Description
Familiarity with treatment
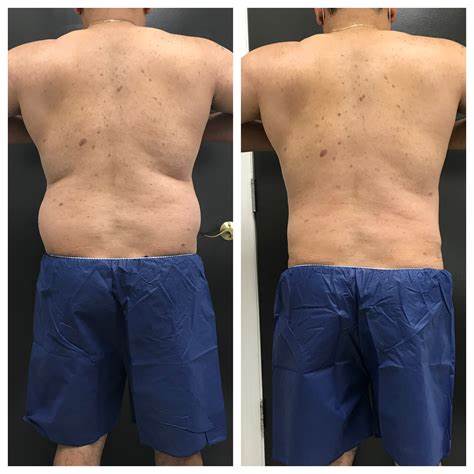
Water-Assisted Liposuction (WAL) is a specialized technique used in the treatment of conditions such as lipedema. It is considered to be a gentle approach to fat removal compared to traditional liposuction techniques. Here is an explanation of the WAL procedure based on the information from the search results:
Tumescent Fluid Injection: During the WAL procedure, a tumescent fluid solution is injected into the treatment area. This solution typically consists of saline (sterile saltwater), medication, and a local anesthetic. The tumescent fluid helps numb the area, reduce bleeding, and facilitate the dislodging of fat cells.
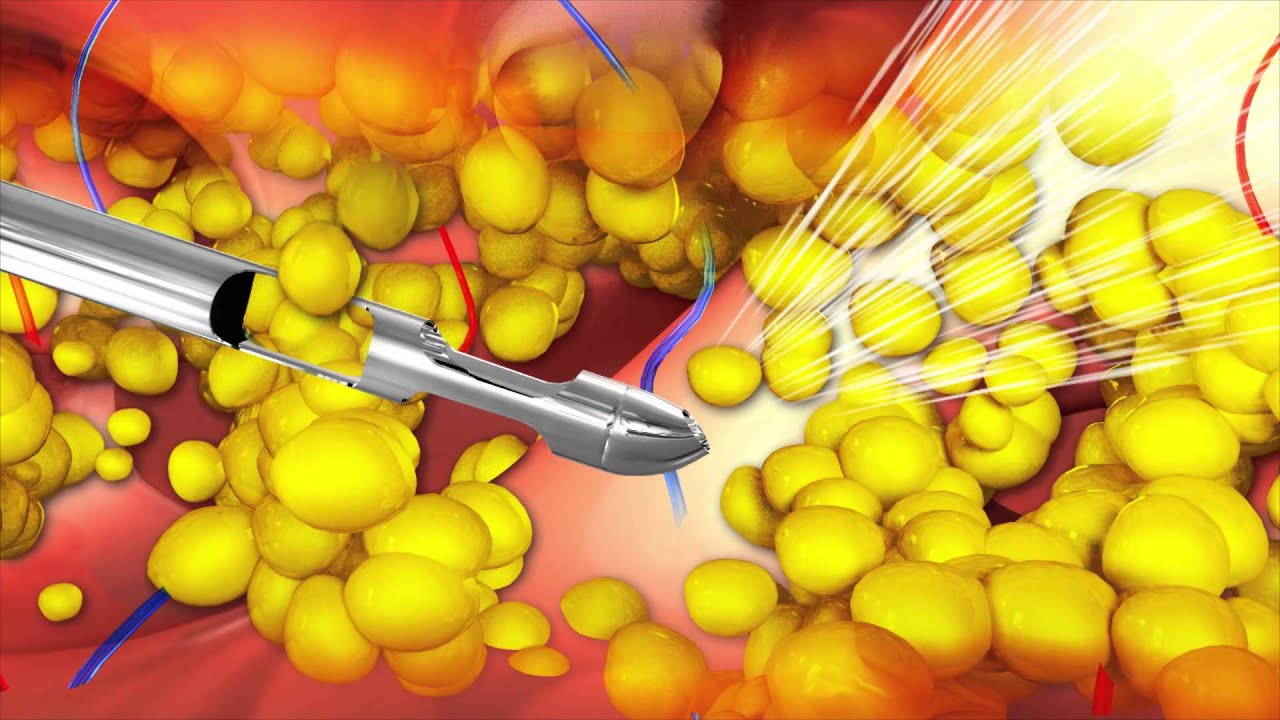
Water-Jet Dislodgement: Unlike traditional liposuction techniques that use a cannula and suction, WAL utilizes a pressure spray of tumescent fluid to dislodge the fat cells from the connective tissue. A fan-shaped water-jet is used to gently detach the fat cells from the surrounding tissue structure.
Simultaneous Aspiration: As the fat cells are dislodged by the water-jet, they are simultaneously aspirated or suctioned out. The gentle water pressure dislodges the fat cells, reducing trauma to the surrounding tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
Lymph Sparing: WAL is often used in the treatment of lipedema, a condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in certain areas of the body. It is considered a lymph-sparing liposuction technique, meaning it aims to preserve the lymphatic system while removing excess fat.
Potential for Fat Transfer: In some cases, the fat cells removed during WAL can be harvested and transferred to other areas of the body where additional fat is desired. This can be beneficial for restoring fullness and contour in specific regions.
Minimally Invasive and Gentle: The WAL procedure is considered minimally invasive and gentle. It is performed under local tumescent anesthesia, which helps minimize discomfort during the procedure. The use of water-jet dislodgement and simultaneous aspiration contributes to a potentially quicker recovery and reduced risk of side effects.
Who is it suitable for?
Water-Assisted Liposuction (WAL) is suitable for individuals who are considering liposuction as an option to address specific areas of excess fat, particularly those with lipedema. Here is an overview of the suitability of WAL based on the information from the search results:
Lipedema Patients: WAL is commonly used in the treatment of lipedema, a condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in certain areas of the body. It is considered a suitable option for lipedema patients who experience pain and discomfort due to the condition. WAL is a lymph-sparing liposuction technique that can help reduce lipedema pain and stop its progression.
Good Physical Shape: Like other liposuction techniques, WAL is optimal for individuals who are in reasonably good physical shape and wish to address specific parts of their body. It is important to note that liposuction, including WAL, is not a weight loss measure but a body contouring modality.
Desire for Gentle Fat Removal: WAL is known for its gentle approach to fat removal compared to traditional liposuction techniques. It uses a pressure spray of tumescent fluid to dislodge fat cells from the connective tissue, rather than utilizing a cannula and suction. This can result in potentially less trauma to the surrounding tissues, nerves, and blood vessels.
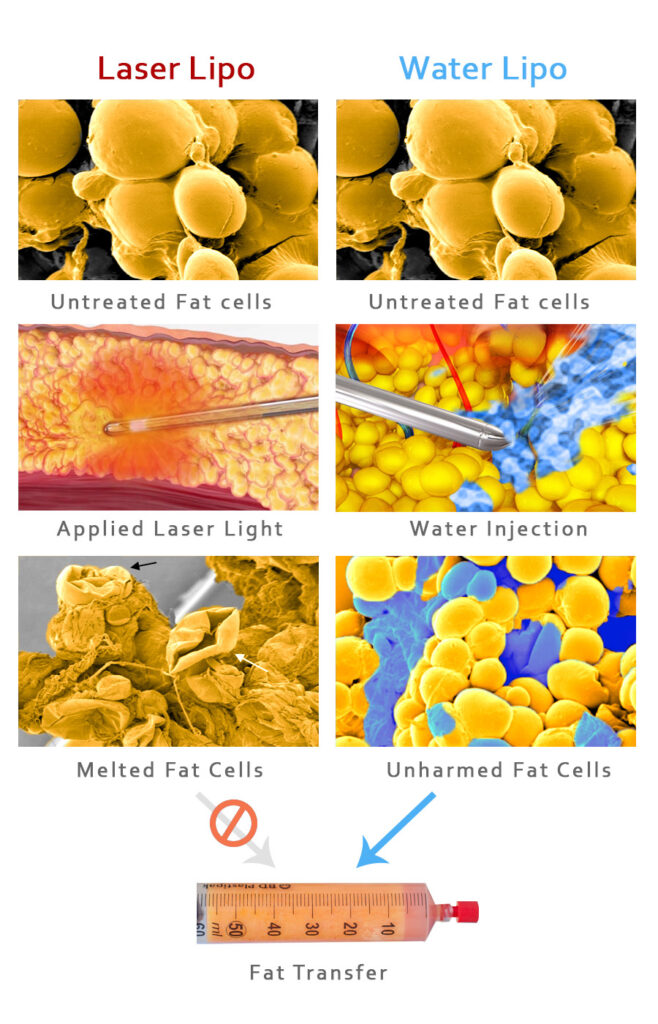
Potential for Fat Transfer: In some cases, the fat cells removed during WAL can be harvested and transferred to other areas of the body where additional fat is desired. This can be beneficial for restoring fullness and contour in specific regions.
Who is it not suitable for?
Based on the information from the search results, there are certain factors that may make Water-Assisted Liposuction (WAL) less suitable for some individuals. Here are some considerations:
Unhealthy or Unstable Weight: WAL may not be recommended for individuals who are at an unhealthy or unstable weight. It is important to have a stable weight and be in reasonably good physical shape before considering any liposuction procedure.
Certain Medical Conditions: There may be specific medical conditions that could make WAL less suitable. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if any underlying health conditions may affect the suitability of WAL.
Realistic Expectations: Like any cosmetic procedure, it is important to have realistic expectations about the outcomes of WAL. It is not a weight loss measure but a body contouring modality. Understanding the limitations and potential results of the procedure is crucial.
Individual Assessment: The suitability of WAL can vary depending on individual factors. It is important to consult with a qualified and experienced surgeon who can evaluate your specific circumstances and provide personalized advice based on your needs and goals.
Advantages
Water-Assisted Liposuction (WAL) offers several advantages compared to traditional liposuction techniques. Here are some of the advantages mentioned in the search results:
Gentle Approach: WAL is considered to be a gentle approach to fat removal. It causes less injury to the connective tissue compared to traditional liposuction techniques 1. The use of a pressure spray of tumescent fluid to dislodge fat cells from the connective tissue, instead of a cannula and suction, contributes to its gentle nature 1.
Lymph Sparing: WAL is often used in the treatment of lipedema, a condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in certain areas of the body. It is considered a lymph-sparing liposuction technique, meaning it aims to preserve the lymphatic system while removing excess fat 2. Research suggests that WAL can yield good long-term results in reducing lipedema pain and stopping its progression.
Reduced Trauma: The use of water pressure in WAL results in less trauma to the surrounding connective tissue, nerves, and blood vessels compared to traditional liposuction techniques 1. This can potentially lead to a faster recovery and reduced risk of side effects.
Potential for Fat Transfer: In some cases, the fat cells removed during WAL can be harvested and transferred to other areas of the body where additional fat is desired. This can be beneficial for restoring fullness and contour in specific regions 3.
Effectiveness: WAL is considered an effective technique for fat removal and body contouring It has been shown to be effective in treating lipedema, a condition that causes fluid buildup in the lower body.
Complications
Water-Assisted Liposuction (WAL) offers several advantages, but it’s important to be aware of potential complications as well. Here are some points to consider based on the information from the search results:
Complications: While WAL is generally considered a safe procedure, like any surgical intervention, it carries some risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, bruising, swelling, numbness, asymmetry, contour irregularities, fluid accumulation, skin irregularities, and changes in sensation. It’s important to discuss these potential complications with a qualified healthcare professional before undergoing the procedure.
Individual Factors: The risk of complications can vary depending on individual factors such as overall health, medical history, and the specific technique used. It’s crucial to have a thorough evaluation by a qualified surgeon who can assess your suitability for the procedure and discuss the potential risks and benefits based on your individual circumstances.
Surgeon’s Experience: The experience and skill of the surgeon performing the WAL procedure can significantly impact the outcome and the risk of complications. It’s important to choose a board-certified plastic surgeon or a surgeon with expertise in liposuction techniques who has a proven track record of successful outcomes.
Realistic Expectations: It’s essential to have realistic expectations about the results of WAL. While it can effectively remove excess fat and improve body contour, it is not a weight loss method. Understanding the limitations and potential outcomes of the procedure is crucial to avoid disappointment.
Post-Operative Care: Following proper post-operative care instructions is essential to minimize the risk of complications and promote optimal healing. This may include wearing compression garments, taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous activities, and attending follow-up appointments with your surgeon.
preoperative care
Preoperative care is an essential part of preparing a patient for surgery and ensuring their safety and well-being throughout the process. While the specific preoperative care may vary depending on the type of surgery and individual patient needs, here are some general aspects of preoperative care mentioned in the search results:
Medical Assessment: Before surgery, a healthcare provider will assess the patient’s overall health and fitness for the procedure. This assessment may include a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specific tests or evaluations as needed 1.
Patient Education: Preoperative care involves providing patients with information about their surgery, including what to expect before, during, and after the procedure. This education may cover topics such as preoperative fasting, medication instructions, postoperative pain management, and potential risks and complications 2.
Preoperative Testing: Depending on the type of surgery and patient’s medical condition, various preoperative tests may be conducted. These tests can include blood work, imaging studies, electrocardiogram (ECG), and other specific evaluations to ensure the patient is in the best possible condition for surgery 3.
Preparation for Anesthesia: If the surgery requires anesthesia, preoperative care involves assessing the patient’s suitability for anesthesia and preparing them accordingly. This may involve reviewing the patient’s medical history, discussing anesthesia options, and providing instructions for pre-anesthetic fasting.
Consent and Documentation: Preoperative care includes obtaining informed consent from the patient or their legal guardian. The consent process involves explaining the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternatives to the patient, and ensuring they have a clear understanding before signing the consent form. Proper documentation of the consent and other preoperative assessments is also important 2.
Preoperative Instructions: Patients are typically given specific instructions to follow before surgery. These instructions may include guidelines for fasting, medication management, hygiene practices (such as showering with antiseptic soap), and restrictions on eating or drinking before the procedure.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care refers to the care and support provided to a patient after a surgical procedure. The specific postoperative care required can vary depending on the type of surgery, the patient’s individual needs, and the surgeon’s recommendations. Here are some general aspects of postoperative care mentioned in the search results:
Monitoring: After surgery, patients are typically monitored closely in a recovery area or hospital setting. This monitoring may include vital sign checks, pain assessment, wound assessment, and observation for any signs of complications.
Pain Management: Managing postoperative pain is an important aspect of postoperative care. This may involve administering pain medications as prescribed by the healthcare provider, using non-pharmacological pain relief techniques, and ensuring patients are comfortable.
Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential for optimal healing and to minimize the risk of infection. This may include cleaning and dressing the wound as instructed by the surgeon, monitoring for signs of infection, and following any specific wound care instructions provided.
Activity and Mobility: Depending on the surgery, patients may need to follow specific guidelines regarding activity and mobility. This may involve restrictions on certain activities, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise, and gradually increasing activity levels as recommended by the surgeon.
Medication Management: Patients may be prescribed medications to take during the postoperative period. It’s important to follow the prescribed medication regimen, including dosage, frequency, and any specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider.
Nutrition and Hydration: Proper nutrition and hydration are important for the healing process. Patients may receive specific dietary instructions from the healthcare provider, including recommendations for adequate fluid intake and a balanced diet to support recovery.
Follow-up Appointments: Postoperative care often includes scheduling follow-up appointments with the surgeon or healthcare provider. These appointments allow for monitoring of the healing process, removal of any sutures or dressings, and addressing any concerns or questions that may arise.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.