Free
Embark on a transformative journey with our exceptional range of medical treatments. As a leading medical tour operator, we offer a comprehensive selection of world-class treatments and procedures to address your unique healthcare needs. From advanced surgeries to cutting-edge therapies, our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing top-notch care and ensuring your comfort and satisfaction. Discover a new level of healthcare excellence with our tailored treatment options. Book now to start your journey towards a healthier and happier you.
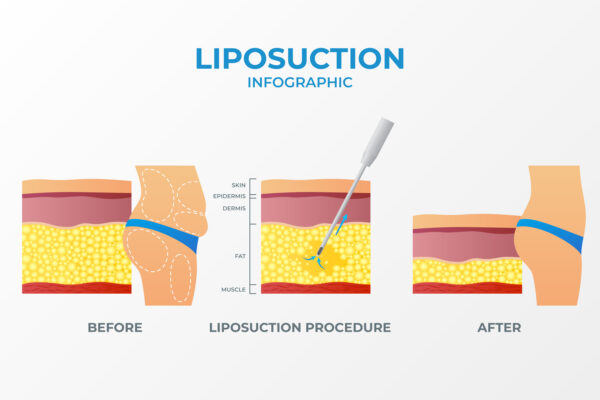
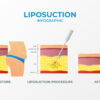
Traditional liposuction, also known as suction-assisted liposuction (SAL), is a surgical procedure that aims to remove excess fat from specific areas of the body to improve body contour and shape. Here is an explanation of the procedure based on the information from the search results:
Anesthesia: Before the procedure, anesthesia is administered to ensure patient comfort. The options for anesthesia include general anesthesia, intravenous sedation, or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s needs and the extent of the procedure 1.
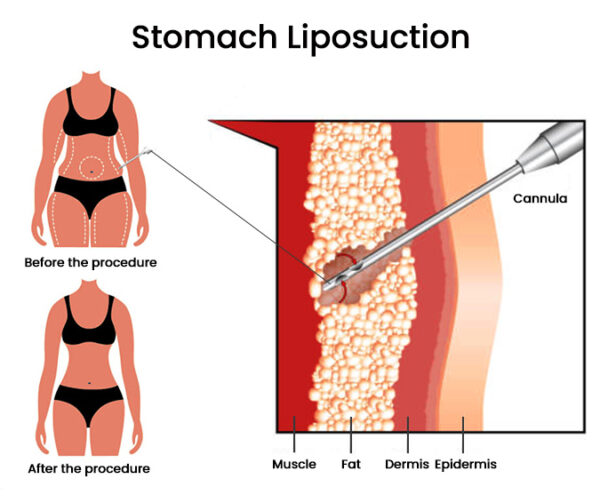
Incisions: Small, inconspicuous incisions are made in the targeted areas of the body. These incisions allow the insertion of a hollow stainless steel tube called a cannula 1. The size and number of incisions may vary depending on the specific technique used and the amount of fat being removed.
Tumescent Solution: Prior to the fat removal process, a tumescent solution is infused into the targeted area. This solution typically consists of a saline solution mixed with a local anesthetic (lidocaine) and a vessel-constrictor (epinephrine). The tumescent solution helps to numb the area, minimize bleeding, and facilitate fat removal 2.
Fat Removal: Once the tumescent solution has taken effect, the surgeon inserts the cannula through the incisions and uses a back-and-forth motion to break up and suction out the excess fat cells. The cannula is connected to a vacuum or suction device that removes the fat from the body 1.
Techniques and Advances: Traditional liposuction techniques have evolved over time, and there have been advancements to improve patient safety and outcomes. For example, laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) uses laser energy to liquefy fat cells before removal, while power-assisted liposuction (PAL) uses a reciprocating motion of the cannula to facilitate fat removal. These techniques aim to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the procedure 3.
Areas of Treatment: Traditional liposuction can be performed on various areas of the body, including the abdomen, hips, thighs, buttocks, arms, neck, and face 1. It is important to note that the specific areas that can be treated may vary depending on individual patient needs and the surgeon’s expertise.
Liposuction is a highly individualized procedure, and the suitability for traditional liposuction can vary depending on several factors. Here are some points to consider based on the information from the search results:
Ideal Candidates: Ideal candidates for liposuction, including traditional liposuction, are typically adults within 30% of their ideal weight, have firm and elastic skin, and good muscle tone. They should be in good overall health without any life-threatening illnesses or medical conditions that can impair healing. Non-smokers and individuals with a positive outlook and specific goals for body contouring are also considered suitable candidates.
Excess Fat Deposits: Liposuction, including traditional liposuction, is suitable for individuals who are bothered by excess fat deposits that do not respond to diet or exercise. It is important to note that liposuction is not a weight-loss method but rather a procedure to remove localized areas of excess fat and improve body contour.
Skin Elasticity: The elasticity of the skin is an important factor in determining the suitability for liposuction. Patients with firm and elastic skin tend to have better results as the skin can reshape well after fat removal. However, individuals with soft and thin skin due to factors such as stretch marks, weight loss, or natural aging may not experience the same level of reshaping and may require additional surgeries to remove and tighten excess skin.
Health Considerations: The overall health of the individual is an important consideration for liposuction. Candidates should be in good health and free from any medical conditions that can increase the risk of complications or impair the healing process.
Consultation with a Surgeon: The best way to determine if traditional liposuction is suitable for an individual is through a consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon. The surgeon will assess the patient’s specific needs, evaluate their health status, and discuss the potential risks and benefits of the procedure.
While liposuction, including traditional liposuction, can be beneficial for many individuals, there are certain cases where it may not be suitable. Here are some factors to consider based on the information from the search results:
Obesity: Liposuction is not a weight loss solution for individuals who are significantly overweight or obese. It is important to note that liposuction is intended to remove localized areas of excess fat and improve body contour, not for overall weight reduction. For individuals who are obese, other weight loss methods, such as diet and exercise, may be more appropriate.
Poor General Health: Liposuction is a surgical procedure, and individuals with certain medical conditions may not be suitable candidates. Conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, heart disease, blood clotting disorders, compromised immune systems, or other serious health conditions may increase the risk of complications during or after the surgery.
Unrealistic Expectations: Liposuction can provide significant improvements in body contour, but it is important for individuals to have realistic expectations. It is not a magical solution for achieving the “perfect” body. Patients should have a clear understanding of the limitations and potential outcomes of the procedure.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Liposuction is not recommended for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It is generally advisable to wait until after pregnancy and breastfeeding to undergo liposuction to ensure the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Poor Skin Elasticity: Individuals with poor skin elasticity may not achieve the desired results from liposuction alone. Liposuction removes fat, but it does not address sagging or loose skin. In such cases, additional procedures like a tummy tuck or body lift may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome.
Psychological Considerations: Liposuction is not suitable for individuals with unrealistic body image expectations or those seeking the procedure as a solution to underlying psychological issues. It is important to have a positive body image and realistic expectations before undergoing any cosmetic procedure.
Based on the information from the search results, there are certain cases where liposuction, including traditional liposuction, may not be suitable. Here are some factors to consider:
Obesity: Liposuction is not a weight loss solution for individuals who are significantly overweight or obese. It is important to note that liposuction is intended to remove localized areas of excess fat and improve body contour, not for overall weight reduction. For individuals who are obese, other weight loss methods, such as diet and exercise, may be more appropriate.
Poor General Health: Liposuction is a surgical procedure, and individuals with certain medical conditions may not be suitable candidates. Conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, heart disease, blood clotting disorders, compromised immune systems, or other serious health conditions may increase the risk of complications during or after the surgery.
Poor Skin Elasticity: Individuals with poor skin elasticity may not achieve the desired results from liposuction alone. Liposuction removes fat, but it does not address sagging or loose skin. In such cases, additional procedures like a tummy tuck or body lift may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome.
Unrealistic Expectations: Liposuction can provide significant improvements in body contour, but it is important for individuals to have realistic expectations. It is not a magical solution for achieving the “perfect” body. Patients should have a clear understanding of the limitations and potential outcomes of the procedure.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Liposuction is not recommended for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It is generally advisable to wait until after pregnancy and breastfeeding to undergo liposuction to ensure the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Psychological Considerations: Liposuction is not suitable for individuals with unrealistic body image expectations or those seeking the procedure as a solution to underlying psychological issues. It is important to have a positive body image and realistic expectations before undergoing any cosmetic procedure.
Liposuction, including traditional liposuction, is a surgical procedure that carries certain risks and potential complications. Here are some points to consider based on the information from the search results:
Anesthesia Risks: Liposuction requires anesthesia, and there are inherent risks associated with anesthesia administration. These risks can include allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and adverse reactions to medications. An anesthesiologist or qualified healthcare professional will closely monitor the patient during the procedure to minimize these risks.
Bruising and Swelling: Bruising and swelling are common after liposuction and can vary in severity depending on the extent of the procedure. These side effects typically subside over time but can cause discomfort and temporary changes in the appearance of the treated area.
Infection: Infection is a potential risk after any surgical procedure, including liposuction. To minimize the risk of infection, surgeons typically prescribe antibiotics and provide instructions for proper wound care. It’s important for patients to follow these instructions diligently.
Irregular Contours or Asymmetries: Liposuction aims to improve body contour and shape, but there is a risk of irregular contours or asymmetries in the treated area. Factors such as uneven fat removal, uneven healing, or individual variations in tissue response can contribute to these outcomes. Revision surgery may be necessary to address these issues.
Fluid Accumulation: Fluid accumulation, known as seroma, can occur after liposuction. Surgeons may place drains or use compression garments to minimize the risk of seroma formation. In some cases, aspiration or drainage of the fluid may be necessary.
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Complications: Liposuction, like any surgery, carries a risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary complications such as blood clots. Surgeons take precautions to minimize these risks, including the use of compression stockings, early ambulation, and the administration of blood thinners when necessary.
Skin Sensation Changes: Temporary changes in skin sensation, such as numbness or altered sensitivity, can occur after liposuction. These changes typically resolve over time, but in some cases, they may persist.
Preoperative care refers to the physical and psychosocial care provided to patients before undergoing surgery. The goal of preoperative care is to ensure the patient’s safety and optimize their outcomes after the surgical procedure. Here are some key points about preoperative care based on the information from the search results:
Assessment and Evaluation: Preoperative care begins with a thorough assessment and evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical condition, and specific needs. This includes obtaining a detailed medical history, conducting a physical examination, and performing any necessary tests or evaluations to assess the patient’s fitness for surgery 1.
Patient Education: Patient education is an essential component of preoperative care. During this phase, healthcare professionals provide information to the patient about the surgical procedure, potential risks and benefits, expected outcomes, and postoperative care instructions. This helps the patient understand what to expect and actively participate in their own care 2.
Preoperative Testing: Depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s medical condition, various preoperative tests and assessments may be conducted. These tests can include blood work, imaging studies, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and consultations with other specialists to ensure the patient is in the best possible condition for surgery 2.
Medication and Preparation: Preoperative care involves reviewing the patient’s current medications and making any necessary adjustments or modifications. This may include discontinuing certain medications that can interfere with the surgery or adjusting the dosage of others. Additionally, patients may be instructed to fast for a specific period before surgery to minimize the risk of complications related to anesthesia 3.
Addressing Anxiety and Comfort: Preoperative care aims to address the patient’s anxiety and ensure their comfort before surgery. This can involve providing emotional support, answering questions, and offering relaxation techniques or medications to help alleviate anxiety.
Consent and Documentation: Obtaining informed consent from the patient is an important part of preoperative care. The healthcare team ensures that the patient understands the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the procedure and signs the necessary consent forms. Documentation of the preoperative assessment, education, and consent is essential for accurate and comprehensive patient care 3.
Postoperative care refers to the care provided to patients after they have undergone surgery. The goal of postoperative care is to promote healing, manage pain, prevent complications, and support the patient’s recovery. Here are some key points about postoperative care based on the information from the search results:
Monitoring Vital Signs: After surgery, healthcare professionals closely monitor the patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature. This helps ensure the patient’s stability and allows for early detection of any potential complications.
Pain Management: Effective pain management is an important aspect of postoperative care. Healthcare professionals may prescribe pain medications or use other techniques such as epidurals, patient-controlled analgesia (PCA), or non-pharmacological methods to help control pain and discomfort.
Wound Care: Proper wound care is crucial for preventing infection and promoting healing. This may involve regularly cleaning and dressing the surgical incision site, as well as monitoring for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage.
Mobility and Ambulation: Early mobilization and ambulation are encouraged as soon as the patient’s condition allows. Moving and walking help prevent complications such as blood clots and promote circulation and healing.
Nutrition and Hydration: Adequate nutrition and hydration are essential for the healing process. Healthcare professionals may provide guidance on a balanced diet and encourage the patient to drink fluids to maintain hydration.
Respiratory Care: Depending on the type of surgery, patients may receive respiratory care to prevent complications such as pneumonia or atelectasis. This may involve deep breathing exercises, the use of incentive spirometry, or the administration of respiratory treatments.
Preventing Complications: Postoperative care includes measures to prevent complications such as infections, blood clots, and pressure ulcers. This may involve administering prophylactic medications, using compression stockings, assisting with frequent position changes, and providing appropriate skin care.
Patient Education: Patient education continues during the postoperative period. Healthcare professionals provide instructions on postoperative care, including medication management, wound care, activity restrictions, and signs of potential complications. This empowers the patient to actively participate in their recovery process.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
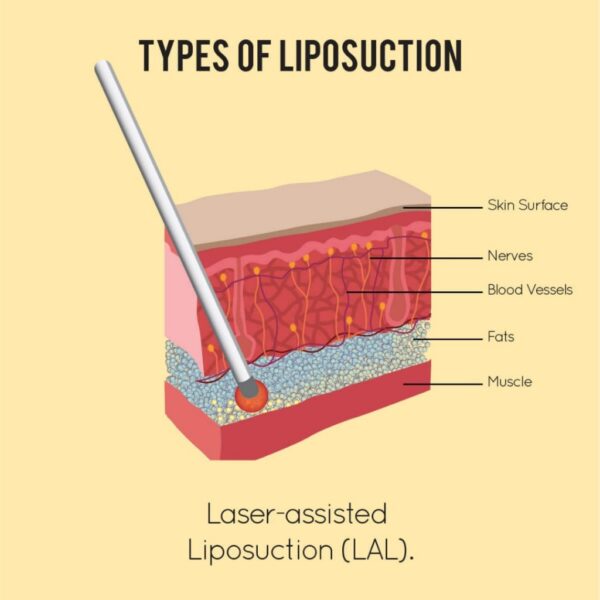
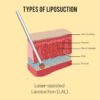
Laser-Assisted Liposuction (LAL) is a cosmetic surgical procedure that combines traditional liposuction techniques with the use of laser energy to remove excess fat from specific areas of the body. Here’s an overview of the procedure based on the information from the search results:
Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is typically given anesthesia, which can be local anesthesia, intravenous sedation, or general anesthesia. A saline solution containing medication to minimize pain and bleeding is infused into the area where liposuction will be performed.
Laser Energy Application: Once the patient is prepared, a small incision is made in the skin, and a thin laser fiber is inserted through the incision into the fat layer beneath the skin. The laser energy is then applied to the targeted area.
Fat Liquefaction: The laser energy emitted by the fiber heats and liquefies the fat cells, making them easier to remove. The liquefied fat is then suctioned out of the body using a small hollow tube called a cannula, which is attached to a vacuum device.
Selective Fat Removal: The laser energy selectively targets and breaks down fat cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Skin Tightening: Laser energy has been suggested to promote skin tightening by stimulating collagen production and improving the overall contour and appearance of the treated area.
Recovery and Results: The recovery period after laser-assisted liposuction can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. Patients may experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort, which can be managed with pain medication and compression garments. The results of laser-assisted liposuction are typically visible immediately after the procedure, but they will continue to improve over several weeks as swelling subsides.
Based on the information from the search results, laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) is generally suitable for individuals who meet certain criteria. Here’s a summary of the suitability factors mentioned in the search results:
Moderate Skin Laxity: Laser-assisted liposuction is often recommended for individuals with moderate skin laxity. It can help tighten the skin in addition to removing excess fat. However, it may not be suitable for those with significant loose, hanging skin.
Stubborn Fat Deposits: LAL is effective for targeting and removing stubborn fat deposits that may not respond to diet or exercise. It can be used in various areas of the body, such as the abdomen, thighs, arms, flanks (love handles), and chin.
Healthy Weight: LAL is typically not recommended for individuals who are at an unhealthy or unstable weight. It is important to be near your ideal weight before considering the procedure.
General Health: Candidates for LAL should generally be in good overall health. It is important to undergo a medical assessment to determine if you are a suitable candidate for the procedure.
Realistic Expectations: It is important to have realistic expectations about the results of laser-assisted liposuction. While it can help improve body contour and remove excess fat, it is not a substitute for weight loss or a solution for obesity.
Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) may not be suitable for everyone. While it can be an effective procedure for many individuals, there are certain factors that may make someone ineligible or less suitable for the procedure. Here are some factors that may indicate laser-assisted liposuction is not suitable:
Obesity: Laser-assisted liposuction is not intended as a weight loss solution or a treatment for obesity. It is most effective for individuals who are at or near their ideal weight and have specific areas of stubborn fat that are resistant to diet and exercise.
Poor General Health: Individuals with significant underlying health issues or medical conditions may not be suitable candidates for laser-assisted liposuction. This is because the surgery and the recovery process can place additional stress on the body. It is important to undergo a medical evaluation to determine if you are in good enough health for the procedure.
Unrealistic Expectations: It is important to have realistic expectations about the results of laser-assisted liposuction. While it can improve body contour and remove excess fat, it may not achieve the same results as more extensive surgical procedures like body lifts or tummy tucks. It’s essential to discuss your goals and expectations with a qualified plastic surgeon.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Laser-assisted liposuction is generally not recommended for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the appropriate timing of the procedure.
Poor Skin Elasticity: Laser-assisted liposuction is most effective for individuals with moderate skin laxity. If you have significant loose, hanging skin, the procedure may not provide the desired results. In such cases, other procedures like a body lift or tummy tuck may be more appropriate.
Blood Clotting Disorders: Individuals with blood clotting disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications may not be suitable candidates for laser-assisted liposuction. These conditions can increase the risk of complications during and after the surgery.
Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) offers several advantages compared to traditional liposuction procedures. Here are some advantages mentioned in the search results:
Minimally Invasive: Laser-assisted liposuction is considered a minimally invasive procedure. It involves smaller incisions and less trauma to the surrounding tissues compared to traditional liposuction. This can result in reduced scarring, bruising, and swelling.
Improved Skin Tightening: Laser energy used during the procedure can stimulate collagen production and promote skin tightening. This can help improve the overall contour and appearance of the treated area, especially in individuals with moderate skin laxity.
Faster Recovery: Due to the minimally invasive nature of the procedure, the recovery time for laser-assisted liposuction is generally shorter compared to traditional liposuction. Patients may experience less post-operative pain, discomfort, and downtime.
Selective Fat Removal: Laser energy selectively targets and breaks down fat cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues such as blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. This precision allows for more targeted and controlled fat removal.
Potential for Enhanced Results: Some studies suggest that laser-assisted liposuction may lead to better skin shrinkage and tightening compared to traditional liposuction alone. This can result in improved body contouring outcomes.
Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) is generally considered safe, but like any surgical procedure, it carries potential risks and complications. Here are some complications that may be associated with laser-assisted liposuction based on the information from the search results:
Infection: Any surgical procedure carries a risk of infection. It is important to follow proper wound care instructions and take prescribed antibiotics, if necessary, to minimize the risk of infection.
Bleeding: Laser-assisted liposuction involves the use of laser energy to break down fat cells, which can cause bleeding. Surgeons take precautions to minimize bleeding during the procedure, but excessive bleeding can occur in some cases.
Skin Irregularities: In some cases, laser-assisted liposuction may result in uneven or irregular skin contours. This can include lumps, bumps, or indentations. Proper technique and experience of the surgeon can help minimize the risk of such complications.
Burns or Thermal Injury: The use of laser energy during the procedure carries a risk of burns or thermal injury to the skin or underlying tissues. Surgeons take precautions to minimize this risk, but it is important to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to perform the procedure.
Fluid Accumulation: After the procedure, fluid may accumulate in the treated area, leading to swelling and discomfort. This is a common occurrence and can be managed with proper postoperative care, including wearing compression garments and following the surgeon’s instructions.
Numbness or Sensation Changes: Some individuals may experience temporary or permanent numbness or changes in sensation in the treated area. This can occur due to nerve damage during the procedure.
Scarring: While laser-assisted liposuction involves smaller incisions compared to traditional liposuction, there is still a risk of scarring. Proper wound care and following the surgeon’s instructions can help minimize the appearance of scars.
Preoperative care refers to the physical and psychosocial care provided to patients before undergoing surgery. The goal of preoperative care is to ensure the patient is prepared for surgery and to optimize their overall well-being. Here are some key points about preoperative care based on the information from the search results:
Assessment and Evaluation: The preoperative period begins when the patient is scheduled for surgery and ends with their transfer to the operating room. During this time, healthcare providers assess the patient’s fitness for surgery, which includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, risk assessment, and specific evaluations based on the type of surgery.
Patient Education: Preoperative care involves providing information to the patient about their surgical procedure, expectations before and after surgery, and any necessary lifestyle modifications. This education is typically provided during outpatient appointments, often led by nurse specialists or advanced nurse practitioners. It may also involve remote consultations via telephone or email.
Preoperative Testing: Depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s medical condition, various preoperative tests and clinical assessments may be conducted. These tests can include blood work, imaging studies, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and other specific evaluations to ensure the patient is in the best possible condition for surgery.
Consent and Documentation: Informed consent is an essential part of preoperative care. The patient or their legal guardian must sign a consent form after understanding the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the procedure. The consent form should be properly documented and placed in the patient’s chart before they go to the operating room.
Preoperative Medications: Depending on the patient’s medical condition and the planned surgery, preoperative medications may be administered. These medications can include pain control medications, antibiotics to prevent infection, and medications to manage specific conditions such as diabetes.
Preparation and Comfort: Preoperative care involves preparing the patient’s body for surgery, which may include activities such as washing with an antiseptic. Additionally, addressing the patient’s anxiety and providing emotional support to make them comfortable is an important aspect of preoperative care.
Postoperative care refers to the care and management provided to patients after they have undergone surgery. The goal of postoperative care is to facilitate the patient’s recovery, manage any potential complications, and ensure their overall well-being. Here are some key points about postoperative care based on the information from the search results:
Monitoring Vital Signs: After surgery, patients are closely monitored in the recovery area. Vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation are regularly checked to ensure stability and detect any potential complications.
Pain Management: Postoperative pain management is a crucial aspect of care. Healthcare providers administer pain medications as needed to keep the patient comfortable. Pain levels are regularly assessed, and adjustments to the pain management plan are made accordingly.
Wound Care and Dressings: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. Depending on the type of surgery, specific wound care instructions are provided, including how to clean the wound, change dressings, and monitor for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or drainage.
Mobility and Ambulation: Depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s condition, healthcare providers encourage early mobilization and ambulation. This helps prevent complications such as blood clots and promotes faster recovery.
Fluid and Nutrition: Adequate hydration and nutrition are important for the healing process. Patients are encouraged to drink fluids and consume a balanced diet as tolerated. In some cases, intravenous fluids or specialized diets may be provided.
Monitoring and Managing Complications: Postoperative care involves monitoring for potential complications such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to medications. If any complications arise, appropriate interventions are initiated promptly.
Patient Education and Discharge Planning: During the postoperative period, patients and their caregivers are provided with instructions regarding wound care, medication management, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments. Discharge planning ensures a smooth transition from the hospital to home or a rehabilitation facility, if necessary.
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment. The preferred choice for many patients is choosing private care.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.