Description
Familiarity with Treatment
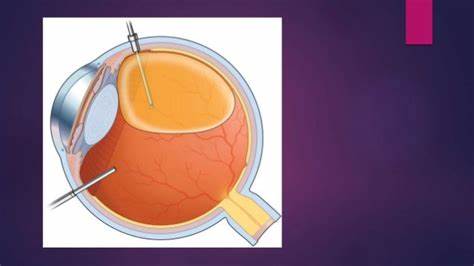
Silicone oil is often used in vitreoretinal surgery to provide long-term internal tamponade in cases of complicated retinal detachment. Once the retina has stabilized, the silicone oil is typically removed to prevent complications and improve visual outcomes.
Procedure Explanation
- Preparation: The eye is numbed with local or general anesthesia.
- Incision: Small incisions are made in the sclera (the white part of the eye).
- Oil Removal: A cannula is inserted to aspirate the silicone oil from the eye. This may involve a hybrid technique using both 20-gauge and 23-gauge instruments for efficient removal.
- Completion: The incisions are closed, and the eye is monitored for any immediate complications.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Patients who have had silicone oil placed for retinal detachment repair.
- Individuals whose retina has stabilized and no longer requires the tamponade effect of the silicone oil.
- Patients experiencing complications from the silicone oil, such as increased intraocular pressure or oil emulsification.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Patients with unstable retinal conditions that still require the support of silicone oil.
- Individuals with active eye infections or severe inflammation.
- Those with significant ocular trauma or other conditions that may complicate the removal process.
Advantages
- Reduces the risk of complications such as glaucoma, cataracts, and keratopathy.
- Improves visual acuity by removing the refractive interference of the oil.
- Reduces intraocular pressure.
- Prevents silicone oil emulsification and associated complications.
Complications
- Recurrent retinal detachment.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Hypotony (low intraocular pressure).
- Infection or inflammation.
- Corneal decompensation.
- Adherence of oil droplets to intraocular structures.
Previous Care
- Comprehensive eye examination to determine suitability.
- Routine monitoring of intraocular pressure and retinal status.
- Detailed discussion of potential risks and benefits with the ophthalmologist.
Aftercare
- Use of prescribed antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops.
- Avoid rubbing the eyes.
- Regular follow-up visits to monitor healing.
- Temporary use of protective eyewear.
- Avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities for a few weeks.
Stay at Hospital?
- This is typically an outpatient procedure, so an overnight stay at the hospital is not required. Patients can usually go home the same day after a brief observation period.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.