Description
Familiarity with treatment
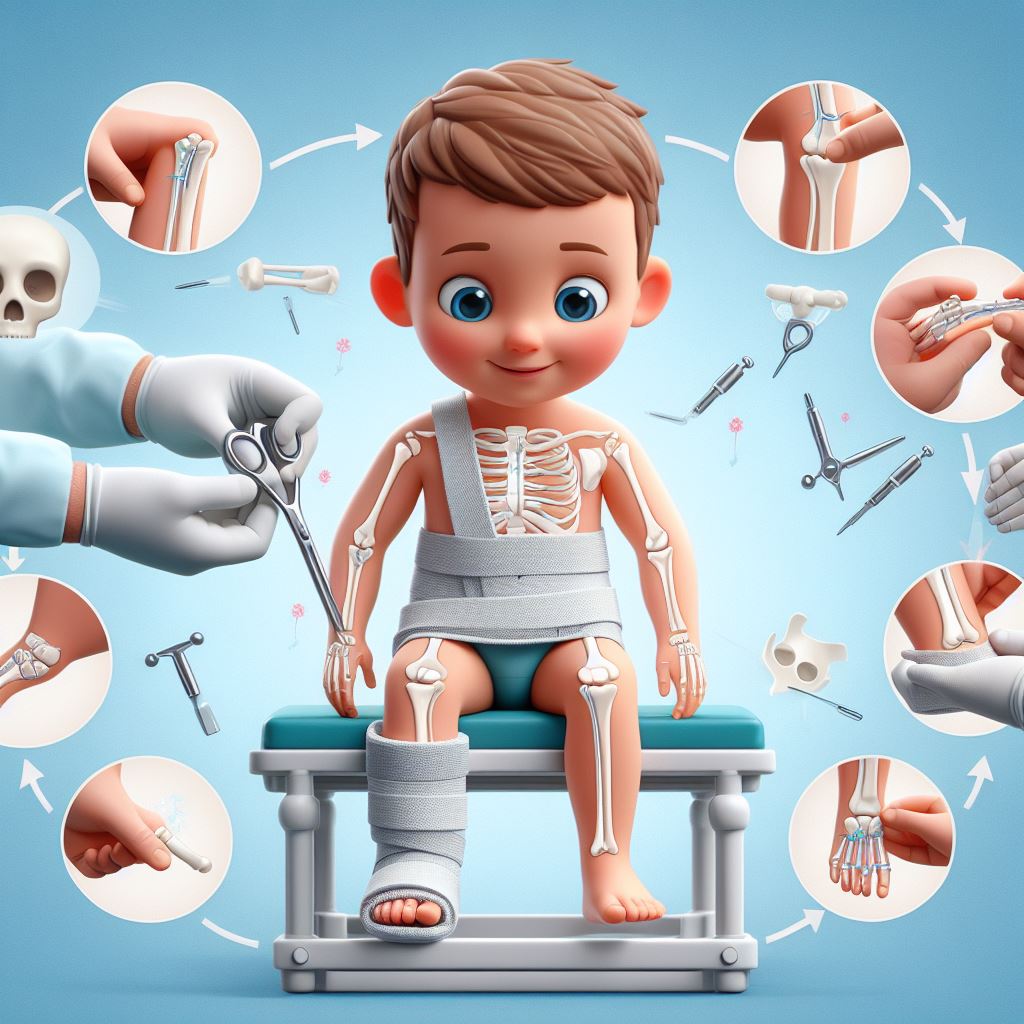
Pediatric fracture repair involves the surgical intervention to address complex or displaced fractures in children. Fractures in children can vary widely in severity and type, and surgical repair may be necessary in cases where non-surgical methods such as casting or bracing are deemed insufficient for optimal healing and alignment.
Procedure
The procedure for pediatric fracture repair involves the surgical realignment and stabilization of the fractured bone using various techniques such as internal fixation with plates, screws, or rods, or external fixation with pins and wires. The goal is to restore proper alignment, promote healing, and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Who is it suitable for?
Pediatric fracture repair is suitable for children who have:
- Complex fractures that cannot be adequately realigned or stabilized with non-surgical methods
- Fractures that are at risk of healing in a malaligned position, leading to potential long-term functional impairment
- Fractures that involve growth plates or critical weight-bearing bones
Who is it not suitable for?
Pediatric fracture repair may not be suitable for children who:
- Have fractures that can be effectively managed with non-surgical methods such as casting or bracing
- Have medical conditions that pose a high risk for surgery and recovery
- Have fractures that are not amenable to surgical intervention due to their location or severity
Advantages
- Precise realignment and stabilization of the fracture, promoting optimal healing and minimizing the risk of long-term complications
- Earlier mobilization and return to normal activities for the child in some cases
Complications
Complications associated with pediatric fracture repair can include:
- Infection
- Delayed or non-union of the fracture
- Damage to nerves or blood vessels
- Potential for growth disturbances, especially if the growth plates are involved
Preoperative care
Preoperative care for pediatric fracture repair involves comprehensive evaluation, including imaging studies to assess the fracture’s characteristics and impact on the child’s growth and development. It also involves optimizing the child’s overall health and addressing any specific medical conditions to prepare for surgery.
Postoperative care
After pediatric fracture repair, close monitoring for wound healing, pain management, and rehabilitation is essential. Physical therapy and exercises may be recommended to aid in the child’s recovery and functional restoration. Long-term follow-up care is crucial to monitor for any signs of complications, assess bone healing, and ensure proper growth and development of the affected limb.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.