Description
Familiarity with treatment
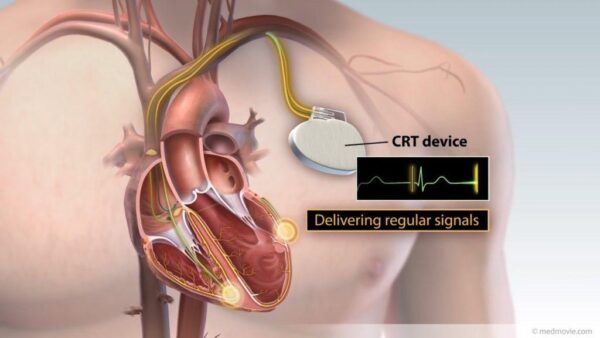
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a treatment option for individuals with heart failure who have a specific type of electrical conduction abnormality known as left bundle branch block (LBBB). CRT involves the implantation of a special type of pacemaker called a biventricular pacemaker or cardiac resynchronization therapy device.
Here are some key points about Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT):
- Purpose: The main goal of CRT is to improve the coordination and synchronization of the heart’s electrical signals, particularly in individuals with heart failure and LBBB. By synchronizing the contractions of the heart’s chambers, CRT can improve the heart’s pumping efficiency and overall cardiac function.
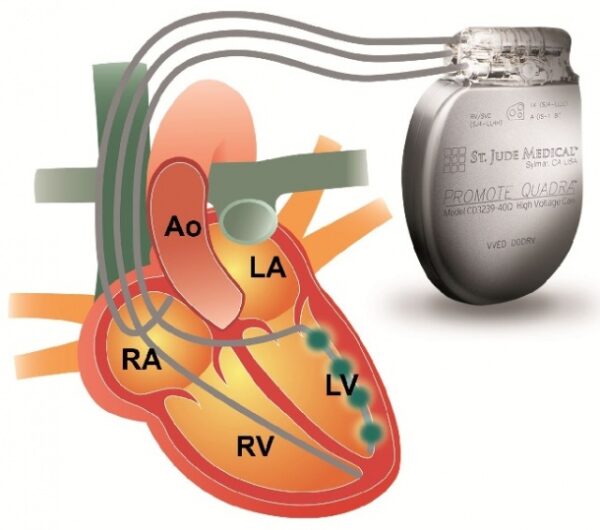
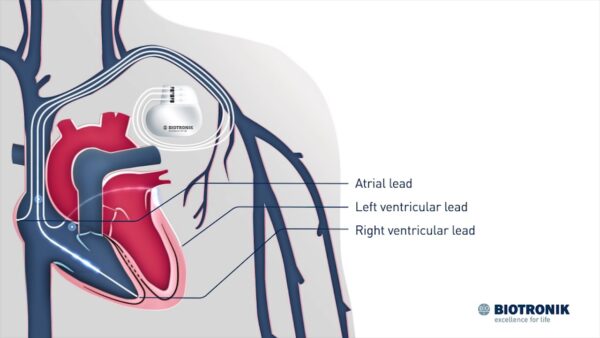
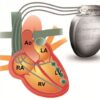
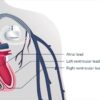
- Procedure: CRT involves the surgical implantation of a biventricular pacemaker. This pacemaker has three leads: one in the right atrium, one in the right ventricle, and one in the left ventricle. The leads deliver electrical impulses to the heart to coordinate the contractions of the ventricles.
- Indications: CRT is typically recommended for individuals with moderate to severe heart failure symptoms, despite optimal medical therapy. It is specifically indicated for individuals who have LBBB on their electrocardiogram (ECG) and a reduced ejection fraction (a measure of the heart’s pumping ability).
- Benefits: CRT can improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and exercise intolerance. It can also reduce hospitalizations and improve overall quality of life. In some cases, CRT may also improve the heart’s pumping ability and reverse certain heart remodeling changes.
- Evaluation: Before undergoing CRT, individuals will undergo a thorough evaluation to determine if they are suitable candidates. This may include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, echocardiogram, and other tests to assess heart function and electrical conduction.
- Implantation: CRT implantation is typically performed in a hospital setting under local anesthesia. The pacemaker leads are inserted through veins and positioned in the right atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The pacemaker generator is usually placed under the skin in the upper chest.
- Follow-up: After CRT implantation, regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the function of the pacemaker, adjust settings if needed, and assess the patient’s response to therapy. These appointments may include device checks, echocardiograms, and discussions about symptoms and quality of life.
- Potential Complications: Like any surgical procedure, CRT implantation carries some risks, including infection, bleeding, lead dislodgement, and complications related to anesthesia. It is important for individuals to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider.
Who is it suitable for?
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is suitable for individuals with heart failure who meet specific criteria. Here are some factors that determine suitability for CRT:
- Heart Failure Symptoms: CRT is typically recommended for individuals with moderate to severe heart failure symptoms, despite optimal medical therapy. These symptoms may include shortness of breath, fatigue, exercise intolerance, and fluid retention.
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB): CRT is specifically indicated for individuals who have a specific type of electrical conduction abnormality known as left bundle branch block (LBBB). LBBB is diagnosed through an electrocardiogram (ECG) and is characterized by a delay in the electrical signals that coordinate the contractions of the heart’s ventricles.
- Reduced Ejection Fraction: CRT is generally recommended for individuals with a reduced ejection fraction. Ejection fraction is a measure of the heart’s pumping ability and is expressed as a percentage. A reduced ejection fraction indicates that the heart is not pumping blood effectively.
- QRS Duration: The QRS duration on the ECG is an indicator of the electrical conduction delay. CRT is typically recommended for individuals with a prolonged QRS duration, usually greater than 150 milliseconds.
- Cardiac Evaluation: Before undergoing CRT, individuals will undergo a comprehensive cardiac evaluation to assess their overall heart function, electrical conduction, and suitability for the procedure. This may include a thorough medical history, physical examination, echocardiogram, and other tests.
Who is it not suitable for?
While Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) can be beneficial for many individuals with heart failure and left bundle branch block (LBBB), there are certain situations where it may not be suitable. Here are some factors that may make an individual not suitable for CRT:
- Absence of LBBB: CRT is specifically indicated for individuals with left bundle branch block (LBBB), as it aims to correct the electrical conduction delay associated with this condition. If an individual does not have LBBB, CRT may not be the appropriate treatment option.
- Normal Ejection Fraction: CRT is generally recommended for individuals with a reduced ejection fraction, which indicates impaired heart function. If an individual has a normal ejection fraction, CRT may not provide significant benefits.
- Inability to Tolerate the Procedure: Some individuals may have medical conditions or factors that make them unable to tolerate the surgical implantation of a biventricular pacemaker. This may include individuals with severe comorbidities, advanced age, or other factors that increase the risks associated with the procedure.
- Limited Life Expectancy: CRT is typically recommended for individuals with a reasonable life expectancy, as it aims to improve symptoms and quality of life over the long term. If an individual has a limited life expectancy due to advanced age, severe comorbidities, or other factors, the potential benefits of CRT may be outweighed by the risks and burdens of the procedure.
- Other Contraindications: There may be other specific contraindications or factors that make an individual not suitable for CRT. These can vary depending on the individual’s specific medical condition, overall health, and other factors. It is important for the healthcare provider to carefully evaluate each individual case to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Advantages
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) offers several advantages for individuals with heart failure and left bundle branch block (LBBB). Here are some of the key advantages of CRT:
- Improved Symptoms: CRT can significantly improve symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and exercise intolerance. By synchronizing the contractions of the heart’s chambers, CRT improves the heart’s pumping efficiency and overall cardiac function, leading to symptom relief and improved quality of life.
- Enhanced Exercise Capacity: CRT can improve exercise capacity and tolerance in individuals with heart failure. By optimizing the coordination of the heart’s contractions, CRT allows for more efficient blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body’s tissues during physical activity.
- Reduced Hospitalizations: CRT has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of heart failure exacerbations, leading to a decrease in hospitalizations. This can result in improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and a better overall quality of life.
- Reverse Remodeling: In some cases, CRT can lead to reverse remodeling of the heart. This means that the heart’s structure and function can improve over time with CRT, potentially leading to a partial recovery of the heart’s pumping ability.
- Prolonged Survival: CRT has been associated with improved long-term survival in certain individuals with heart failure. By optimizing cardiac function and reducing the risk of heart failure exacerbations, CRT can help prolong life expectancy in eligible patients.
- Combination with Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD): CRT can be combined with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) in individuals who are at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. This combination therapy, known as CRT-D, provides both resynchronization of the heart’s contractions and protection against dangerous heart rhythms.
- Personalized Therapy: CRT can be tailored to each individual’s specific needs. The pacemaker settings can be adjusted and optimized during follow-up visits to ensure the best possible response to therapy.
Complications
While Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) can be beneficial for individuals with heart failure and left bundle branch block (LBBB), like any medical procedure, it carries some potential risks and complications. Here are some of the possible complications associated with CRT:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the site of the pacemaker implantation. This can include superficial infections of the skin or deeper infections involving the pacemaker leads or the heart itself. Infections may require antibiotic treatment or, in severe cases, removal of the pacemaker system.
- Bleeding or Hematoma: During the implantation procedure, there is a risk of bleeding or the formation of a hematoma at the incision site. This can lead to swelling, pain, or, in rare cases, require additional intervention to control bleeding or drain the hematoma.
- Lead Dislodgement or Malposition: The leads that are placed in the heart during CRT can become dislodged or positioned incorrectly. This can affect the effectiveness of the therapy and may require repositioning or replacement of the leads.
- Pneumothorax: In rare cases, the insertion of the pacemaker leads can cause a pneumothorax, which is the accumulation of air in the space between the lung and the chest wall. This can cause difficulty breathing and may require treatment such as chest tube placement.
- Perforation of the Heart or Blood Vessels: During the implantation procedure, there is a small risk of perforation of the heart or blood vessels by the pacemaker leads. This can lead to bleeding, tamponade (compression of the heart by accumulated blood), or other complications that may require immediate intervention.
- Allergic Reaction: Some individuals may have an allergic reaction to the materials used in the pacemaker system, such as the metal components or the adhesive used to secure the leads. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin irritation to more severe systemic reactions.
- Device-related Complications: Over time, the pacemaker system may experience device-related complications, such as lead fracture, battery depletion, or malfunction. These complications may require additional procedures to replace or repair the pacemaker system.
Preoperative care
The preoperative care for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) involves specific considerations to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the procedure. Here are some key aspects of preoperative care for CRT:
- Evaluation and Assessment: The patient will undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their eligibility for CRT. This may include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, echocardiogram, and other tests to evaluate heart function, electrical conduction, and the presence of left bundle branch block (LBBB).
- Medication Review: The patient’s current medications will be reviewed to ensure they are optimized for the procedure. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before surgery, especially those that can interfere with the pacemaker implantation or anesthesia.
- Informed Consent: The patient will be provided with detailed information about the CRT procedure, its risks, benefits, and alternatives. Informed consent will be obtained, ensuring that the patient understands the procedure and gives their voluntary agreement to undergo it.
- Preoperative Testing: Additional tests may be ordered to further evaluate the patient’s heart function and assess their readiness for CRT. These tests may include blood tests, imaging studies, and electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess the electrical conduction system.
- Fasting: The patient will be instructed to fast for a certain period of time before the CRT procedure. This is to ensure that the stomach is empty, reducing the risk of aspiration during anesthesia.
- Preoperative Medications: The healthcare team may prescribe specific medications to be taken before the CRT procedure. These may include antibiotics to prevent infection or medications to manage heart failure symptoms and optimize the patient’s condition before the surgery.
- Arrangements for Transportation and Support: The patient will need to arrange for transportation to and from the surgical facility, as they may not be able to drive themselves after the procedure. They may also need to arrange for someone to accompany them and provide support during the preoperative and postoperative period.
- Lifestyle Modifications: The patient may be advised to make certain lifestyle modifications before CRT, such as quitting smoking, losing weight, or managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. These modifications can help optimize the patient’s health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Preoperative Counseling: The healthcare team will provide counseling and education to the patient about the CRT procedure, including what to expect during and after the surgery, potential risks and complications, and postoperative care instructions.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) involves monitoring the patient’s recovery, managing any potential complications, and providing support for optimal healing. Here are some key aspects of postoperative care for CRT:
- Monitoring Vital Signs: The patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, will be closely monitored in the immediate postoperative period. This helps ensure stability and detect any signs of complications.
- Pain Management: The healthcare team will assess and manage the patient’s pain levels to ensure their comfort. Pain medications may be prescribed or administered as needed.
- Wound Care: The incision site(s) will be monitored for signs of infection or complications. The healthcare team will provide instructions on how to care for the incision site, including keeping it clean and dry, changing dressings, and monitoring for any signs of infection.
- Activity and Mobility: The patient will be gradually encouraged to resume activity and mobility as tolerated. This may include sitting up, walking, and engaging in light activities. The healthcare team will provide guidance on the appropriate level of activity and any restrictions that need to be followed.
- Medication Management: The patient will be prescribed medications to manage heart failure symptoms, prevent infection, and support the healing process. It is important for the patient to take medications as prescribed and follow up with their healthcare provider for any necessary adjustments.
- Follow-up Appointments: The patient will have scheduled follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor their progress, assess the functioning of the CRT device, and make any necessary adjustments to the settings. These appointments are important for optimizing the benefits of CRT and addressing any concerns or complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: The patient may receive guidance on lifestyle modifications to support their heart health and overall well-being. This may include recommendations for diet, exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management.
- Education and Support: The healthcare team will provide education and support to the patient and their caregivers regarding the CRT device, its functioning, and any necessary precautions or lifestyle adjustments. This helps ensure that the patient understands how to manage their condition and optimize the benefits of CRT.
- Emotional Support: Undergoing a surgical procedure can be emotionally challenging. The healthcare team may provide resources or referrals for emotional support, such as counseling or support groups, to help the patient and their caregivers cope with any emotional or psychological aspects of the recovery process.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.