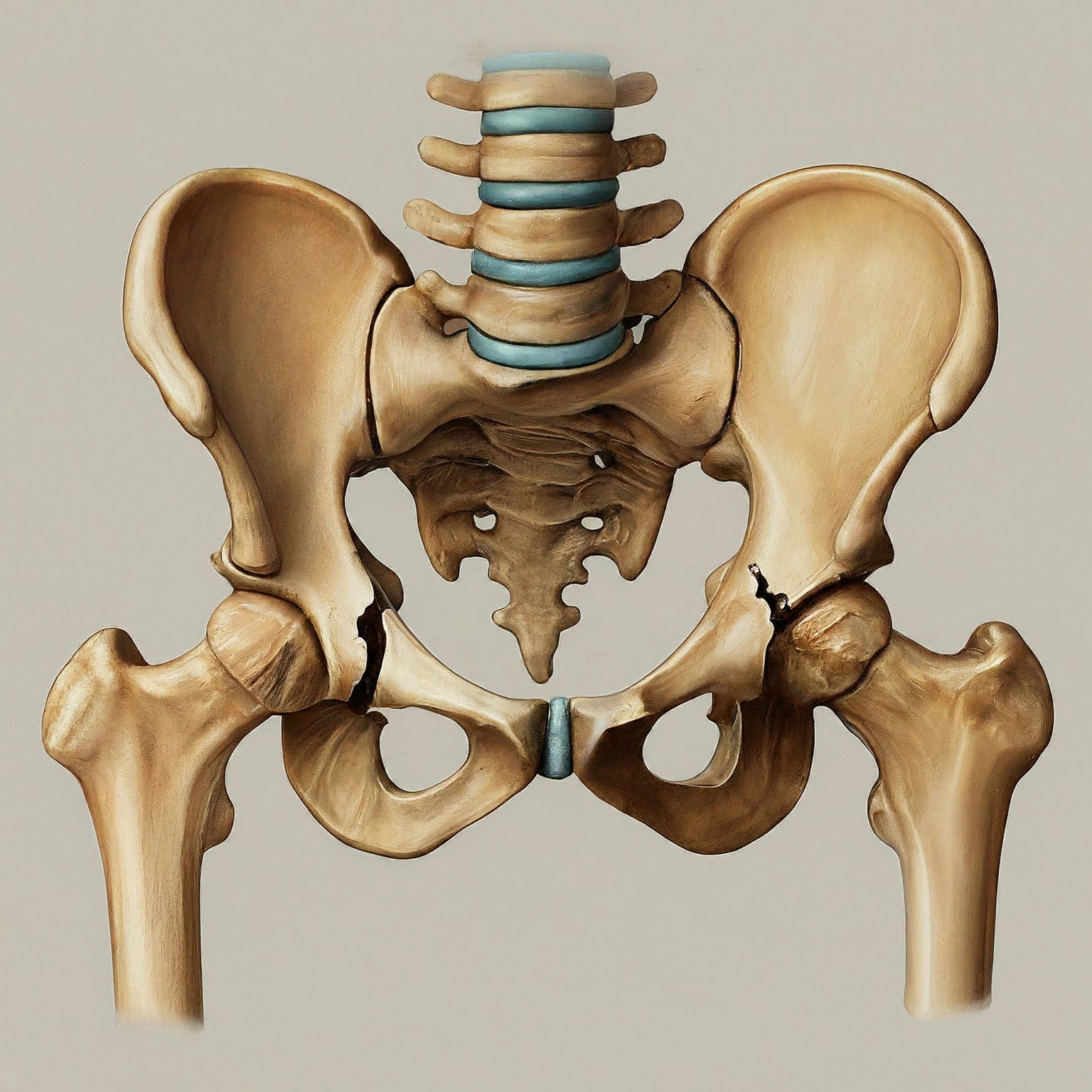
A pelvic fracture is a break in one or more of the bones that make up the pelvis. These fractures can range from mild to severe and are often caused by high-impact trauma such as car accidents or falls. Treatment varies depending on the severity and stability of the fracture.
Procedure:
- Non-Surgical Treatment:
- Stable Fractures: Mild fractures that do not displace the bones can often be treated with bed rest, pain management, and physical therapy.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Preparation: The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Realignment: The bone fragments are realigned using various techniques.
- Fixation: Screws, plates, or external fixators are used to stabilize the bones.
- Closure: The surgical site is closed with sutures or staples.
Additional Information
Who is it suitable for?
- Patients with unstable or displaced pelvic fractures.
- Individuals with severe pain or inability to walk due to the fracture.
- Those with fractures that involve significant bleeding or damage to surrounding organs.
Who is it not suitable for?
- Patients with stable, non-displaced fractures that can heal with conservative treatment.
- Individuals with severe medical conditions that may increase surgical risks.
Advantages:
- Stabilizes the pelvic ring, allowing for proper healing.
- Reduces pain and improves mobility.
- Decreases the risk of complications such as nonunion or malunion of the bones.
Complications:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding or blood clots.
- Damage to surrounding organs or tissues.
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Potential for chronic pain or mobility issues.
Previous Care:
- Preoperative evaluation including imaging tests (X-rays, CT scans) to assess the fracture.
- Blood tests to check overall health and rule out other injuries.
- Discussion of medical history and any medications being taken.
Aftercare:
- Monitoring in the recovery room until anesthesia wears off.
- Pain management with prescribed medications.
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
- Avoiding strenuous activities and heavy lifting for several weeks.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor healing and ensure no complications



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.