Description
Familiarity with treatment
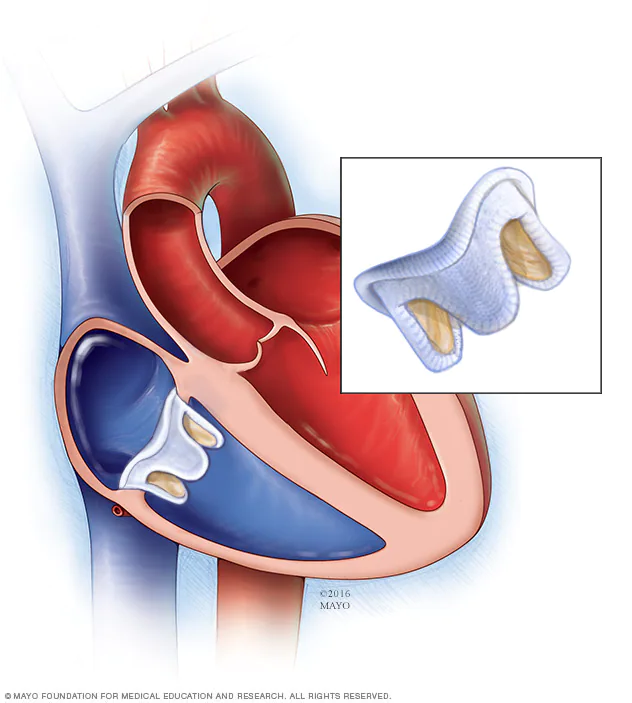
Tricuspid valve repair (TVR) is a surgical procedure to repair a damaged or malfunctioning tricuspid valve, which is one of the four valves in the heart. The tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle and prevents blood from flowing back into the atrium during ventricular contraction.
**Indications for TVR:**
– Severe tricuspid regurgitation, which is the backward flow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium
– Tricuspid stenosis, which is the narrowing of the tricuspid valve opening
– Infective endocarditis involving the tricuspid valve
– Rheumatic heart disease
– Congenital heart defects affecting the tricuspid valve
**Preoperative Evaluation:**
– Comprehensive history and physical examination
– Echocardiography to assess the severity of tricuspid regurgitation or stenosis, as well as the anatomy of the tricuspid valve
– Other imaging studies, such as cardiac MRI or CT, may be necessary in some cases
**Surgical Techniques:**
There are two main surgical approaches for TVR:
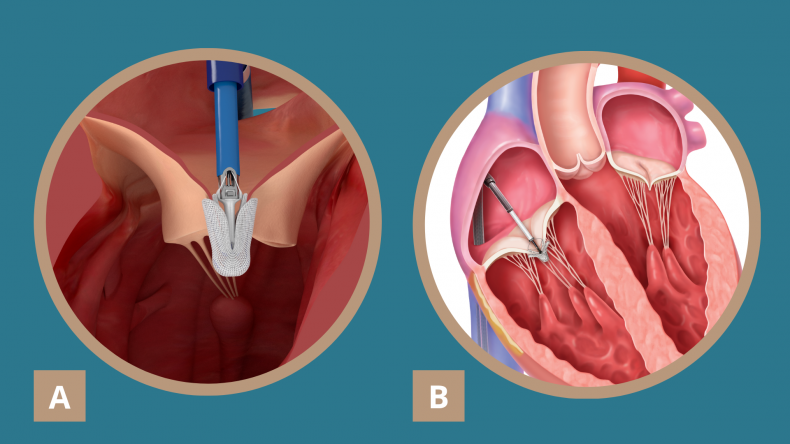
1. **Open-heart surgery:** This involves opening the chest and directly visualizing the tricuspid valve. The surgeon may perform various techniques to repair the valve, such as:
– **Annuloplasty:** This involves tightening the ring around the tricuspid valve to reduce regurgitation.
– **Valve leaflet repair:** This involves repairing or replacing the damaged valve leaflets.
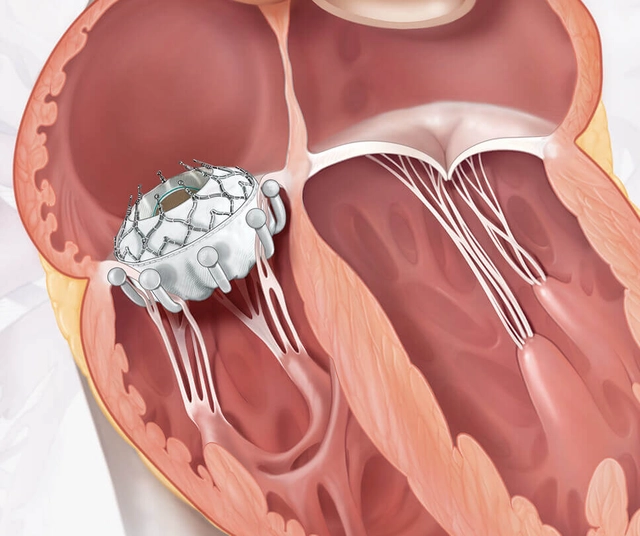
– **Valve replacement:** This involves removing the damaged valve and replacing it with a mechanical or biological prosthesis.
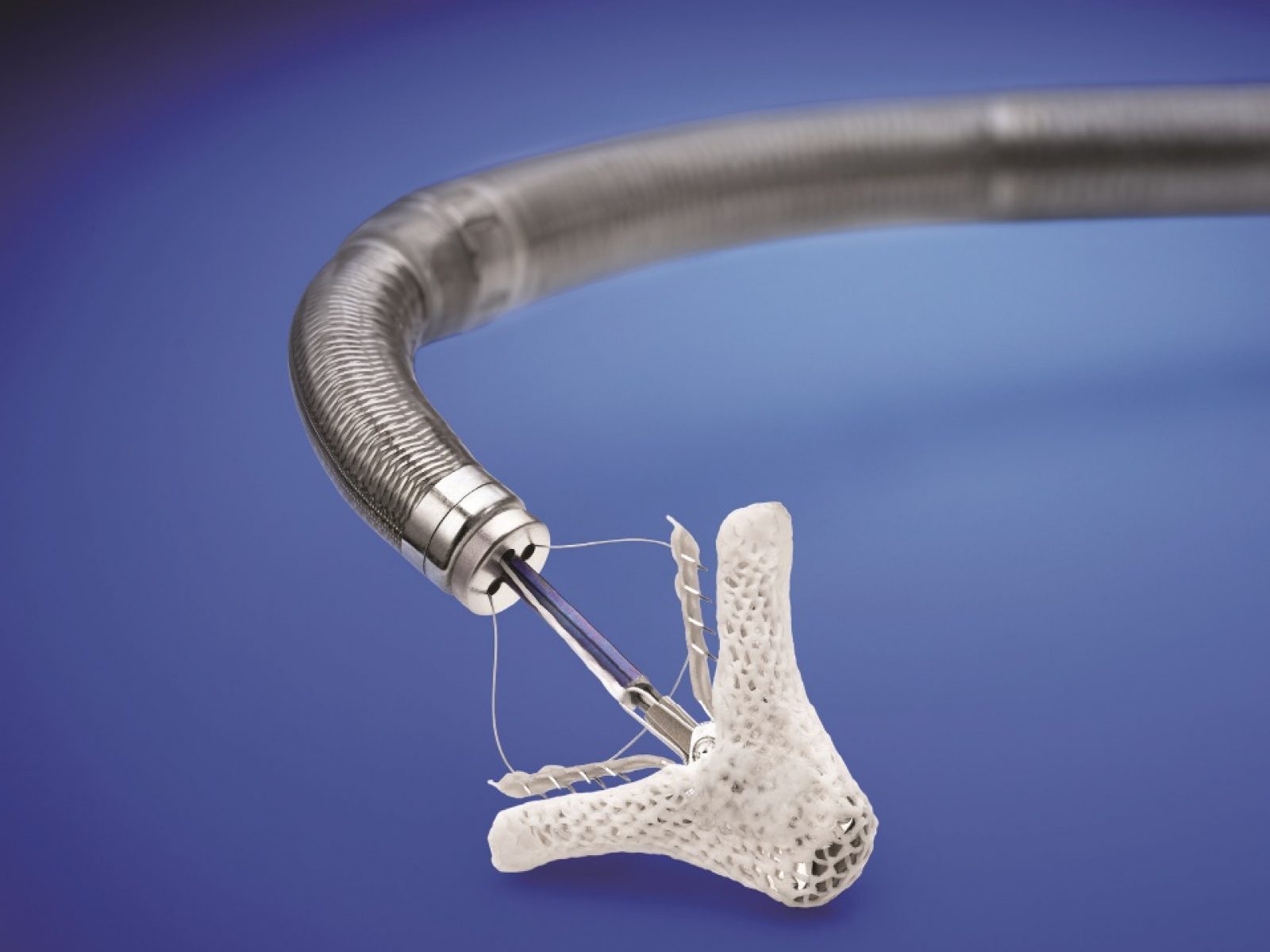
2. **Transcatheter tricuspid valve repair:** This is a minimally-invasive procedure that involves delivering a device to the tricuspid valve through a catheter inserted into a vein. The device is then used to repair the valve without the need for open-heart surgery.
**Postoperative Care:**
– After surgery, patients will typically stay in the hospital for several days for monitoring and recovery.
– Medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
– Regular follow-up appointments will be necessary to monitor the function of the repaired tricuspid valve.
**Outcomes:**
– The success of TVR depends on various factors, including the underlying cause of the tricuspid valve dysfunction, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s overall health.
– In general, most patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life after successful TVR.
– The long-term durability of TVR varies depending on the type of repair performed and the underlying cause of the valve dysfunction.
Who is it suitable for?
Tricuspid valve repair is suitable for individuals who have a malfunctioning tricuspid valve and meet certain criteria. The decision to undergo tricuspid valve repair is made on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration factors such as the severity of the valve dysfunction, the overall health of the patient, and the potential benefits of the procedure.
Tricuspid valve repair may be suitable for individuals who:
- Have Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation: Tricuspid valve regurgitation occurs when the valve does not close properly, causing blood to flow backward into the right atrium. If the regurgitation is severe and causing symptoms or affecting heart function, tricuspid valve repair may be considered.
- Have Tricuspid Valve Stenosis: Tricuspid valve stenosis is a condition where the valve becomes narrowed, obstructing blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. If the stenosis is significant and causing symptoms or affecting heart function, tricuspid valve repair may be considered.
- Have a Structurally Repairable Valve: Tricuspid valve repair is typically performed when the valve is structurally repairable. This means that the valve leaflets, annulus, and chordae tendineae can be repaired or reconstructed to restore proper valve function.
- Are in Good Overall Health: Tricuspid valve repair is a surgical procedure that requires general anesthesia and carries some risks. Therefore, individuals who are in good overall health and can tolerate the surgery are more likely to be suitable candidates.
- Have Realistic Expectations: It is important for individuals considering tricuspid valve repair to have realistic expectations about the potential outcomes of the procedure. While tricuspid valve repair can improve symptoms and heart function, it may not completely eliminate all symptoms or reverse all damage.
Who is it not suitable for?
Tricuspid valve repair may not be suitable for certain individuals depending on their specific condition and circumstances. The decision to pursue tricuspid valve repair is made on a case-by-case basis, and there are some factors that may make a person not suitable for the procedure. These factors may include:
- Severe Heart Failure: If an individual has severe heart failure that is not manageable with medications or other interventions, tricuspid valve repair may not be recommended. In such cases, the risks of the surgery may outweigh the potential benefits.
- Advanced Age or Poor Overall Health: Tricuspid valve repair is a surgical procedure that requires general anesthesia and carries some risks. If an individual is of advanced age or has significant underlying health conditions that make them high-risk for surgery, tricuspid valve repair may not be suitable.
- Irreparable Valve Damage: In some cases, the tricuspid valve may be severely damaged or calcified, making it impossible to repair. If the valve is deemed irreparable, the surgeon may recommend valve replacement instead of repair.
- Other Significant Heart Conditions: If an individual has other significant heart conditions, such as severe coronary artery disease or aortic valve disease, tricuspid valve repair may not be the primary focus of treatment. In such cases, the tricuspid valve may be addressed during other necessary heart surgeries.
- Limited Life Expectancy: If an individual has a limited life expectancy due to advanced age, underlying health conditions, or other factors, the risks and benefits of tricuspid valve repair may need to be carefully considered. The potential benefits of the procedure may not outweigh the risks in individuals with a limited life expectancy.
Advantages
Tricuspid valve repair offers several advantages compared to other treatment options or not undergoing any intervention. Some of the advantages of tricuspid valve repair include:
- Preserving the Natural Valve: Tricuspid valve repair aims to preserve the patient’s own valve rather than replacing it with an artificial valve. This can help maintain the normal anatomy and function of the heart, potentially leading to better long-term outcomes.
- Avoiding Long-Term Anticoagulation: Tricuspid valve repair eliminates the need for long-term anticoagulation therapy, which is often required with mechanical valve replacement. This can reduce the risk of bleeding complications associated with anticoagulant medications.
- Improved Quality of Life: Tricuspid valve repair can improve symptoms and quality of life for individuals with tricuspid valve dysfunction. Repairing the valve can help restore proper blood flow and alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention.
- Lower Risk of Infection: Compared to valve replacement, tricuspid valve repair carries a lower risk of infection. With repair, there is no need for a foreign material (prosthetic valve) to be implanted, reducing the risk of infection-related complications.
- Potential for Better Long-Term Outcomes: Tricuspid valve repair, when successful, can lead to better long-term outcomes compared to valve replacement. Repairing the native valve can help maintain its normal function and durability, potentially reducing the need for additional surgeries in the future.
- Shorter Hospital Stay and Recovery Time: Tricuspid valve repair is generally associated with a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery compared to valve replacement. This can allow individuals to return to their normal activities and daily routines sooner.
Complications
Like any surgical procedure, tricuspid valve repair carries some risks and potential complications. While complications are relatively rare, it is important to be aware of them. Some possible complications of tricuspid valve repair include:
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during or after the surgery. In some cases, additional procedures or blood transfusions may be necessary to control the bleeding.
- Infection: Infection at the surgical site or in the heart can occur after tricuspid valve repair. This may require antibiotics or, in severe cases, additional surgery to treat the infection.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in the heart or blood vessels after tricuspid valve repair. These clots can potentially travel to other parts of the body and cause serious complications, such as stroke or pulmonary embolism.
- Valve Dysfunction: Despite repair efforts, the tricuspid valve may not function optimally after the surgery. This can result in residual leakage (regurgitation) or narrowing (stenosis) of the valve, requiring further treatment or additional surgeries.
- Arrhythmias: Tricuspid valve repair can sometimes disrupt the normal electrical signals in the heart, leading to irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias). Medications or additional procedures may be needed to manage these arrhythmias.
- Heart Failure: In rare cases, tricuspid valve repair may not effectively improve heart function, and heart failure may persist or worsen after the surgery. This may require additional interventions or treatments to manage heart failure symptoms.
- Anesthetic Complications: General anesthesia carries its own risks, including allergic reactions, respiratory problems, or adverse reactions to medications used during the procedure.
- Other General Surgical Risks: Tricuspid valve repair is a surgical procedure, and as with any surgery, there are risks associated with anesthesia, blood clots, wound healing, and other general surgical complications.
Previous care
Before undergoing tricuspid valve repair, there are several important aspects of care that may be involved. These can include:
- Preoperative Evaluation: Prior to the surgery, you will undergo a thorough evaluation to assess your overall health and determine if you are a suitable candidate for tricuspid valve repair. This may involve medical history review, physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests (such as echocardiogram), and other diagnostic tests.
- Medication Management: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage your symptoms and optimize your heart function before the surgery. These medications may include diuretics to reduce fluid retention, medications to control blood pressure, and medications to prevent blood clots.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Your healthcare provider may recommend certain lifestyle modifications to improve your heart health and prepare you for the surgery. This can include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise within your physical limitations, quitting smoking if you are a smoker, and managing stress.
- Education and Counseling: You may receive education and counseling about the tricuspid valve repair procedure, including the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes. This can help you make informed decisions and alleviate any concerns or anxieties you may have.
- Preoperative Instructions: Your healthcare provider will provide you with specific instructions to follow before the surgery. This may include fasting for a certain period of time before the procedure, discontinuing certain medications, and arranging for transportation to and from the hospital.
- Coordination with the Surgical Team: Your healthcare provider will work closely with the surgical team to ensure a smooth transition from preoperative care to the surgical procedure. They will provide the necessary medical information and collaborate on the surgical plan.
Aftercare
After undergoing tricuspid valve repair, proper aftercare is essential to promote healing, minimize complications, and ensure a successful recovery. Here are some important aspects of aftercare for tricuspid valve repair:
Hospital Stay: Following the surgery, you will typically stay in the hospital for a few days. During this time, your healthcare team will closely monitor your condition, manage pain and discomfort, and administer medications as needed.
Wound Care: Take care of the surgical incision site as instructed by your healthcare provider. Keep the incision clean, dry, and protected to prevent infection. Follow any specific dressing changes or wound care instructions provided to you.
Medications: Your healthcare provider will prescribe medications to support your recovery. These may include pain medications, antibiotics to prevent infection, and medications to manage any underlying heart conditions. Take all medications as directed and notify your healthcare provider if you experience any adverse reactions.
Activity and Rest: It is important to balance rest and activity during your recovery period. While it is crucial to get up and move around to prevent complications such as blood clots, you should also listen to your body and avoid overexertion. Gradually increase your activity level as advised by your healthcare provider.
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider. These appointments allow your provider to monitor your progress, assess the effectiveness of the repair, and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes: Depending on the underlying cause of your tricuspid valve disease, your healthcare provider may recommend certain lifestyle modifications. These may include dietary changes, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and managing any underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Emotional Support: The recovery process from heart surgery can be challenging both physically and emotionally. Seek support from family, friends, or support groups to cope with any emotional difficulties you may encounter during your recovery.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.