





Free
Embark on a transformative journey with our exceptional range of medical treatments. As a leading medical tour operator, we offer a comprehensive selection of world-class treatments and procedures to address your unique healthcare needs. From advanced surgeries to cutting-edge therapies, our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing top-notch care and ensuring your comfort and satisfaction. Discover a new level of healthcare excellence with our tailored treatment options. Book now to start your journey towards a healthier and happier you.
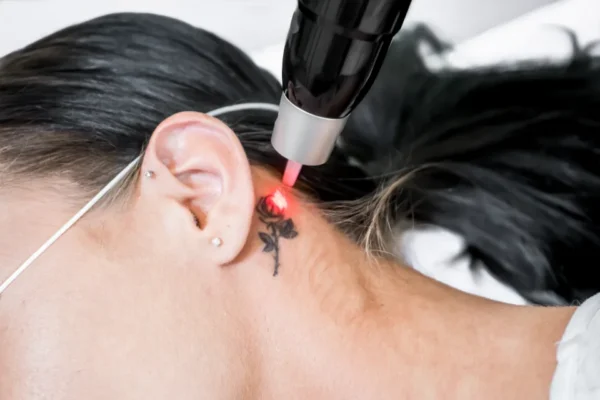
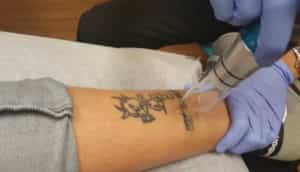
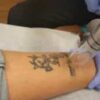
Laser treatment for pigmentation involves the use of specific laser devices to target and reduce the appearance of pigmented lesions on the skin. The lasers emit concentrated beams of light that are absorbed by the pigment in the skin, causing it to break down or disperse.
There are different types of lasers used for pigmentation treatment, including intense pulsed light (IPL) devices, pico lasers, and ablative or non-ablative fractional lasers. The specific laser used depends on the nature and depth of the pigmentation being treated.
During the procedure, the patient is positioned comfortably, and protective eyewear is provided to shield the eyes from the laser light. The clinician applies a gliding gel or cooling mechanism to the treatment area to maximize contact between the laser and the skin.
The laser device is then used to deliver controlled pulses of light to the targeted pigmented areas. The energy from the laser is absorbed by the pigment, causing it to break down or disperse. The specific settings and parameters of the laser are adjusted based on the individual’s skin type, the type of pigmentation being treated, and the desired outcome.
The procedure may cause minimal discomfort, often described as a sensation similar to the snapping of a rubber band on the skin. Some laser devices incorporate cooling mechanisms to soothe and protect the skin during treatment.
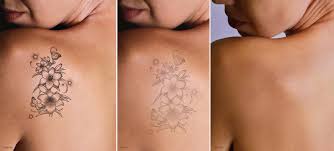
After the procedure, there may be temporary redness, swelling, and darkening of the pigmented lesions. These effects typically subside within a few days to a couple of weeks. It is important to follow postoperative care instructions provided by the healthcare professional, which may include avoiding sun exposure, using gentle skincare products, and moisturizing the treated area.
Multiple laser treatment sessions may be recommended to achieve optimal results, depending on the severity of the pigmentation and the desired outcome. These sessions are usually spaced several weeks apart to allow for proper healing and skin rejuvenation.
Laser treatment for pigmentation is suitable for individuals who have specific pigmented conditions, such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), freckles, sun spots, age spots, and uneven pigmentation overall. It can be used for various skin types and tones.
Different types of lasers, such as intense pulsed light (IPL), pico lasers, and ablative or non-ablative fractional lasers, can be used for pigmentation treatment. The choice of laser depends on factors such as the type and depth of pigmentation, the individual’s skin type, and the desired outcome.
Laser treatment for pigmentation may not be suitable for everyone. There are certain factors and conditions that may make someone ineligible or less suitable for laser treatment. Here are some examples:
Darker Skin Types: Laser treatment for pigmentation can be more challenging and carry a higher risk of complications in individuals with darker skin types, including Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI. This is because the laser energy can also target the natural pigment in the skin, potentially causing hypopigmentation (lightening) or hyperpigmentation (darkening) of the treated area.
Active Skin Infections or Inflammation: If you have an active skin infection, such as herpes simplex virus (cold sores), or inflammatory skin conditions, like eczema or psoriasis, laser treatment may not be recommended. These conditions can be exacerbated or spread by the laser energy.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Laser treatment for pigmentation is generally not performed on pregnant or breastfeeding individuals due to the lack of safety data regarding the effects on the fetus or breastfeeding infants. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the safety of laser treatment during these periods.
History of Keloid or Hypertrophic Scarring: Individuals with a history of keloid or hypertrophic scarring may be at a higher risk of developing excessive scarring or skin reactions after laser treatment. It’s important to discuss your medical history with a healthcare professional before undergoing laser treatment.
Photosensitivity or Medications: Some medications or medical conditions can make the skin more sensitive to light, increasing the risk of adverse reactions to laser treatment. It’s important to inform your healthcare professional about any medications, supplements, or medical conditions you have before considering laser treatment.
Uncontrolled Medical Conditions: Laser treatment may not be suitable for individuals with uncontrolled medical conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or certain skin conditions. These conditions can affect the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Recent Sun Exposure or Tanning: It’s generally recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure or tanning before laser treatment, as it can increase the risk of adverse reactions, such as burns or pigmentation changes.
Laser treatment for pigmentation offers several advantages, as mentioned in the search results:
Effective Treatment: Laser treatment can be highly effective in reducing the appearance of pigmented lesions, such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), freckles, sun spots, age spots, and uneven pigmentation overall 1.
Suitable for Various Skin Types: Different types of lasers can be used for pigmentation treatment, including lasers suitable for both light and darker skin types.
Targeted Treatment: Laser devices emit concentrated beams of light that specifically target the pigmented areas, allowing for precise treatment and minimal impact on the surrounding skin 1.
Minimal Discomfort: Laser treatments, especially non-ablative procedures, are generally associated with minimal discomfort. Some lasers incorporate cooling mechanisms to enhance patient comfort during the procedure.
Minimal Downtime: Laser treatments typically have little to no downtime, with minimal reactions such as temporary redness, swelling, and warmth that subside within a few hours to a few days 2.
Long-Lasting Results: Laser treatments for pigmentation can provide long-lasting results, with effects that can last for years.
Versatility: Laser treatments can address various pigmented conditions, including hyperpigmentation, sunspots, melasma, birthmarks, and more.
Safe and Reliable: Laser treatments for pigmentation are generally considered safe when performed by a qualified healthcare professional. However, it’s important to choose a board-certified dermatologist or expert who is familiar with treating different skin tones.
Laser treatment for pigmentation, like any medical procedure, carries potential risks and complications. Here are some of the complications that may occur:
Discomfort, Redness, and Swelling: It is common to experience some discomfort, redness, and swelling for a few hours to a few days after laser treatment. This is a normal reaction and typically resolves on its own.
Bruising, Blisters, or Scabs: In some cases, lasers used for pigmentation treatment can result in bruising, blisters, or scabs. These adverse reactions are uncommon but can occur.
Temporary or Permanent Pigment Changes: Laser treatment may cause temporary or, rarely, permanent changes in pigmentation. This can manifest as temporary loss or gain of pigment in the treated area, which may last for several months or longer.
Increased Pigmentation: In some cases, laser treatment may trigger increased pigmentation in the treated area. If this occurs, the laser treatment may need to be delayed until the increased pigmentation resolves.
Cold Sore Activation: Laser treatment can trigger cold sores in individuals who have a history of cold sores. The herpes virus can infect the laser treatment site, leading to the development of a cold sore.
Secondary Bacterial Infection: If the skin is broken or compromised following laser treatment, there is a small risk of a secondary bacterial infection. This can present as spreading redness and pain around the treatment site.
Scarring: Scarring following laser treatment is very uncommon but can occur, particularly if the laser settings are not appropriate or if there is excessive tissue damage.
Preoperative care for laser treatment for pigmentation may vary depending on the specific procedure and the recommendations of the healthcare professional. However, here are some general preoperative care considerations that may be advised:
Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a dermatologist or skincare professional who specializes in laser treatments for pigmentation. During the consultation, they will assess your skin condition, discuss your goals and expectations, and determine the most suitable laser treatment approach for your specific pigmentation concerns.
Skin Assessment: The healthcare professional will evaluate your skin type, the type and depth of pigmentation, and any underlying skin conditions. This assessment helps determine the appropriate laser device, settings, and treatment plan.
Sun Protection: It is generally recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure and tanning for at least four weeks before laser treatment. Sun exposure can increase the risk of complications and affect the effectiveness of the treatment. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF daily to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
Avoid Certain Medications and Products: Some medications and skincare products can increase the risk of complications or interfere with the laser treatment. Your healthcare professional may advise you to avoid certain medications, such as photosensitizing drugs or retinoids, before the procedure. It’s important to follow their instructions and disclose all medications and skincare products you are using.
Skin Preparation: Depending on the specific laser treatment, your healthcare professional may recommend a pre-treatment skincare regimen to prepare your skin for the procedure. This may include gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and avoiding harsh exfoliants or irritants.
Medical History and Allergies: Provide your healthcare professional with a comprehensive medical history, including any allergies or previous adverse reactions to treatments. This information helps ensure your safety and minimize the risk of complications.
Preparation Instructions: Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare professional regarding fasting, avoiding certain substances (such as alcohol or blood-thinning medications), and any other preoperative preparations.
Postoperative care is crucial to ensure proper healing and minimize complications after laser treatment for pigmentation. Here are some general postoperative care considerations:
Follow Post-Treatment Instructions: Follow the specific post-treatment instructions provided by your healthcare professional. These instructions may include guidelines for cleansing, moisturizing, and protecting the treated area. It’s important to adhere to these instructions to promote healing and optimize the results.
Protect Your Skin from the Sun: Protecting your skin from the sun is essential after laser treatment for pigmentation. The treated skin is more vulnerable to UV damage, which can lead to pigmentation changes and other complications. Avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF on a daily basis. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses, when going outside.
Avoid Picking or Scratching: It’s important to resist the urge to pick, scratch, or peel any scabs or crusts that may form on the treated area. Allow the skin to heal naturally to minimize the risk of scarring or infection.
Moisturize the Treated Area: Keeping the treated area moisturized can help promote healing and reduce dryness or discomfort. Use a gentle, non-irritating moisturizer as recommended by your healthcare professional.
Avoid Harsh Skincare Products: Avoid using harsh skincare products, such as exfoliants or products containing strong active ingredients, on the treated area until it has fully healed. These products can irritate the skin and interfere with the healing process.
Avoid Heat and Excessive Sweating: Avoid activities that can generate excessive heat or cause sweating, such as hot showers, saunas, steam rooms, or intense physical exercise. Heat and sweat can increase the risk of complications and delay the healing process.
Attend Follow-Up Appointments: Follow up with your healthcare professional as scheduled. They will assess your progress, monitor the healing process, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Laser treatment for pigmentation involves the use of specific laser devices to target and reduce the appearance of pigmented lesions on the skin. The lasers emit concentrated beams of light that are absorbed by the pigment in the skin, causing it to break down or disperse.
There are different types of lasers used for pigmentation treatment, including intense pulsed light (IPL) devices, pico lasers, and ablative or non-ablative fractional lasers. The specific laser used depends on the nature and depth of the pigmentation being treated.
During the procedure, the patient is positioned comfortably, and protective eyewear is provided to shield the eyes from the laser light. The clinician applies a gliding gel or cooling mechanism to the treatment area to maximize contact between the laser and the skin.
The laser device is then used to deliver controlled pulses of light to the targeted pigmented areas. The energy from the laser is absorbed by the pigment, causing it to break down or disperse. The specific settings and parameters of the laser are adjusted based on the individual’s skin type, the type of pigmentation being treated, and the desired outcome.
The procedure may cause minimal discomfort, often described as a sensation similar to the snapping of a rubber band on the skin. Some laser devices incorporate cooling mechanisms to soothe and protect the skin during treatment.
After the procedure, there may be temporary redness, swelling, and darkening of the pigmented lesions. These effects typically subside within a few days to a couple of weeks. It is important to follow postoperative care instructions provided by the healthcare professional, which may include avoiding sun exposure, using gentle skincare products, and moisturizing the treated area.
Multiple laser treatment sessions may be recommended to achieve optimal results, depending on the severity of the pigmentation and the desired outcome. These sessions are usually spaced several weeks apart to allow for proper healing and skin rejuvenation.
Laser treatment for pigmentation is suitable for individuals who have specific pigmented conditions, such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), freckles, sun spots, age spots, and uneven pigmentation overall. It can be used for various skin types and tones.
Different types of lasers, such as intense pulsed light (IPL), pico lasers, and ablative or non-ablative fractional lasers, can be used for pigmentation treatment. The choice of laser depends on factors such as the type and depth of pigmentation, the individual’s skin type, and the desired outcome.
Laser treatment for pigmentation may not be suitable for everyone. There are certain factors and conditions that may make someone ineligible or less suitable for laser treatment. Here are some examples:
Darker Skin Types: Laser treatment for pigmentation can be more challenging and carry a higher risk of complications in individuals with darker skin types, including Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI. This is because the laser energy can also target the natural pigment in the skin, potentially causing hypopigmentation (lightening) or hyperpigmentation (darkening) of the treated area.
Active Skin Infections or Inflammation: If you have an active skin infection, such as herpes simplex virus (cold sores), or inflammatory skin conditions, like eczema or psoriasis, laser treatment may not be recommended. These conditions can be exacerbated or spread by the laser energy.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding: Laser treatment for pigmentation is generally not performed on pregnant or breastfeeding individuals due to the lack of safety data regarding the effects on the fetus or breastfeeding infants. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on the safety of laser treatment during these periods.
History of Keloid or Hypertrophic Scarring: Individuals with a history of keloid or hypertrophic scarring may be at a higher risk of developing excessive scarring or skin reactions after laser treatment. It’s important to discuss your medical history with a healthcare professional before undergoing laser treatment.
Photosensitivity or Medications: Some medications or medical conditions can make the skin more sensitive to light, increasing the risk of adverse reactions to laser treatment. It’s important to inform your healthcare professional about any medications, supplements, or medical conditions you have before considering laser treatment.
Uncontrolled Medical Conditions: Laser treatment may not be suitable for individuals with uncontrolled medical conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or certain skin conditions. These conditions can affect the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Recent Sun Exposure or Tanning: It’s generally recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure or tanning before laser treatment, as it can increase the risk of adverse reactions, such as burns or pigmentation changes.
Laser treatment for pigmentation offers several advantages, as mentioned in the search results:
Effective Treatment: Laser treatment can be highly effective in reducing the appearance of pigmented lesions, such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), freckles, sun spots, age spots, and uneven pigmentation overall 1.
Suitable for Various Skin Types: Different types of lasers can be used for pigmentation treatment, including lasers suitable for both light and darker skin types.
Targeted Treatment: Laser devices emit concentrated beams of light that specifically target the pigmented areas, allowing for precise treatment and minimal impact on the surrounding skin 1.
Minimal Discomfort: Laser treatments, especially non-ablative procedures, are generally associated with minimal discomfort. Some lasers incorporate cooling mechanisms to enhance patient comfort during the procedure.
Minimal Downtime: Laser treatments typically have little to no downtime, with minimal reactions such as temporary redness, swelling, and warmth that subside within a few hours to a few days 2.
Long-Lasting Results: Laser treatments for pigmentation can provide long-lasting results, with effects that can last for years.
Versatility: Laser treatments can address various pigmented conditions, including hyperpigmentation, sunspots, melasma, birthmarks, and more.
Safe and Reliable: Laser treatments for pigmentation are generally considered safe when performed by a qualified healthcare professional. However, it’s important to choose a board-certified dermatologist or expert who is familiar with treating different skin tones.
Laser treatment for pigmentation, like any medical procedure, carries potential risks and complications. Here are some of the complications that may occur:
Discomfort, Redness, and Swelling: It is common to experience some discomfort, redness, and swelling for a few hours to a few days after laser treatment. This is a normal reaction and typically resolves on its own.
Bruising, Blisters, or Scabs: In some cases, lasers used for pigmentation treatment can result in bruising, blisters, or scabs. These adverse reactions are uncommon but can occur.
Temporary or Permanent Pigment Changes: Laser treatment may cause temporary or, rarely, permanent changes in pigmentation. This can manifest as temporary loss or gain of pigment in the treated area, which may last for several months or longer.
Increased Pigmentation: In some cases, laser treatment may trigger increased pigmentation in the treated area. If this occurs, the laser treatment may need to be delayed until the increased pigmentation resolves.
Cold Sore Activation: Laser treatment can trigger cold sores in individuals who have a history of cold sores. The herpes virus can infect the laser treatment site, leading to the development of a cold sore.
Secondary Bacterial Infection: If the skin is broken or compromised following laser treatment, there is a small risk of a secondary bacterial infection. This can present as spreading redness and pain around the treatment site.
Scarring: Scarring following laser treatment is very uncommon but can occur, particularly if the laser settings are not appropriate or if there is excessive tissue damage.
Preoperative care for laser treatment for pigmentation may vary depending on the specific procedure and the recommendations of the healthcare professional. However, here are some general preoperative care considerations that may be advised:
Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a dermatologist or skincare professional who specializes in laser treatments for pigmentation. During the consultation, they will assess your skin condition, discuss your goals and expectations, and determine the most suitable laser treatment approach for your specific pigmentation concerns.
Skin Assessment: The healthcare professional will evaluate your skin type, the type and depth of pigmentation, and any underlying skin conditions. This assessment helps determine the appropriate laser device, settings, and treatment plan.
Sun Protection: It is generally recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure and tanning for at least four weeks before laser treatment. Sun exposure can increase the risk of complications and affect the effectiveness of the treatment. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF daily to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
Avoid Certain Medications and Products: Some medications and skincare products can increase the risk of complications or interfere with the laser treatment. Your healthcare professional may advise you to avoid certain medications, such as photosensitizing drugs or retinoids, before the procedure. It’s important to follow their instructions and disclose all medications and skincare products you are using.
Skin Preparation: Depending on the specific laser treatment, your healthcare professional may recommend a pre-treatment skincare regimen to prepare your skin for the procedure. This may include gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and avoiding harsh exfoliants or irritants.
Medical History and Allergies: Provide your healthcare professional with a comprehensive medical history, including any allergies or previous adverse reactions to treatments. This information helps ensure your safety and minimize the risk of complications.
Preparation Instructions: Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare professional regarding fasting, avoiding certain substances (such as alcohol or blood-thinning medications), and any other preoperative preparations.
Postoperative care is crucial to ensure proper healing and minimize complications after laser treatment for pigmentation. Here are some general postoperative care considerations:
Follow Post-Treatment Instructions: Follow the specific post-treatment instructions provided by your healthcare professional. These instructions may include guidelines for cleansing, moisturizing, and protecting the treated area. It’s important to adhere to these instructions to promote healing and optimize the results.
Protect Your Skin from the Sun: Protecting your skin from the sun is essential after laser treatment for pigmentation. The treated skin is more vulnerable to UV damage, which can lead to pigmentation changes and other complications. Avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and use broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF on a daily basis. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses, when going outside.
Avoid Picking or Scratching: It’s important to resist the urge to pick, scratch, or peel any scabs or crusts that may form on the treated area. Allow the skin to heal naturally to minimize the risk of scarring or infection.
Moisturize the Treated Area: Keeping the treated area moisturized can help promote healing and reduce dryness or discomfort. Use a gentle, non-irritating moisturizer as recommended by your healthcare professional.
Avoid Harsh Skincare Products: Avoid using harsh skincare products, such as exfoliants or products containing strong active ingredients, on the treated area until it has fully healed. These products can irritate the skin and interfere with the healing process.
Avoid Heat and Excessive Sweating: Avoid activities that can generate excessive heat or cause sweating, such as hot showers, saunas, steam rooms, or intense physical exercise. Heat and sweat can increase the risk of complications and delay the healing process.
Attend Follow-Up Appointments: Follow up with your healthcare professional as scheduled. They will assess your progress, monitor the healing process, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
There are no reviews yet.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment. The preferred choice for many patients is choosing private care.
Choosing the right hospital and physician are important factors to consider that significantly influence a patient’s treatment.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.