From: 100.00$
The Iran Health Clinic is a reputable medical center that specializes in providing advanced fat transfer treatment to its patients. With a team of experienced doctors who have been trained in the latest fat transfer techniques, the clinic is committed to delivering high-quality care that is tailored to meet the unique needs of each patient.
Using state-of-the-art technology and equipment, the clinic can perform fat transfer procedures that are safe, effective, and minimally invasive. Whether you are looking to restore volume to your face, increase the size of your breasts, or enhance your buttocks, the Iran Health Clinic can help you achieve your desired results.
With a warm and welcoming environment, the clinic strives to make every patient feel comfortable and relaxed throughout their entire treatment process. If you are looking for a trusted medical center for your fat transfer needs, then the Iran Health Clinic is the right choice for you.
Familiarity with Treatment:
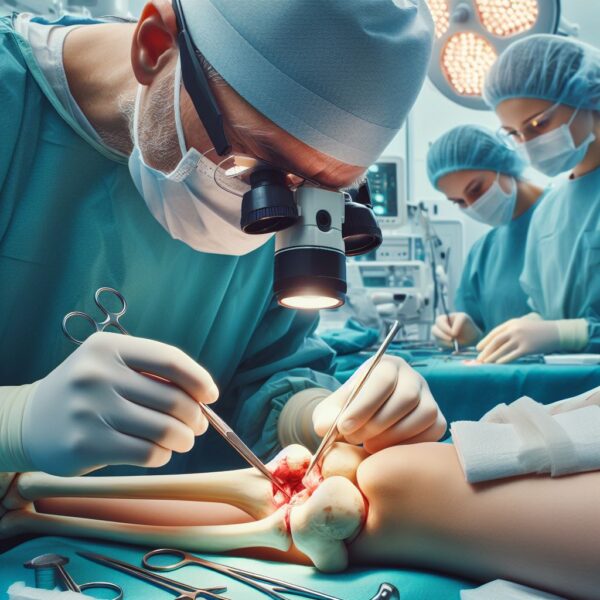
Orthopedic bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves the transplantation of bone tissue from a donor site to a recipient site to promote bone healing, fill bone defects, or enhance bone fusion. This procedure is commonly used in orthopedic surgery, spine surgery, and dental procedures.
Procedure:
There are three main types of bone grafts:
1. Autograft: Bone is harvested from the patient’s own body, usually from the hip or tibia. This is considered the gold standard due to its excellent success rate but may have donor site morbidity.
2. Allograft: Bone is obtained from a human donor, processed, and sterilized. It is then stored in a tissue bank for future use. This option avoids donor site morbidity but may have a slightly lower success rate.
3. Xenograft: Bone is derived from another species, usually a cow or a pig. This option has a lower success rate but is less expensive and avoids the need for a second surgical site.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthopedic bone grafting is suitable for patients who require bone grafting for various reasons, such as:
1. Fracture nonunion: When a bone fails to heal after a fracture, bone grafting may be necessary to promote healing.
2. Bone defects: Bone grafting can fill bone defects caused by tumor removal, infection, or congenital abnormalities.
3. Spinal fusion: Bone grafting can be used to fuse vertebrae in the spine for conditions like degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis.
4. Dental procedures: Bone grafting can help rebuild jawbone structure for dental implants in cases of periodontal disease or tooth loss.
Who is it not suitable for?
Bone grafting may not be suitable for patients with active infections, severe medical conditions, or those who cannot tolerate surgery. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if bone grafting is appropriate for your specific situation.
Advantages:
1. Promotes bone healing and fusion
2. Helps fill bone defects and correct deformities
3. Enhances the success rate of spinal fusion and dental implant procedures
4. Can be used as an alternative to metal implants
Complications:
Like any surgical procedure, bone grafting carries potential risks and complications, including:
1. Infection
2. Bleeding
3. Blood clots
4. Nerve damage
5. Donor site pain or complications
6. Graft failure or resorption
7. Limited mobility or stiffness
Preoperative Care:
Before the surgery, your healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and necessary imaging studies. They may also adjust your current medications or ask you to stop taking certain ones temporarily. It is essential to follow any specific preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare team, such as fasting guidelines and avoiding certain medications or substances.
Postoperative Care:
After the surgery, you will be closely monitored in a hospital or surgical facility. You may experience pain, swelling, and discomfort, for which your healthcare team will provide appropriate pain management. Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be necessary to regain mobility and function
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.




Familiarity with Treatment:
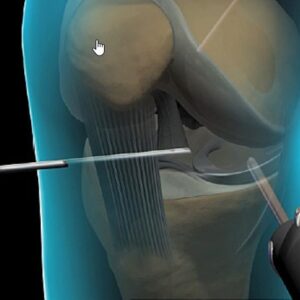
Orthopedic bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves the transplantation of bone tissue from a donor site to a recipient site to promote bone healing, fill bone defects, or enhance bone fusion. This procedure is commonly used in orthopedic surgery, spine surgery, and dental procedures.
Procedure:
There are three main types of bone grafts:
1. Autograft: Bone is harvested from the patient’s own body, usually from the hip or tibia. This is considered the gold standard due to its excellent success rate but may have donor site morbidity.
2. Allograft: Bone is obtained from a human donor, processed, and sterilized. It is then stored in a tissue bank for future use. This option avoids donor site morbidity but may have a slightly lower success rate.
3. Xenograft: Bone is derived from another species, usually a cow or a pig. This option has a lower success rate but is less expensive and avoids the need for a second surgical site.
Who is it suitable for?
Orthopedic bone grafting is suitable for patients who require bone grafting for various reasons, such as:
1. Fracture nonunion: When a bone fails to heal after a fracture, bone grafting may be necessary to promote healing.
2. Bone defects: Bone grafting can fill bone defects caused by tumor removal, infection, or congenital abnormalities.
3. Spinal fusion: Bone grafting can be used to fuse vertebrae in the spine for conditions like degenerative disc disease or spondylolisthesis.
4. Dental procedures: Bone grafting can help rebuild jawbone structure for dental implants in cases of periodontal disease or tooth loss.
Who is it not suitable for?
Bone grafting may not be suitable for patients with active infections, severe medical conditions, or those who cannot tolerate surgery. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if bone grafting is appropriate for your specific situation.
Advantages:
1. Promotes bone healing and fusion
2. Helps fill bone defects and correct deformities
3. Enhances the success rate of spinal fusion and dental implant procedures
4. Can be used as an alternative to metal implants
Complications:
Like any surgical procedure, bone grafting carries potential risks and complications, including:
1. Infection
2. Bleeding
3. Blood clots
4. Nerve damage
5. Donor site pain or complications
6. Graft failure or resorption
7. Limited mobility or stiffness
Preoperative Care:
Before the surgery, your healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history review, and necessary imaging studies. They may also adjust your current medications or ask you to stop taking certain ones temporarily. It is essential to follow any specific preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare team, such as fasting guidelines and avoiding certain medications or substances.
Postoperative Care:
After the surgery, you will be closely monitored in a hospital or surgical facility. You may experience pain, swelling, and discomfort, for which your healthcare team will provide appropriate pain management. Physical therapy and rehabilitation may be necessary to regain mobility and function
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment. The preferred choice for many patients is choosing private care.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.