Description
Familiarity with treatment
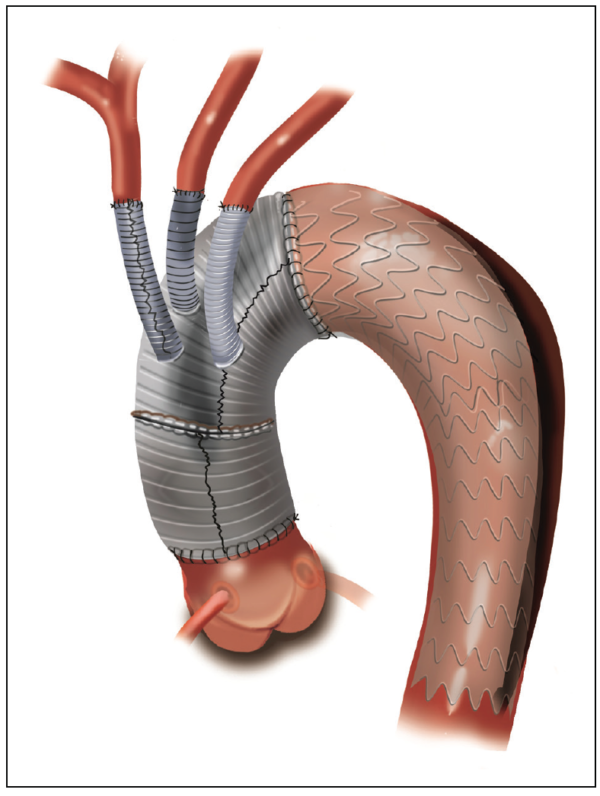
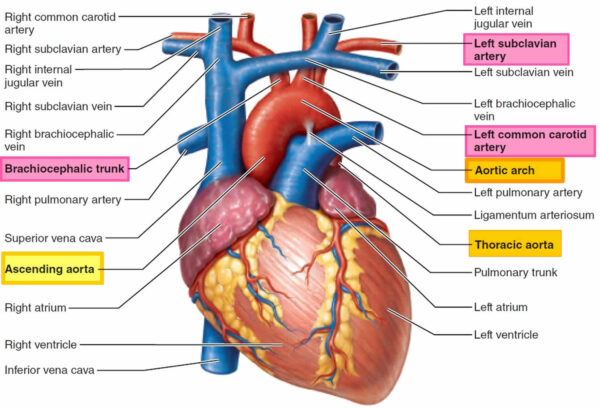
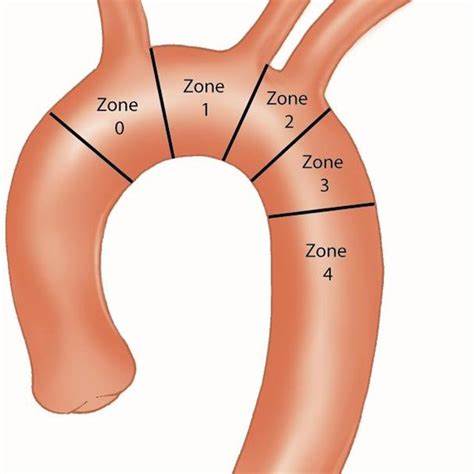
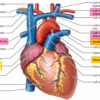
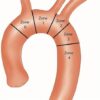
Aortic arch surgery is a complex procedure involving the repair or replacement of the curved portion of the aorta that extends upward from the heart. It is typically performed to address conditions such as aortic aneurysms, aortic dissections, or other abnormalities affecting the aortic arch.
Surgical Techniques
- Open Surgical Techniques: These can include procedures such as hemiarch or total arch replacement, where the damaged section of the aortic arch is replaced with a synthetic graft. Arch debranching and stent grafting is another technique that involves rerouting blood flow to vital arteries branching off from the aortic arch using bypass grafts, followed by the insertion of a stent graft to reinforce the damaged area.
- Endovascular Techniques: Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a stent graft through small incisions in the groin and guiding it to the site of the aortic arch using imaging technology.
- Hybrid Procedures: These combine elements of both open surgical and endovascular techniques. For example, a surgeon may perform debranching of the arch vessels using traditional open surgery, followed by the insertion of a stent graft via an endovascular approach to repair the aortic arch.
Who is it suitable for?
Aortic arch surgery is suitable for individuals who have certain conditions affecting the aortic arch, such as:
- Aortic Aneurysms: When the aortic arch becomes abnormally widened or bulges, it can lead to the formation of an aneurysm. Aneurysms can pose a risk of rupture, making surgical intervention necessary.
- Aortic Dissections: Aortic dissections occur when there is a tear in the inner layer of the aortic wall, leading to the abnormal separation of the layers of the aorta. Surgery may be required to repair the dissection and prevent further complications.
- Other Aortic Abnormalities: Various congenital or acquired conditions, such as aortic arch abnormalities or connective tissue disorders, may necessitate aortic arch surgery to address the underlying issues and prevent potential complications.
Who is it not suitable for?
Aortic arch surgery may not be suitable for individuals who are at high risk due to certain factors. These may include:
- Severe Underlying Health Conditions: Patients with severe underlying health issues, such as advanced heart or lung disease, may not be suitable candidates for aortic arch surgery due to the increased risks associated with the procedure.
- Advanced Age: Age can be a factor in determining the suitability for aortic arch surgery. In some cases, older individuals with additional health concerns may not be considered ideal candidates for the procedure.
- Unmanageable Surgical Risks: Individuals with a combination of factors that significantly increase the risks associated with surgery, such as extensive previous surgeries, uncontrolled coagulopathies, or severe frailty, may not be suitable for aortic arch surgery.
- Patient Preference: In some cases, a patient’s personal preferences and values may lead them to opt for non-surgical treatment options, especially if the potential benefits of surgery are outweighed by the risks in their specific situation.
Advantages
Aortic arch surgery offers several potential advantages for individuals with certain aortic conditions. Some of these advantages include:
- Prevention of Rupture: Aortic arch surgery can prevent the rupture of an aortic aneurysm, which is a life-threatening emergency. By repairing or replacing the weakened or bulging section of the aorta, the risk of rupture is significantly reduced.
- Treatment of Aortic Dissections: Surgery can effectively repair aortic dissections, which involve a tear in the aortic wall. By addressing the dissection, the surgery can help restore the integrity of the aortic wall and prevent further complications.
- Improved Blood Flow: In cases where the aortic arch is narrowed or obstructed due to aortic abnormalities, surgery can restore proper blood flow, reducing the risk of complications related to inadequate blood supply to vital organs.
- Prevention of Complications: Aortic arch surgery can prevent potential complications associated with aortic abnormalities, such as strokes or other cardiovascular events, by addressing the underlying structural issues in the aorta.
- Improved Long-Term Outcomes: For individuals with certain aortic conditions, surgery can lead to improved long-term outcomes and quality of life, especially when compared to the risks associated with leaving the condition untreated.
Complications
Aortic arch surgery, like any major surgical procedure, carries potential risks and complications. Some of the complications associated with aortic arch surgery may include:
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery can occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.
- Infection: Surgical site infections or systemic infections can occur following aortic arch surgery, requiring prompt treatment with antibiotics.
- Neurological Complications: There is a risk of neurological complications, such as stroke or transient ischemic attacks, which can occur due to emboli dislodging during the procedure or during the post-operative period.
- Respiratory Issues: Complications such as pneumonia or atelectasis (partial lung collapse) can arise due to the effects of anesthesia, the surgical procedure, or post-operative immobility.
- Cardiac Complications: Post-operative cardiac issues, such as arrhythmias or myocardial infarction, can occur, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
- Reperfusion Injury: During surgery, there is a risk of reperfusion injury when blood flow is restored to tissues that have been deprived of oxygen, potentially leading to tissue damage.
- Graft Complications: Complications related to the synthetic graft used in the surgical repair, such as graft infection, graft thrombosis, or graft-related structural issues, can occur.
- Long-Term Complications: Some individuals may experience long-term complications related to aortic arch surgery, such as aneurysm formation at the surgical site or issues with the repaired or replaced aortic arch segment.
Previous care
Before undergoing aortic arch surgery, there are several important aspects of care and preparation that should be addressed:
Pre-Surgical Evaluation
-
- Medical Assessment: A comprehensive medical evaluation is conducted to assess the patient’s overall health, including cardiac and pulmonary function, to determine their fitness for surgery.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging tests, such as CT scans, MRIs, or angiograms, are performed to precisely visualize the aortic arch and assess the nature and extent of the condition requiring surgery.
- Medication Review: A review of the patient’s current medications is conducted to identify any that may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued before surgery.
Patient Preparation
-
- Informed Consent: The patient is provided with detailed information about the surgical procedure, including the potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatment options, and is required to provide informed consent for the surgery.
- Pre-Operative Instructions: Patients are given specific instructions regarding dietary restrictions, medication adjustments, and pre-surgical preparations, such as fasting before the procedure.
- Education and Support: Patients and their families are provided with education and support to address any concerns or questions they may have about the surgery, post-operative care, and recovery.
Surgical Planning
-
- Multidisciplinary Team Consultation: A team of specialists, including cardiovascular surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other healthcare professionals, collaborates to plan the surgical approach and post-operative care.
- Blood Management: Strategies for blood conservation and transfusion management, if needed, are discussed with the patient, particularly if they have specific blood-related concerns or conditions.
- Post-Operative Care Planning: Plans for post-operative care, including monitoring, pain management, and rehabilitation, are established to ensure a smooth transition to the recovery phase.
Emotional and Psychological Support
-
- Psychosocial Assessment: The patient’s emotional and psychological well-being is assessed, and appropriate support is provided to address any concerns or anxieties related to the surgery.
- Family Involvement: Involving the patient’s family or support system in the pre-surgical process can provide additional emotional support and help with post-operative care arrangements.
Aftercare
After undergoing aortic arch surgery, comprehensive aftercare is essential to promote healing and minimize the risk of complications. The specific aftercare plan may vary based on the individual’s condition and the type of surgery performed, but some general aspects of aftercare commonly include:
Hospital Stay
-
- Monitoring: Close monitoring of vital signs, cardiac function, and neurological status in the intensive care unit (ICU) immediately after surgery.
- Pain Management: Adequate pain management to ensure comfort while promoting early mobility and recovery.
- Prevention of Complications: Measures to prevent post-operative complications, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), respiratory issues, and infection, through appropriate medications and interventions.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
-
- Physical Therapy: Gradual introduction of physical therapy to aid in mobility, strength, and endurance, as well as to prevent muscle atrophy and promote overall recovery.
- Activity Gradation: Structured programs to gradually increase activity levels, in coordination with the healthcare team, to facilitate a safe and effective recovery.
- Wound Care: Monitoring and care of surgical incisions to prevent infection and promote proper healing.
Medication Management
-
- Anticoagulation Therapy: Management of anticoagulation medications to prevent blood clots and ensure the patency of any grafts or stents used during surgery.
- Pain Control: Continued management of pain through medications and other modalities as needed during the recovery period.
- Other Medications: Administration of medications to manage specific conditions or to support the healing process.
Follow-Up Care
-
- Medical Visits: Scheduled follow-up appointments with the surgical team and other healthcare providers to monitor recovery progress and address any post-operative concerns.
- Imaging Studies: Periodic imaging studies, such as CT scans or MRIs, to assess the integrity of the surgical repair and the condition of the aortic arch.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Guidance on lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, to promote cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Emotional Support
-
- Psychological Care: Access to emotional and psychological support resources to address any anxiety or emotional challenges related to the surgery and recovery process.
- Family Education: Education and support for the patient’s family or caregivers to assist in the recovery process and address any related concerns.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.