Description
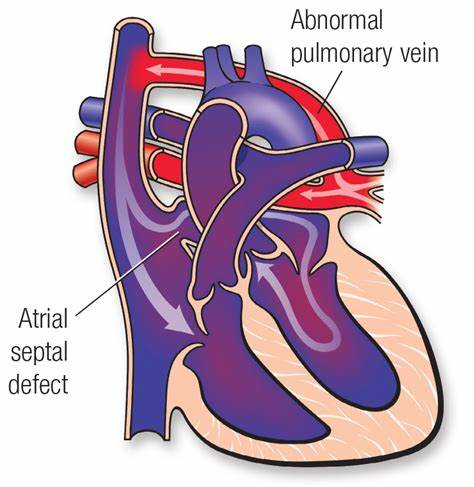
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC) is a rare congenital heart defect where the pulmonary veins do not connect normally to the left atrium. Instead, they connect to other parts of the heart or systemic veins, causing oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to mix with oxygen-poor blood from the body12.
Key Features:
- Location: The pulmonary veins connect to the right atrium or other veins instead of the left atrium1.
- Blood Flow Issues: This abnormal connection results in oxygen-rich blood mixing with oxygen-poor blood, leading to reduced oxygen levels in the body2.
- Types: TAPVC can be classified into four types based on where the pulmonary veins connect: supracardiac, cardiac, infracardiac, and mixed2.
Symptoms:
- Cyanosis (bluish skin due to lack of oxygen)
- Difficulty breathing
- Poor feeding
- Fatigue
Treatment:
- Surgery: The primary treatment is surgical repair, which involves reconnecting the pulmonary veins to the left atrium and closing any associated defects, such as an atrial septal defect12.
Familiarity with Treatment
Treatment for TAPVC typically involves surgical repair. The surgery is usually performed in early infancy and involves reconnecting the pulmonary veins to the left atrium and closing any associated defects, such as an atrial septal defect12. Advances in surgical techniques and postoperative care have significantly improved outcomes3.
Who is it Suitable For?
Surgical treatment is suitable for:
- Infants diagnosed with TAPVC, especially those showing symptoms like cyanosis (bluish skin due to lack of oxygen), difficulty breathing, or poor feeding1.
- Children with obstructed TAPVC, where the pulmonary veins are blocked, causing severe symptoms2.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
Surgical treatment may not be suitable for:
- Patients with severe, irreversible pulmonary hypertension, as the risks of surgery may outweigh the benefits2.
- Patients with other severe health conditions that increase surgical risk.
Advantages
- Improved oxygenation: Correcting the defect allows proper oxygenation of blood, improving overall health1.
- Reduced symptoms: Surgery can alleviate symptoms such as difficulty breathing and cyanosis2.
- Prevention of complications: Early intervention can prevent long-term complications like heart failure and pulmonary hypertension1.
Complications
- Surgical risks: As with any major surgery, there are risks of infection, bleeding, and complications from anesthesia2.
- Residual defects: Some patients may have residual issues that require further treatment1.
- Heart rhythm problems: Arrhythmias can occur after surgery and may need additional management2.
Previous Care
Before surgery, care typically includes:
- Monitoring and managing symptoms: Using medications to control symptoms like heart failure1.
- Nutritional support: Ensuring the child receives adequate nutrition to support growth and development2.
Aftercare
Post-surgery care involves:
- Regular follow-up visits: Monitoring heart function and overall health1.
- Medications: To prevent infection and manage any residual symptoms2.
- Activity restrictions: Gradually reintroducing physical activity as the child recovers1.
If you have any more questions or need further details, feel free to ask!



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.