Description
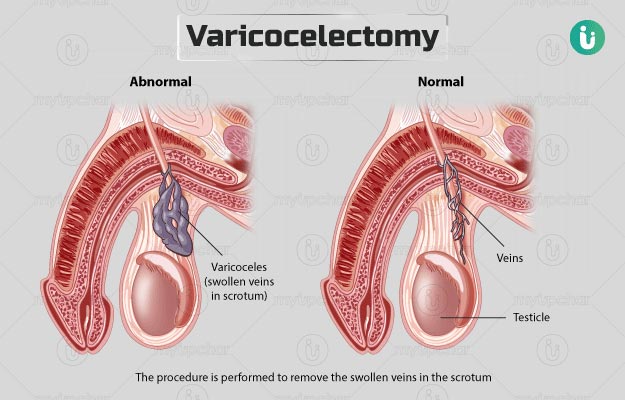
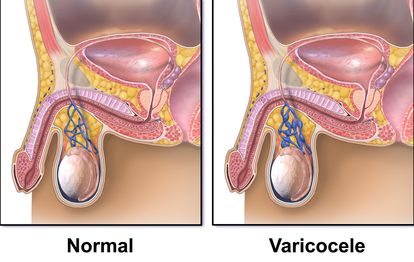
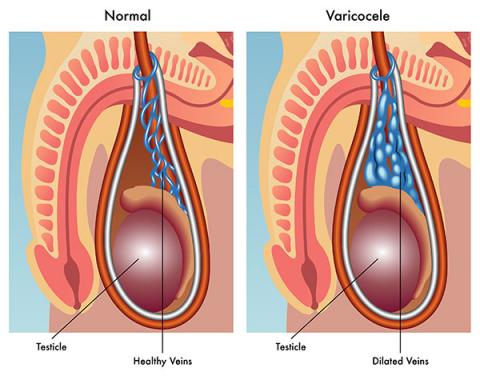
Varicocele surgery, also known as varicocelectomy, is a procedure to treat varicoceles, which are enlarged veins within the scrotum. These veins can cause pain, testicular atrophy, or infertility. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Types of Varicocele Surgery
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: This is an open surgery where the surgeon makes a small incision in the groin and uses a microscope to tie off the affected veins.
- Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: This minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to access and tie off the veins.
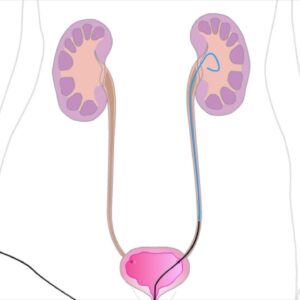
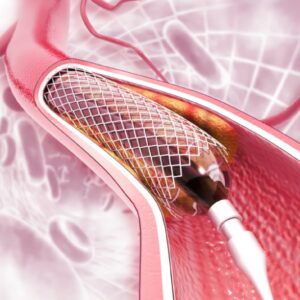
- Percutaneous Embolization: This is a non-surgical procedure where a catheter is inserted through a vein in the groin or neck, and materials are used to block the affected veins.
Familiarity with Treatment
Varicocelectomy is a common procedure, especially for treating male infertility and chronic testicular pain. It is generally safe and effective, with a high success rate in improving symptoms and fertility.
Procedure
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: The surgeon makes a small incision in the groin, identifies the affected veins using a microscope, and ties them off to redirect blood flow.
- Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: Small incisions are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope is used to locate and tie off the veins.
- Percutaneous Embolization: A catheter is inserted into a vein, and materials like coils or chemicals are used to block the varicocele.
Who is it Suitable For?
- Men experiencing chronic testicular pain due to varicoceles.
- Men with infertility issues linked to varicoceles.
- Adolescents with testicular atrophy or significant discomfort.
Who is it Not Suitable For?
- Men without symptoms or fertility issues, as varicoceles often do not cause problems.
- Those with other underlying health conditions that may complicate surgery.
Advantages
- Pain Relief: Reduces or eliminates testicular pain.
- Improved Fertility: Increases sperm count and quality, enhancing fertility.
- Minimally Invasive Options: Laparoscopic and percutaneous procedures offer quicker recovery times.
Complications
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection.
- Hydrocele Formation: Fluid accumulation around the testicle.
- Recurrence: Varicoceles can recur in some cases.
- Injury to Testicular Artery: Rare but possible, leading to testicular damage.
Previous Care
- Consultation: Detailed discussion with a urologist to determine the best treatment option.
- Preoperative Tests: Blood tests, ultrasound, and semen analysis to assess the condition.
Aftercare
- Rest: Avoid strenuous activities for a few weeks.
- Pain Management: Use prescribed pain relievers and ice packs to reduce swelling.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups to monitor recovery and ensure no complications.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.