Description
Familiarity with treatment
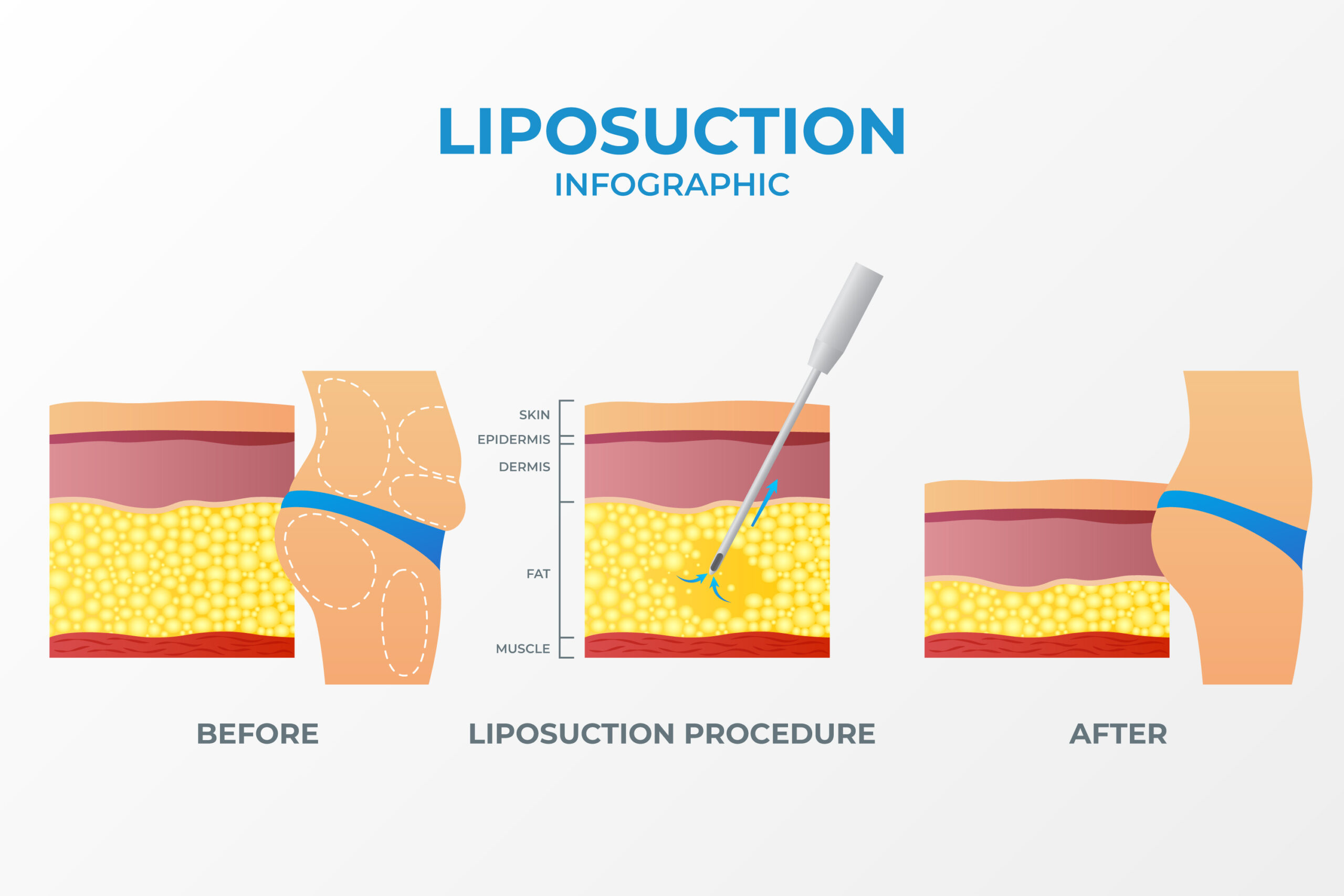
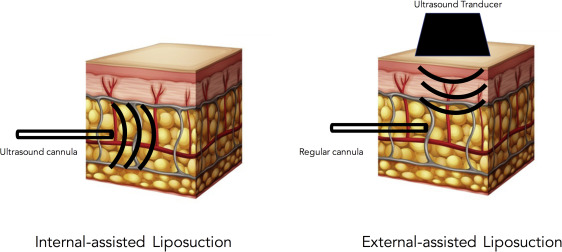
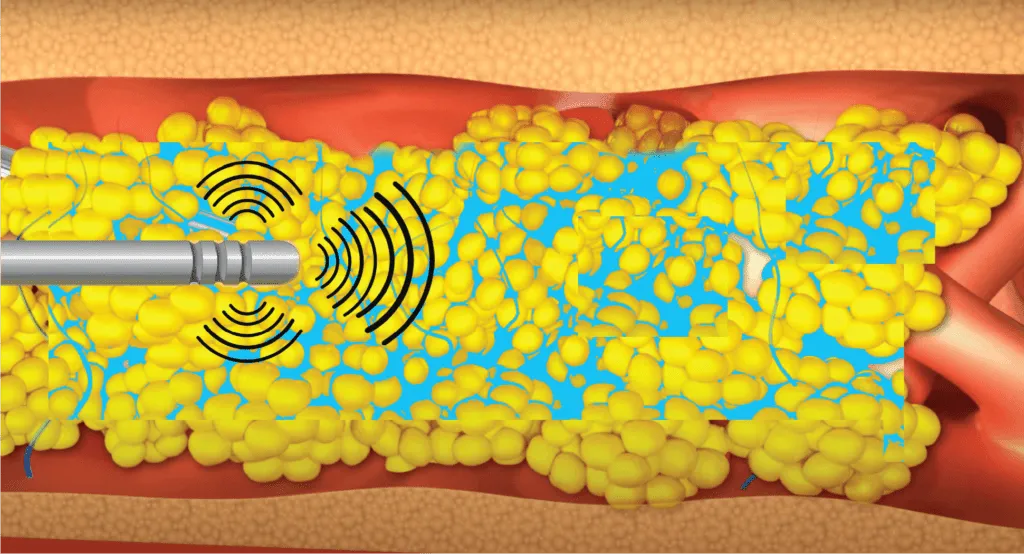
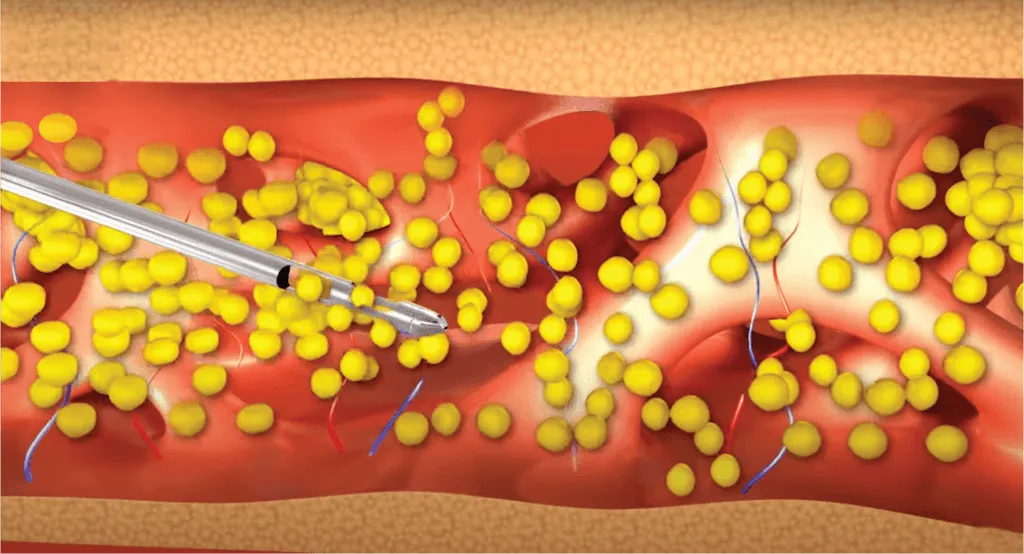
Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL) is a technique used in liposuction procedures to help facilitate the removal of fat cells. It involves the use of ultrasound energy to emulsify or liquefy the fat cells before their removal. UAL can be performed externally or internally, depending on the specific approach used by the surgeon.
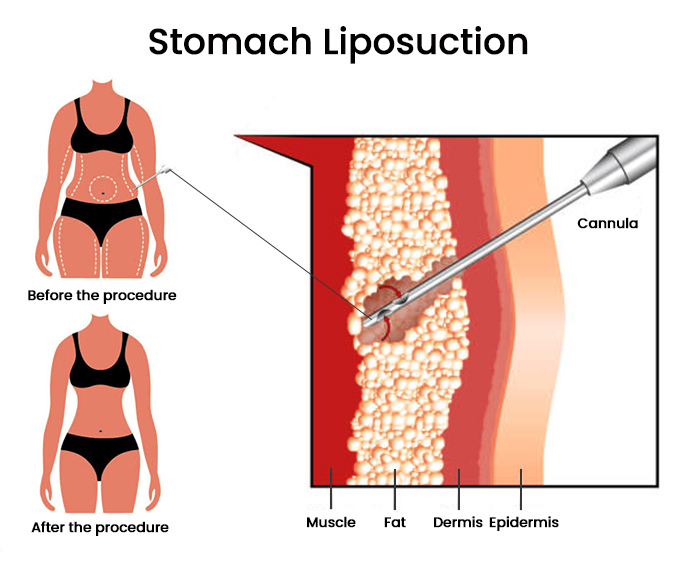
External Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL): In external UAL, high-frequency ultrasonic waves are delivered into the treatment area through the skin using a handheld device. The ultrasound energy targets the fat cells, causing them to vibrate and break apart. The emulsified fat is then suctioned out through small incisions using a cannula, a thin tube-like instrument.
Internal Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL): Internal UAL involves the insertion of a long metal probe or paddle into the treatment area through a larger incision. The probe or paddle emits ultrasound energy directly into the subcutaneous fat, causing the fat cells to break down. The emulsified fat is then removed using a cannula.
The use of ultrasound energy in UAL offers several potential benefits. The ultrasound waves can selectively target fat cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. Additionally, UAL has been suggested to promote skin tightening due to the thermal effect of the ultrasound energy on collagen fibers.
It’s important to note that UAL is typically performed under local anesthesia, which reduces the risks associated with general anesthesia. The specific technique used and the extent of fat removal will depend on the individual patient’s needs and the surgeon’s expertise.
Who is it suitable for?
Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL) can be suitable for individuals who are looking to remove localized areas of stubborn fat that have not responded well to diet and exercise. It is important to note that UAL is not intended for weight loss purposes but rather for aesthetic fat reduction.
The best candidates for UAL are generally individuals who are in good overall health, have realistic expectations about the procedure, and have specific areas of fat that they would like to target. UAL can be particularly effective for removing fat from fibrous body areas, such as the male breasts or the back, or for removing larger volumes of fat in a single procedure.
Who is it not suitable for?
While Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL) can be an effective procedure for many individuals, there are certain cases where it may not be suitable. It’s important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine if UAL is appropriate for you. Here are some factors that may make UAL not suitable for certain individuals:
General Health Concerns: Individuals with significant medical conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, or compromised immune systems, may not be suitable candidates for UAL. These conditions can increase the risks associated with surgery and affect the healing process.
Skin Elasticity: UAL may not be as effective for individuals with poor skin elasticity. The procedure can remove fat but may not adequately address loose or sagging skin. In such cases, alternative procedures like a tummy tuck or body lift may be more suitable.
Obesity: UAL is not intended as a weight loss procedure. It is best suited for individuals who are already close to their ideal body weight and have specific areas of localized fat that are resistant to diet and exercise. For individuals who are significantly overweight or obese, other weight loss methods should be considered before considering UAL.
Pregnancy or Nursing: UAL is generally not recommended for individuals who are pregnant or currently breastfeeding. It is important to wait until after pregnancy and breastfeeding to undergo this procedure.
Unrealistic Expectations: It’s important to have realistic expectations about the outcomes of UAL. While it can effectively remove localized areas of fat, it may not achieve the desired results if there are other issues such as loose skin or muscle laxity. A thorough consultation with a plastic surgeon can help manage expectations and explore alternative treatment options if necessary.
Advantages
Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL) offers several advantages compared to traditional liposuction techniques. Here are some of the potential benefits of UAL:
Effective Fat Removal: UAL can be particularly effective for removing fat from fibrous body areas, such as the male breasts or the back, or for removing larger volumes of fat in a single procedure 1.
Selective Fat Targeting: The ultrasound energy used in UAL can selectively target fat cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Improved Skin Tightening: UAL has been suggested to promote skin tightening due to the thermal effect of the ultrasound energy on collagen fibers. This can help improve the overall contour and appearance of the treated area 2.
Reduced Surgical Trauma: UAL can potentially result in less surgical trauma compared to traditional liposuction techniques. The emulsification of fat cells by ultrasound energy may allow for easier and gentler removal of fat, potentially reducing tissue trauma and postoperative discomfort.
Local Anesthesia: UAL is typically performed under local anesthesia, which can reduce the risks associated with general anesthesia and allow for a faster recovery.
Complications
Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction (UAL) has several potential advantages compared to traditional liposuction techniques. Here are some of the advantages mentioned in the search results:
Effective Fat Removal: UAL can be particularly effective in removing dense, fibrous fat tissue, such as in cases of gynecomastia (enlarged male breasts). It has been found to be efficient in treating most grades of gynecomastia 1.
Selective Fat Targeting: UAL allows for selective targeting of fat cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Improved Skin Tightening: UAL has been suggested to promote skin tightening due to the thermal effect of the ultrasound energy on collagen fibers This can help improve the overall contour and appearance of the treated area.
Reduced Surgical Trauma: UAL may result in less surgical trauma compared to traditional liposuction techniques. The emulsification of fat cells by ultrasound energy may allow for easier and gentler removal of fat, potentially reducing tissue trauma and postoperative discomfort 1.
Local Anesthesia: UAL is typically performed under local anesthesia, which can reduce the risks associated with general anesthesia and allow for a faster recovery.
preoperative care
Preoperative care refers to the physical and psychosocial care provided to patients before undergoing surgery. The goal of preoperative care is to ensure the patient’s safety and optimize their outcomes after the surgical procedure. The preoperative period begins when the patient is booked for surgery and ends with their transfer to the operating room or surgical suite.
Here are some key aspects of preoperative care:
Medical Assessment: Before surgery, the healthcare provider will assess the patient’s fitness for the procedure. This assessment includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, risk assessment, and general and system-specific evaluations 1.
Preoperative Tests: Depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s medical condition, various preoperative tests and clinical assessments may be conducted. These tests can include blood work, imaging studies, electrocardiogram (ECG), and other diagnostic tests 2.
Patient Education: During the preoperative period, patients are provided with information about their surgery, including what to expect before, during, and after the procedure. This education helps patients understand the surgical process, manage their expectations, and actively participate in their care 3.
Consent Process: Informed consent is an essential part of preoperative care. The healthcare team ensures that the patient or their legal guardian understands the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the surgery and provides their consent before the procedure. Consent forms are signed and documented in the patient’s chart 4.
Preoperative Instructions: Patients receive specific instructions regarding fasting, medication management, and any necessary preparations before surgery. These instructions may include guidelines on when to stop eating and drinking, which medications to take or avoid, and how to prepare the surgical site.
Psychosocial Support: Preoperative care also addresses the emotional and psychological well-being of the patient. Anxiety and stress related to surgery are addressed through counseling, relaxation techniques, and support from the healthcare team 5.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care refers to the care provided to patients after they have undergone a surgical procedure. The goal of postoperative care is to ensure the patient’s recovery, manage any potential complications, and promote overall well-being. The specific postoperative care plan may vary depending on the type of surgery, the patient’s medical condition, and the healthcare facility’s protocols. Here are some key aspects of postoperative care:
Monitoring Vital Signs: After surgery, patients are closely monitored for vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature. Monitoring helps identify any signs of complications or changes in the patient’s condition.
Pain Management: Effective pain management is an essential component of postoperative care. Depending on the type and extent of the surgery, pain medication may be administered to help manage discomfort. Non-pharmacological pain management techniques such as ice packs, elevation of limbs, and relaxation techniques may also be employed.
Wound Care: Proper care of surgical incisions or wounds is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. This may involve cleaning and dressing the wound, as well as monitoring for any signs of infection or complications.
Mobility and Ambulation: Getting the patient up and moving as soon as possible after surgery is important to prevent complications such as blood clots and to promote healing. Healthcare professionals may assist the patient with early mobility exercises and encourage gradual increases in activity levels.
Fluid and Nutrition Management: Adequate hydration and nutrition are important for the healing process. Depending on the patient’s condition, oral intake may be gradually resumed, or intravenous fluids and nutrition may be provided.
Medication Management: Patients may be prescribed medications for pain management, infection prevention, and other specific needs. It is important for patients to follow medication instructions and inform healthcare providers of any adverse effects or concerns.
Patient Education and Discharge Planning: Patients and their caregivers are provided with detailed instructions for postoperative care at home. This includes information on wound care, medication management, activity restrictions, and signs of potential complications. Discharge planning may also involve arranging follow-up appointments and providing information on when to seek further medical assistance.
Psychosocial Support: Emotional and psychological support is important during the postoperative period. Patients may experience a range of emotions, including anxiety and depression. Healthcare providers may offer counseling, support groups, or referrals to mental health professionals as needed.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.