Description
Familiarity with Treatment:
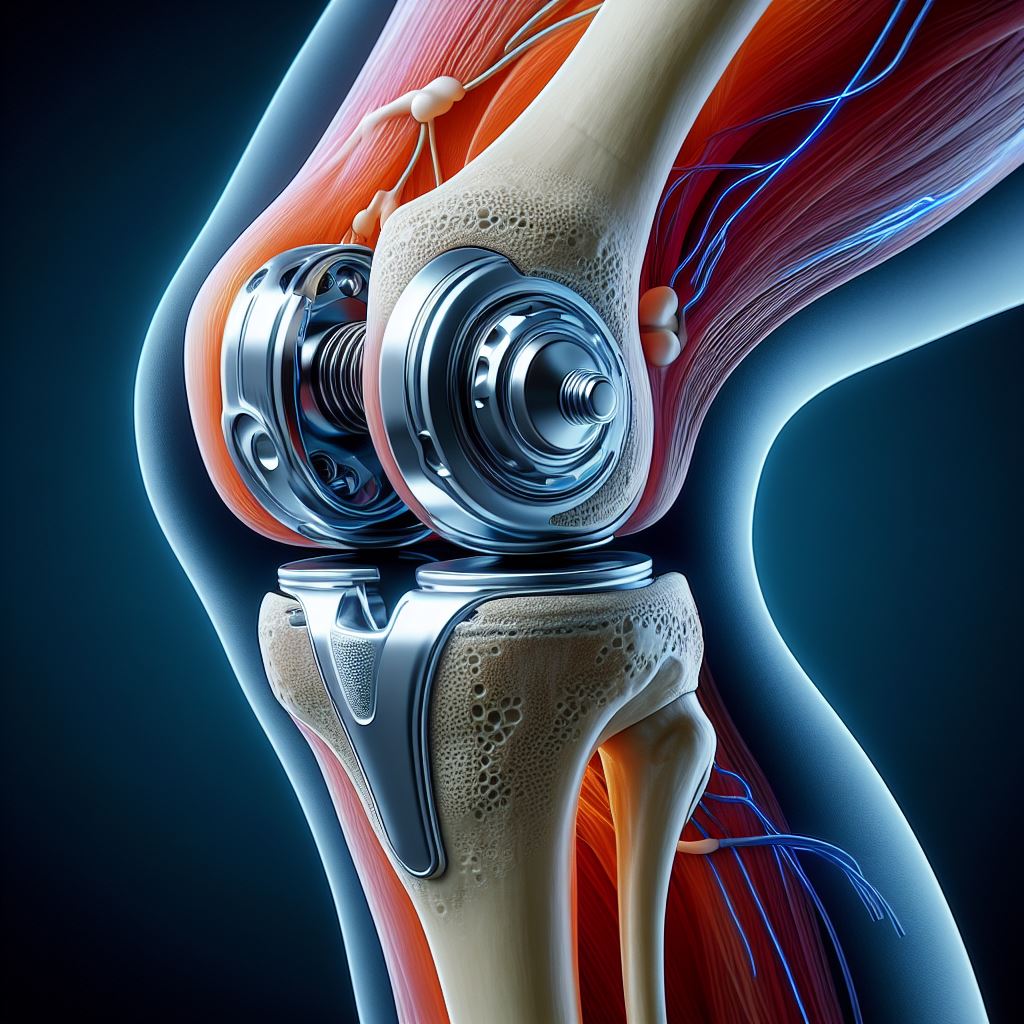
Total knee replacement (TKR), also known as total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the damaged surfaces of the knee joint with artificial components. It is a common treatment for severe knee arthritis or significant knee joint damage, aiming to relieve pain and improve function.
Procedure:
- Preparation: The damaged bone and cartilage within the knee joint are removed.
- Implantation: The ends of the thigh bone (femur) and shin bone (tibia) are replaced with metal components, while a plastic spacer is inserted between them. If necessary, the undersurface of the kneecap (patella) may also be resurfaced with a plastic component.
Who is it Suitable for?
TKR is suitable for individuals with severe knee pain, stiffness, and functional limitations caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, or other joint diseases. It is often considered when non-surgical treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or injections, have not provided sufficient relief.
Who is it Not Suitable for?
TKR may not be suitable for individuals with mild or moderate knee arthritis that can be effectively managed through non-surgical means. Additionally, those with certain medical conditions that increase surgical risks, such as untreated infections or compromised bone quality, may not be good candidates for this procedure.
Advantages:
- Pain Relief: TKR surgery aims to alleviate chronic knee pain, improving overall quality of life and mobility.
- Improved Function: By restoring the damaged knee joint, TKR can enhance the range of motion and stability of the knee, allowing for increased activity levels.
Complications:
- Potential complications of TKR may include infection, blood clots, implant wear, joint stiffness, nerve or blood vessel injury, and rare instances of prosthesis failure or instability.
Preoperative Care:
- Comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s knee condition, including physical examination, imaging studies, and pre-operative laboratory tests.
- Patient education regarding the procedure, including potential risks and benefits, as well as expectations for recovery and rehabilitation.
- Pre-surgical optimization of the patient’s overall health, including management of chronic conditions and cessation of certain medications that may increase surgical risks.
Postoperative Care:
- Pain management to facilitate early mobility and rehabilitation.
- Physical therapy and exercises to regain knee strength, flexibility, and function.
- Monitoring for signs of infection, impaired wound healing, or complications.
- Gradual return to weight-bearing activities under the guidance of the surgical team.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.