Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
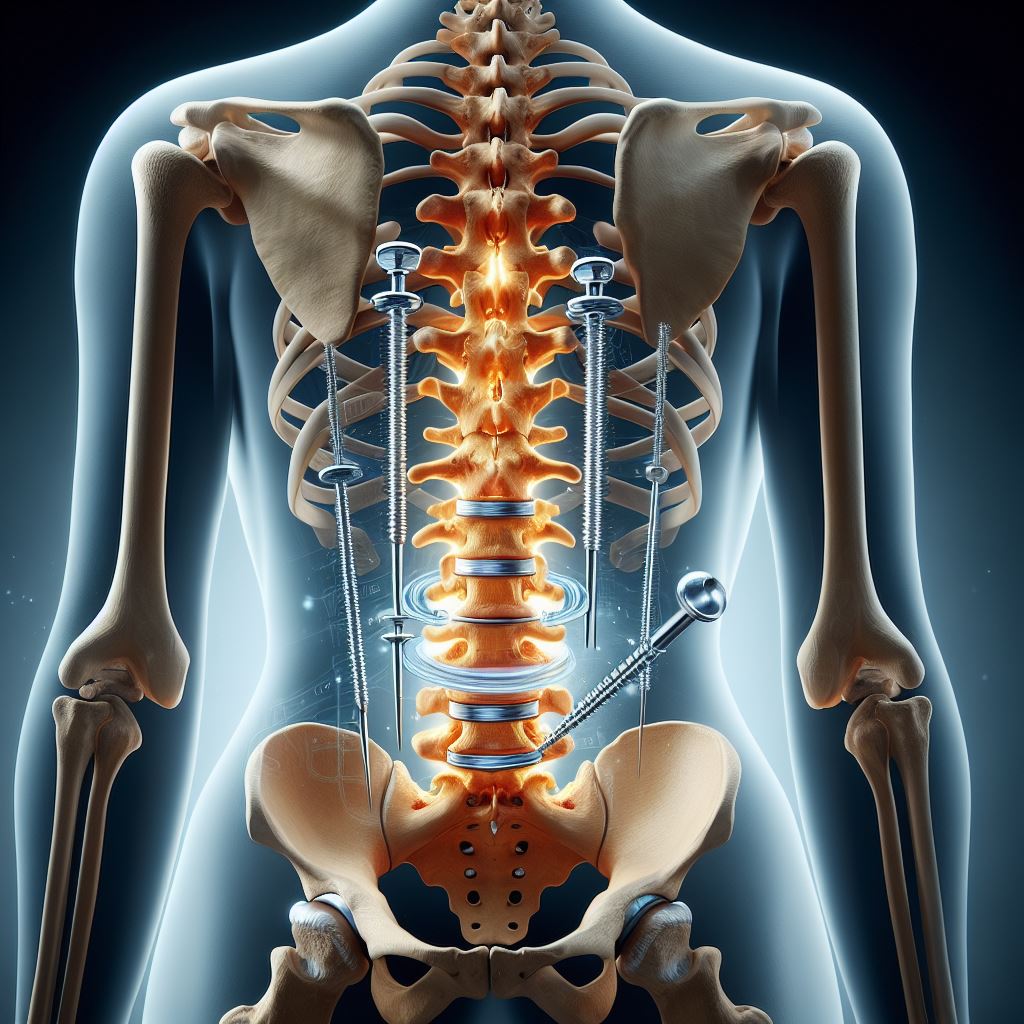
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that involves joining two or more vertebrae together using bone grafts and, in some cases, implants. The goal of this surgery is to stabilize the spine and reduce pain by preventing movement between the vertebrae.
Procedure: During spinal fusion, the surgeon will access the spine through an incision in the back, and then bone grafts are placed between the affected vertebrae. Over time, the bone grafts will fuse with the existing bone, creating a solid union. In some cases, hardware such as rods, screws, or cages may be used to provide additional stability during the fusion process.
Who Is It Suitable For?
- Individuals with conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, spinal deformities, or spinal instability that have not responded to conservative treatments.
- Those experiencing severe back pain, weakness, or numbness due to spinal issues that compromise the stability of the spine.
Who Is It Not Suitable For?
- Patients with minor or manageable symptoms that do not significantly impact daily life.
- Individuals with medical conditions that may increase the risks associated with surgery or hinder the fusion process, such as active infections or certain autoimmune disorders.
Advantages:
- Stabilization of the spine, which can alleviate pain and reduce the risk of further damage to the spinal cord and nerves.
- Potential improvement in overall spinal alignment and function for individuals affected by conditions that compromise the stability of the spine.
Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks of bleeding, infection, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- There is also a risk of the bone graft not fusing properly, hardware failure, or damage to nearby nerves or blood vessels.
Preoperative Care:
- Patients will undergo a thorough evaluation of their medical history and physical condition to assess their suitability for surgery.
- They may be advised to discontinue certain medications or supplements that could increase the risk of bleeding.
Postoperative Care:
- After surgery, patients will need to limit activities that put stress on the back while the fusion site heals and the bone grafts integrate.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be recommended to aid in recovery and to help regain strength and flexibility.
- Patients will be advised on proper lifting techniques and instructed on how to gradually resume normal activities.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.