Description
Familiarity with treatment
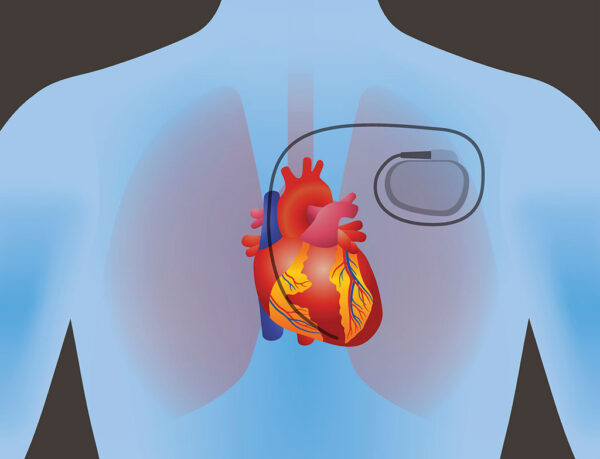
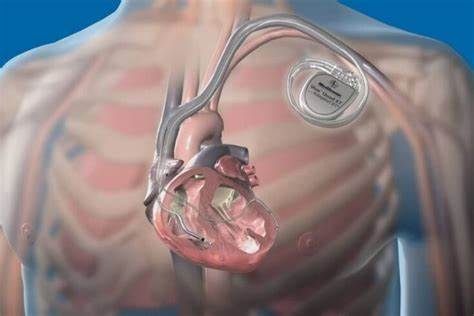
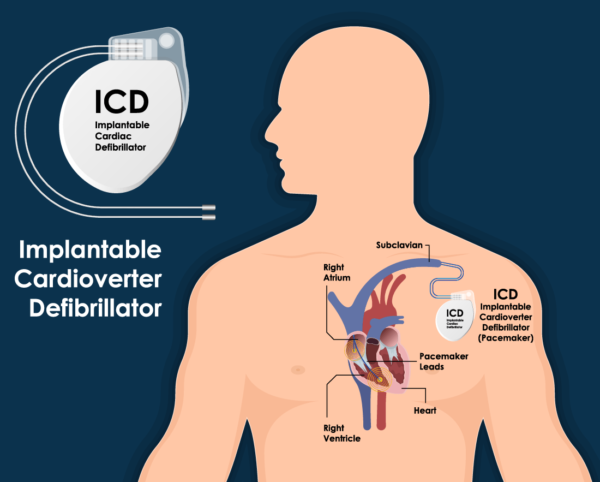
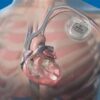
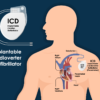
An ICD is a small device that is implanted under the skin to monitor and treat abnormal heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias. It continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity and delivers electrical shocks or pacing to restore normal heart rhythm when needed.
ICD placement is typically performed during a surgical procedure called implantation. The procedure involves making a small incision in the chest, usually below the collarbone, and creating a pocket under the skin to hold the device. The leads, which are thin wires, are then threaded through blood vessels and positioned in the heart. These leads detect abnormal heart rhythms and deliver electrical shocks or pacing as necessary.
ICD placement is commonly recommended for individuals who are at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, such as those with a history of cardiac arrest, ventricular fibrillation, or certain types of heart disease. It is an effective treatment option for preventing sudden cardiac death in these patients.
During the surgery, the patient is usually under general anesthesia, and the procedure typically takes a few hours. After the ICD is implanted, the incision is closed, and the patient is monitored for a short period before being discharged. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the device and to make any necessary adjustments.
Who is it suitable for?
ICD placement is suitable for individuals who are at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. It is typically recommended for the following groups of people:
- Individuals with a history of cardiac arrest: If someone has experienced a sudden loss of heart function, known as cardiac arrest, due to a life-threatening arrhythmia, they are at high risk of recurrence. ICD placement can help prevent future episodes of cardiac arrest by delivering electrical shocks or pacing to restore normal heart rhythm.
- Individuals with ventricular fibrillation: Ventricular fibrillation is a type of arrhythmia characterized by rapid and chaotic electrical activity in the heart’s lower chambers (ventricles). It can lead to a sudden loss of consciousness and can be life-threatening. ICD placement is often recommended for individuals who have experienced ventricular fibrillation or are at high risk of developing it.
- Individuals with certain types of heart disease: Certain heart conditions, such as dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and certain types of inherited heart conditions, can increase the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. ICD placement may be recommended for individuals with these conditions to prevent sudden cardiac death.
- Individuals with a high risk score: Cardiac electrophysiologists use various risk scoring systems to assess an individual’s risk of developing life-threatening arrhythmias. If someone has a high risk score based on their medical history, symptoms, and test results, ICD placement may be recommended as a preventive measure.
Who is it not suitable for?
ICD placement may not be suitable for certain individuals. The decision to undergo ICD placement is made on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration the individual’s specific medical condition, overall health, and potential risks and benefits. Here are some situations where ICD placement may not be recommended:
- Individuals with a short life expectancy: If someone has a limited life expectancy due to advanced age, terminal illness, or other medical conditions, the potential benefits of ICD placement may be outweighed by the risks and burdens associated with the procedure. In such cases, the focus may be on palliative care and improving quality of life rather than aggressive arrhythmia management.
- Individuals with reversible causes of arrhythmias: If an individual’s arrhythmias are caused by a reversible condition, such as an electrolyte imbalance, medication side effects, or a temporary illness, ICD placement may not be necessary. Treating the underlying cause of the arrhythmias can often resolve the issue without the need for an ICD.
- Individuals with significant comorbidities: If someone has significant comorbidities, such as advanced heart failure, severe lung disease, or kidney failure, the risks associated with ICD placement and subsequent follow-up care may outweigh the potential benefits. In such cases, the focus may be on managing the underlying conditions rather than implanting an ICD.
- Individuals with a low risk of life-threatening arrhythmias: If someone has a low risk of developing life-threatening arrhythmias based on their medical history, symptoms, and test results, the potential benefits of ICD placement may not outweigh the risks. In these cases, alternative treatment options or close monitoring without an ICD may be more appropriate.
Advantages
ICD placement offers several advantages for individuals at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Prevention of sudden cardiac death: The primary advantage of ICD placement is its ability to prevent sudden cardiac death. The device continuously monitors the heart’s electrical activity and delivers electrical shocks or pacing when it detects abnormal heart rhythms. This intervention can quickly restore normal heart rhythm and prevent a potentially fatal outcome.
- Improved survival rates: Studies have shown that ICD placement significantly improves survival rates in individuals at high risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. The device’s ability to deliver timely and effective therapy, such as electrical shocks or pacing, can increase the chances of survival during a cardiac event.
- Increased quality of life: For individuals with a history of recurrent arrhythmias or those living in constant fear of sudden cardiac death, ICD placement can provide peace of mind and improve their overall quality of life. Knowing that the device is continuously monitoring their heart and ready to intervene if needed can alleviate anxiety and allow individuals to engage in daily activities with more confidence.
- Customized therapy options: ICDs are programmable devices that can be tailored to an individual’s specific needs. Cardiac electrophysiologists can adjust the device’s settings to deliver therapy based on the individual’s arrhythmia patterns and response to treatment. This customization ensures that the therapy is optimized for each patient, maximizing its effectiveness while minimizing unnecessary interventions.
- Remote monitoring capabilities: Many modern ICDs come with remote monitoring capabilities. This allows healthcare providers to remotely monitor the device’s function, detect any abnormalities, and make necessary adjustments without the need for frequent in-person visits. Remote monitoring can improve convenience for patients and enable early detection of potential issues.
- Combination therapy options: In some cases, ICDs can be combined with other cardiac devices, such as pacemakers or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices. This combination therapy can provide additional benefits for individuals with specific types of arrhythmias or heart conditions, further improving their overall cardiac function and quality of life.
Complications
While ICD placement is generally considered safe and effective, like any medical procedure, it does carry some potential risks and complications. It’s important to be aware of these potential complications before undergoing ICD placement. Here are some of the possible complications:
- Infection: There is a risk of infection at the site of the incision or around the implanted device. This risk is generally low but can occur. Infections may require antibiotic treatment or, in rare cases, removal of the device.
- Bleeding or hematoma: During the procedure, there is a small risk of bleeding or the formation of a hematoma (a collection of blood) at the incision site. Most cases are minor and resolve on their own, but severe bleeding or hematoma may require additional treatment or intervention.
- Lead-related complications: The leads, which are thin wires that connect the ICD to the heart, can sometimes cause complications. These may include lead dislodgement, lead fracture, or lead-related infections. In some cases, additional procedures may be required to reposition or replace the leads.
- Pneumothorax: In rare cases, the insertion of the leads can cause a pneumothorax, which is the accumulation of air in the space between the lung and the chest wall. This can cause difficulty breathing and may require treatment, such as the insertion of a chest tube to remove the air.
- Device-related complications: The ICD itself can have complications, such as device malfunction, inappropriate shocks, or battery depletion. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are necessary to monitor the device’s function and address any potential issues.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may have allergic reactions to the materials used in the ICD or the sutures used to close the incision. These reactions can range from mild irritation to more severe allergic responses.
Preoperative care
Preoperative care for Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) placement involves specific considerations to ensure the safety and success of the procedure. Here are some key aspects of preoperative care for ICD placement:
- Medical evaluation: Before the ICD placement, you will undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation. This may include a review of your medical history, physical examination, and various tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, and blood tests. These evaluations help assess your overall health, identify any underlying conditions, and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
- Medication management: It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are currently taking, including prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before the procedure, especially those that can interfere with blood clotting or interact with anesthesia.
- Fasting instructions: You will receive specific instructions regarding fasting before the procedure. Typically, you will be asked to avoid eating or drinking anything for a certain period of time before the surgery. This is to ensure that your stomach is empty, reducing the risk of complications during anesthesia.
- Pre-procedure instructions: Your healthcare provider will provide you with specific instructions to follow before the ICD placement. This may include guidelines on showering, skin preparation, and any necessary preoperative medications. It’s important to carefully follow these instructions to ensure optimal conditions for the surgery.
- Consent and education: Before the procedure, you will be asked to provide informed consent, indicating that you understand the risks, benefits, and alternatives of ICD placement. Your healthcare provider will also educate you about the procedure, including what to expect during and after the surgery, potential complications, and postoperative care.
- Preoperative counseling: Preoperative counseling may be provided to address any concerns or questions you may have about the ICD placement. This can help alleviate anxiety and ensure that you are well-informed and prepared for the procedure.
- Arrangements for transportation and support: Since ICD placement is typically performed under general anesthesia, you will need to arrange for transportation to and from the hospital or surgical center. It’s also helpful to have a support person accompany you on the day of the procedure to provide emotional support and assist with postoperative care.
- Preoperative testing: Depending on your specific medical condition and the recommendations of your healthcare provider, you may undergo additional preoperative testing. This may include imaging tests, such as a chest X-ray or cardiac MRI, to assess the structure and function of your heart.
Postoperative care
Postoperative care after implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placement is crucial to ensure proper healing and optimal functioning of the device. Here are some important aspects of postoperative care for ICD placement:
- Incision Care: Keep the incision site clean and dry. Follow the surgeon’s instructions regarding dressing changes and wound care. Report any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge, to your healthcare provider.
- Activity Restrictions: Limit physical activity and avoid heavy lifting for the first few weeks after surgery. Gradually increase activity levels as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Medication Management: Take prescribed medications as directed, including any antiarrhythmic drugs or blood thinners. Follow up with your healthcare provider for medication adjustments or changes.
- Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your cardiologist or electrophysiologist. These appointments are essential for monitoring the functioning of the ICD and making any necessary adjustments.
- Device Monitoring: Your ICD will be programmed to monitor your heart rhythm and deliver appropriate therapy if needed. Regular device checks and remote monitoring may be required to ensure proper functioning and detect any issues.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Make necessary lifestyle changes to promote heart health, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly. Discuss any specific recommendations with your healthcare provider.
- Emotional Support: Adjusting to life with an ICD can be challenging. Seek emotional support from family, friends, or support groups to cope with any anxiety or concerns you may have.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.